Abstract
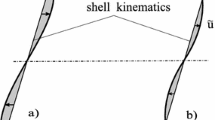
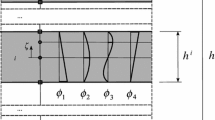
A numerical model for layered composite structures based on a geometrical nonlinear shell theory is presented. The kinematic is based on a multi-director theory, thus the in-plane displacements of each layer are described by independent director vectors. Using the isoparametric apporach a finite element formulation for quadrilaterals is developed. Continuity of the interlaminar shear stresses is obtained within the nonlinear solution process. Several examples are presented to illustrate the performance of the developed numerical model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ω:
-
reference surface
- ξα :
-
convected coordinates of the shell middle surface
- iζ:
-
coordinate in thickness direction
- i h :
-
thickness of layer i
- Xo :
-
position vector of the reference surface
- iXo :
-
position vector of midsurface of layer i
- t k :
-
orthonormal basis system in the reference configuration
- ia k :
-
orthonormal basis system of layer i
- δiW:
-
axial vector
- Ro :
-
orthonormal tensor in the reference configuration
- iR:
-
orthonormal tensor of layer i
- iσ:
-
Cauchy stress tensor
- iP:
-
First Piola-Kirchhoff stress tensor
- iq:
-
vector of interlaminar stresses
- inα,imα :
-
vector of stress resultants and stress couple resultants
- v x :
-
components of the normal vector of boundary Ωα
- iNαβ, iQα, iMαβ :
-
stress resultants and stress couple resultants of First Piola-Kirchhoff tensor
- \({}^i\tilde N^{\alpha \beta } ,{}^i\tilde Q^\alpha ,{}^i\tilde M^{\alpha \beta } \) :
-
stress resultants and stress couple resultants of Second Piola-Kirchhoff tensor
- iεαβ, iκαβ, iγαβ :
-
strains of layer i
- ΛK :
-
transformation matrix
- uo :
-
displacement vector of layer 1
- iβα :
-
local rotational degrees of freedom of layer i
References
Babuška, I.; Szabó, B. A.; Actis, R. L. (1992): Hierarchi models for laminated composites. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng. 33, 503–535
Dorninger, K.; Rammerstorfer, F. (1990): A layered composite shell element for elastic and thermoelastic stress and stability analysis at large deformations. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng. 30, 833–858
Epstein, M.; Glockner, P. G. (1977): Nonlinear analysis of Multilayered shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 13, 1081–1089
Epstein, M.; Huttelmaier, H. P. (1983): A finite element formulation for multilayered and thick plates. Comp. and Struct. 5, 645–650
Gruttmann, F.; Stein, E.; Wriggers, P. (1989): Theory and numerics of thin elastic shells with finite roations. Ingenieur Archiv. 59, 54–67
Huttelmaier, H. P.; Epstein, M. (1990): A large displacement finite element for multilayered plates. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 6, 189–196
Jing, H. S.; Liao, M. L. (1989): Partial hybrid stress element for the analysis of thick laminated composite plates. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng. 28, 2813–2827
Kapania, R. K.; Raciti, S. (1989): Recent advances in analysis of laminated beams and plates, part I: Shear effects and buckling. AIAAJ. 27, 923–934
Ladeur, P. (1992): Presentation of a linear or nonlinear analysis method for multilayered composite plats and shells with edge effects influence. In: Hirsch, C. H.; Zienkiewicz, O. C.; Onate, E. (eds.): Numerical methods in engineering '92, 637–644. London: Elsevier
Ladeur, P.; Batoz, J. L. (1989): Composite plate analysis using a new discrete shear triangular finite element. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng. 27, 343–359
Lee, C.; Liu, D. (1992): An interlaminar stress continuity theory for laminated composite analysis. Comp. and Struct. 42, 69–78
Levinson, M. (1980): An accurate, simple theory of the statics and dynamics of elastic plates. Mechanics research Communications 7, 343–350.
