Abstract
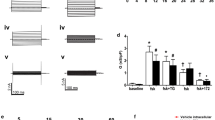
Activation of Cl− and K+ channels is necessary to drive ion secretion in epithelia. There is substantial evidence from previous reports that vesicular transport and exocytosis are involved in the regulation of ion channels. In the present study we examined the role of cytoskeletal elements and components of intracellular vesicle transport on ion channel activation in bronchial epithelial cells. To this end, cells were incubated with a number of different compounds which interact with either microtubules or actin microfilaments, or which interfere with vesicle transport in the Golgi apparatus. The effectiveness of these agents was verified by fluorescence staining of cellular microtubules and actin. The function was examined in 36Cl− efflux studies as well as in whole-cell (WC) patch-clamp and cell-attached studies. The cells were studied under control conditions and after exposure to (in mmol/l) ATP (0.1), forskolin (0.01), histamine (0.01) and hypotonic bath solution (HBS, NaCl 72.5). In untreated control cells, ATP primarily activated a K+ conductance whilst histamine and forskolin induced mainly a Cl− conductance. HBS activated both K+ and Cl− conductances. Incubation of the cells with brefeldin A (up to 100 μmol/l) did not inhibit WC current activation and 36Cl− efflux. Nocodazole (up to 170 μmol/l) reduced the ATP-induced WC current, and mevastatin (up to 100 μmol/l) the cell-swelling-induced WC current. Neither had any effect on the WC current induced by forskolin and histamine. Also 36Cl− efflux induced by HBS, ATP, forskolin and histamine was unaltered by these compounds. Similarly, colchicine (10 μmol/l) and taxol (6 μmol/l) affected neither 36Cl− efflux nor WC current induced by ATP, forskolin, histamine or HBS. In contrast, depolymerisation of actin by cytochalasin D (10 μmol/l) significantly attenuated 36Cl− effluxes and WC current activation by the above-mentioned agonists. Incubation with a C2 clostridial toxin (5 nmol/l) showed similar effects on WC currents. Moreover, when cytochalasin D (10 μmol/l), C2 clostridial toxins (5 nmol/l), or phalloidin (10 μmol/l) were added to the pipette filling solution current activation was markedly reduced. However, in excised inside-out membrane patches, cytochalasin D (10 μmol/l), G-actin (10 μmol/l) and phalloidin (10 μmol/l) had no effect. These data suggest that actin participates in the activation of ion channels in 16HBE14o- epithelial cells and support the concept that exocytosis is a crucial step in the regulation of Cl− and K+ channels in these cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktories K, Bärmann M, Ohishi I, Tsuyama S, Jakobs KH, Habermann E (1986) Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin. Nature 322:390–392
Barak LS, Yocum RR, Nothnagel EA, Webb WW (1980) Fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton in living cells with 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:980–984
Bifulco M, Laezza C, Aloj SM, Garbi C (1993) Mevalonate controls cytoskeleton organization and cell morphology in thyroid epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol 155:340–348
Borisy GG, Taylor EW (1967) The mechanism of action of colchicine. J Cell Biol 34:525–531
Bradbury NA, Jilling T, Gabor B, Sorscher EJ, Bridges RJ, Kirk KL (1992) Regulation of plasma membrane recycling by CFTR. Science 256:530–531
Burgoyne RD, Morgan A (1993) Regulated exocytosis. Biochem J 293:305–316
Burgoyne RD, Hansel SE, Morgan A, Rennison ME, Turner MD, Wilde CJ (1991) Calcium, the cytoskeleton and calpactin (annexin II) in exocytotic secretion from adrenal chromaffin and mammary epithelial cells. Biochem Soc Trans 19:1085–1089
Cantiello HF, Stow JL, Adriana GP, Ausiello DA (1991) Actin filaments regulate epithelial Na+ channel activity. Am J Physiol 261:C882-C888
Cooper JA (1987) Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol 105:1473–1478
Cozens AL, Yezzi MJ, Kunzelmann K, Ohrui T, Chin L, Eng K, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH, Gruenert DC (1994) CFTR expression and chloride secretion in polarized immortal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 10:38–47
Creutz CE (1992) The annexins and exocytosis. Science 258:924–931
Eilers U, Klumperman J, Hauri H-P (1989) Nocodazole, a microtubule-active drug, interferes with apical protein delivery in cultured intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Cell Biol 108:13–22
