Abstract
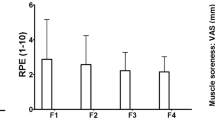
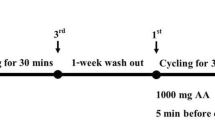
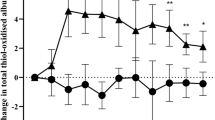
This study monitored plasma and skeletal muscle markers of free-radical-mediated damage following maximum eccentric and concentric exercise, to examine the potential role of free radicals in exercise-induced muscle damage. Fourteen male volunteers performed either (1) a bout of 70 maximum eccentric and a bout of 70 maximum concentric muscle actions of the forearm flexors (the bouts being separated by 4 weeks; n = 8) or (2) a bout of 80 maximum eccentric and a bout of 80 maximum concentric muscle actions of the knee extensors (the bouts being separated by 1 week; n=6). Plasma markers of lipid peroxidation, thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and diene-conjugated compounds (DCC) were monitored in the arm protocol and skeletal muscle markers of oxidative lipid and protein damage, malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl derivatives (PCD) respectively, were monitored in the leg protocol. In both protocols, the contralateral limb was used for the second bout and the order of the bouts was randomised between limbs. Repeated measures ANOVA indicated significant changes from baseline following eccentric arm work on the measures of serum creatine kinase activity (P < 0.05), maximum voluntary torque production (P < 0.01) and relaxed arm angle (P < 0.01). Subjective muscle soreness peaked 2 days after eccentric arm work (P < 0.05, Wilcoxon test). However, there were no changes in the plasma levels of TBARS or DCC following the eccentric or concentric arm exercise. Immediately after concentric leg exercise, skeletal muscle PCD concentrations was significantly higher than that observed immediately after eccentric work (P < 0.05). However, no significant difference between the eccentric and concentric knee extensor bouts was observed on the measure of skeletal muscle MDA concentration. The results of this study offer no support for the involvement of oxygen free radicals in exercise-induced muscle damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong RB, Warren GL, Warren JA (1991) Mechanisms of exercise-induced muscle fibre injury. Sports Med 12:184–207
Asmussen E (1953) Positive and negative muscular work. Acta Physiol Scand 28:364–382
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation: the thiobarbituric acid assay. Methods Enzymol 52:306–310
Cannon JG, Fielding RA, Orencole SF, Dinarello CA, Evans WJ (1989) Interleukin-1β in human skeletal muscle following exercise. Am J Physiol 257:R451-R455
Clarkson PM, Nosaka K, Braun B (1992) Muscle function after exercise-induced muscle damage and rapid adaptation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:512–520
Esterbauer H, Lang J, Zadravec S, Slater TF (1984) Detection of malonaldehyde by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol 105:319–328
Friden J, Sjostrom M, Ekblom B (1983) Myofibrillar damage following intense eccentric exercise in man. Int J Sports Med 4:170–176
Hunter I, Mohamed J (1986) Plasma antioxidants and lipid peroxidation products in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Chim Acta 155:123–132
Kanter MM, Lesumes GR, Kaminsky LA, La Ham-Saeger J, Nequin ND (1988) Serum creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase changes following an eighty kilometer race. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:60–63
Kikugawa K, Beppu M (1987) Involvement of lipid oxidation products in the formation of fluorescent and cross-linked proteins. Chem Phys Lipids 44:277–296
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn BW, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478
Maughan RJ, Donnelly AE, Gleeson M, Whiting PH, Walker KA, Clough PJ (1989) Delayed-onset muscle damage and lipid peroxidation in man after a downhill run. Muscle Nerve 12:332–336
McCully KK, Faulkner JA (1986) Characteristics of lengthening contractions associated with injury to skeletal muscle fibres. J Appl Physiol 61:293–299
Newham DJ, McPhail G, Mills KR, Edwards RHT (1983) Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric contractions of human muscle. J Neurol Sci 61:109–122
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1986) Plasma creatine kinase changes after eccentric and concentric contractions. Muscle Nerve 9:59–63
Park Y, Sarathchandra K, Kehrer JP (1991) Oxidative changes in hypoxic rat heart tissue. Am J Physiol 260: H1395-H1405
Round JM, Jones DA, Cambridge G (1987) Cellular infiltrates in human skeletal muscle: exercise induced damage as a model for inflammatory muscle disease? J Neurol Sci 82:1–11
Smith LL (1991) Acute inflammation: the underlying mechanism in delayed onset muscle soreness? Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:542–551
Stark PE, Oliver CN, Stadtman ER (1987) Modification of hepatic proteins in rats exposed to high oxygen concentration. FASEB J 1:36–39
Szasz G, Gruber W, Bernt E (1976) Creatine kinase in serum I. Determination of optimum reaction conditions. Clin Chem 22:650–656
Witt EH, Reznick AZ, Viguie CA, Stark-Reed P, Packer L (1992) Exercise, oxidative damage and effects of antioxidant manipulation. J Nutr 122:766–773
Zerba E, Komorowski TE, Faulkner JA (1990) Free radical injury to skeletal muscles of young, adult and old mice. Am J Physiol 258:C429-C435
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxton, J.M., Donnelly, A.E. & Roper, H.P. Indices of free-radical-mediated damage following maximum voluntary eccentric and concentric muscular work. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 68, 189–193 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376765
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376765