Li, Z. H.; Owen, D. R. J. (1989): Elastic-plastic analysis of laminated anisotropic shells by a refined finite element laminated model. Comp. and Struct. 32, No. 5, 361–382
Niederstedt, G. (1985): Leichtbau mit kohlefaserversträkten Kunststoffen. Kontakt und Studium Band 167. Sindelfingen: Expert
Noor, A. K.; Burton, W. S.; Peters, J. M. (1989): Assessment of computational models for multilayered composite cylinders. In: Noor, A. K. et al. (eds.): Analytical and Computational models of shells. Vol. 3, ASME 3, 419–441. New York
Pagano, N. J. (1970): Exact solutions for rectangular bidirectional composites and sandwich plates. J. Comp. Mat. 4, 20–34
Peseux, B.; Dubigeon, S. (1991): Equivalent homogeneous finite element for composite materials via Reissner principle. Part II: Finite element for shells. Int. J. Num. Meth. 31, 1497–1509
Pinsky, P.; Jasti, R. V. (1989): A mixed finite etement for laminated composite plates based on the use of bubble functions. Eng. Comp. 6, 316–330
Puchta, N. S.; Reddy, J. N. (1984): A mixed shear flexible element for the analysis of laminated plates. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engng. 44, 213–227
Rammerstorfer, F. G. (1992): Lectures on composite and sandwich shells. In: Rammerstorfer, F. G. (ed.): Nonlinear analysis of shells by finite elements. CISM courses and lectures. No. 328, pp. 131–194. Wien, New York: Springer
Reddy, J. N. (1984): A simple higher theory for laminated composite plates. J. Appl. Mech. ASME 51, 745–752
Reddy, J. N.; Chandrashekhara, K. (1985): Nonlinear analysis of laminated shells including transverse shear strains. AIAA Journal 23, 440–441
Reddy, J. N.; Barbero, E. J.; Teply, J. L. (1989): A plate bending element based on a generalized laminate plate theory. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng. 28, 2275–2292
Simo, J. C.; Fox, D. D.; Rifai, M. S. (1989): On a stress resultant geometrically exact shell model, part I: Formulation and optimal parametrization. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engng. 72, 267–304
Tessler, A.; Saether, E. (1991): A computationally viable higher-order theory for laminated composite plates. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng. 31, 1069–1086
Toledano, A.; Murakami, H. (1987): A high-order laminated plate theory with improved in-plane responses. Int. J. Solids Struct. 23, 111–131
Tsai, S. W.; Hahn, H. T. (1980): Introduction to composite materials. Technomic Publishing, Library of Congress, Westport Lancaster, USA
Wagner, W.; Gruttmann, F. (1991): On the stability behaviour of composite shells. In: Ladevèze, P.; Zienkiewicz O. C. (eds.): Proceeding of the European Conference on New Advances in Computational Structural Mechanics, Giens (France) 2–5.4.1991, pp. 539–546
Wagner, W.; Stein, E. (1992): A new finite element formulation for colindrical shells of composite material. Comp. Eng. (in publication)
Wagner, W.; Gruttmann, F. (1992): A simple finite rotation formulation for composite shell elements. Eng. Comput. (in publication)
Whitney, J. M.; Pagano, N. J. (1970): Shear deformation in heterogeneous anisotropic plates. J. Appl. Mech. ASME, 37, 1031–1036
Wriggers, P.; Gruttmann, F. (1990): Large deformations of thin shells: Theory and finite-element-diskretization. In: Noor, A.; Belytschko, T.; Simo, J. C. (eds.): Analytical and computational models of shells. Vol. 3, ASME CED, 135–159
Yoda, T.; Atluri, S. N. (1992): Postbuckling analysis of stiffened laminated composite panels using a higher-order shear defor-mation theory. Comput. Mech. 9, 390–404
Zienkiewicz, O. C.; Taylor, R. L. (1988): The finite element method. 4th edition, Vol. 1. London: McGraw Hill
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. N. Atluri, May 19, 1993
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gruttmann, F., Wagner, W., Meyer, L. et al. A nonlinear composite shell element with continuous interlaminar shear stresses. Computational Mechanics 13, 175–188 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00370134
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00370134