Flanagan MD, Lin S (1979) Cytochalasins block actin filament elongation by binding to high affinity sites associated with F-actin. J Biol Chem 255:835–838
Fuller CM, Bridges RJ, Benos DJ (1994) Forskolin but not ionomycin-evoked Cl− secretion in colonic epithelia depends on intact microtubules. Am J Physiol 266:C661-C668
Garber SS (1991) Membrane capacitance changes are correlated with [cAMP]i and activation of Cl− conductances in T84 cells. Pediatr Pulmonol suppl 6:256
Gögelein H (1988) Chloride channels in epithelia. Biochim Biophys Acta 947:521–547
Greger R, Allert N, Fröbe U, Normann C (1993) Increase in cytosolic Ca2+ regulates exocytosis and Cl− conductance in HT29 cells. Pflügers Arch 424:329–334
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Klausner RD, Donaldson JG, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1992) Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol 116:1071–1080
Kolb H-A (1990) Potassium channels in excitable and nonexcitable cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 115:51–91
Koslowsky T, Hug T, Ecke D, Klein P, Greger R, Gruenert DC, Kunzelmann K (1994) Ca2+ and swelling induced activation of ion conductances in bronchial epithelial cells. Pflügers Arch 428:597–603
Kunzelmann K, Koslowsky T, Gruenert DC, Greger R (1994) CAMP-dependent activation of ion conductances in bronchial epithelial cells. Pflügers Arch 428:590–596
Kuznetsov SA, Langford GM, Weiss DG (1992) Actin-dependent organelle movement in squid axoplasm. Nature 356:420–424
Machesky LM, Pollard TD (1993) Profilin as a potential mediator of membrane-cytoskeleton communication. Trends Cell Biol 3:381–385
McCann JD, Walsh MJ (1990) Regulation of Cl− and K+ channels in airway epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol 52:115–135
Morris AP, Frizzell RA (1994) Vesicle targeting and ion secretion in epithelial cells:implications for cystic fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 56:371–397
Morris AP, Cunningham SA, Tousson A, Benos DJ, Frizzel RA (1994) Polarization-dependent apical membrane CFTR targeting underlies cAMP-stimulated Cl− secretion in epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 266:C254-C268
O'Brodovich H, Canessa C, Ueda J, Rafii B, Rossier BC, Edelson J (1993) Expression of the epithelial Na+ channel in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol 265:C491-C496
Prince LS, Workman RB, Marchase RB (1994) Rapid endocytosis of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5192–5196
Prydz K, Hansen SH, Sandvig K, van Deurs B (1992) Effects of brefeldin A on endocytosis, transcytosis and transport to the Golgi complex in polarized MDCK cells. J Cell Biol 119:259–271
Schaerer E, Neutra MR, Kraehenbuhl J-P (1991) Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in transepithelial transport. J Membr Biol 123:93–103
Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB (1979) Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature 277:665–667
Schlatter E (1989) Antidiuretic hormone regulation of electrolyte transport in the distal nephron. Renal Physiol Biochem 12:65–84
Schwiebert EM, Mills JW, Stanton BA (1994) Actin-based cytoskeleton regulates a chloride channel and cell volume in a renal cortical collecting duct cell line. J Biol Chem 269:7081–7089
Shapiro M, Matthews J, Hecht G, Delp C, Madara JL (1991) Stabilization of F-actin prevents cAMP-elicited Cl− secretion in T84 cells. J Clin Invest 87:1903–1909
Suzuki M, Miyazaki K, Ikeda M, Kawaguchi Y, Sakai O (1992) F-actin network regulate a Cl− channel in renal proximal tubule cells. J Membr Biol 134:31–39
Verkman AS (1992) Water channels in cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol 54:97–108
Weng K, Wade JB (1994) Effect of brefeldin A on ADH-induced transport responses of toad bladder. Am J Physiol 266:C1069-C1076
Wiegers W, Just I, Müller H, Hellwig A, Traub P, Aktories K (1991) Alteration of the cytoskeleton of mammalien cells cultured in vitro by Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin and C3 ADP-ribosyltransferase. Eur J Cell Biol 54:237–245
Wieland T (1977) Modification of actins by phallotoxins. Naturwissenschaften 64:303–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hug, T., Koslowsky, T., Ecke, D. et al. Actin-dependent activation of ion conductances in bronchial epithelial cells. Pflügers Arch. 429, 682–690 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373989
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373989