Summary
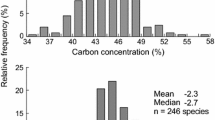
δ13C values were measured for 45 Poaceae species collected in the northern Sahara desert, at the foot of the Saharan Atlas. The results indicate a clear relationship between carbon isotope discrimination and phytogeographical distribution of the grasses. Mediterranean species predominantly had δ13C values indicating the C3 pathway of photosynthesis. By contrast, nearly all species belonging to the Saharo-Arabian and /or Sudanian group showed a C4 like carbon isotope composition. Leaf material of two species, Lygeum spartum and Stipa tenacissima, had δ13C values in the region of-20‰, i.e. intermediate between the mean δ13C values of C3 and C4 plants. However, additional speciments of both these grasses obtained from a different source (herbarium of the Hebrew University, Jerusalem) yielded a C3 like carbon isotope composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender, M.M.: Variations in the 13C/12C ratios of plants in relation to the pathway of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation. Phytochemistry 10, 1239–1244 (1971)
Bisalputra, T., Downton, W.J.S., Tregunna, E.B.: The distribution and ultrastructure of chloroplasts in leaves differing in photosynthetic carbon metabolism. I. Wheat, sorghum, and Aristida (Gramineae). Canad. J. Bot. 47, 15–21 (1969)
Björkman, O.: Comparative photosynthetic CO2 exchange in higher plants. In: Photosynthesis and photorespiration (M.D. Hatch, C.B. Osmond, R.O. Slatyer, eds.), pp. 18–32. New York-London-Sydney-Toronto: Wiley 1971
Black, C.C.: Ecological implications of dividing plants into groups with distinct photosynthetic production capacities. Adv. Ecol. Res. 7, 87–114 (1971)
Black, C.C.: Photosynthetic carbon fixation in relation to net CO2 uptake. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 24, 253–286 (1973)
Brown, W.V.: Variations in anatomy, associations, and origins of Kranz tissue. Amer. J. Bot. 62, 395–402 (1975)
Brown, W.V., Smith, B.N.: Grass evolution, the Kranz syndrome, 13C/12C ratios, and continental drift. Nature (Lond.) 239, 345–346 (1972)
Downes, R.W.: Differences in transpiration rates between tropical and temperate grasses under controlled conditions. Planta (Berl.) 88, 261–273 (1969)
Downes, R.W.: Effect of light intensity and leaf temperature on photosynthesis and transpiration in wheat and sorghum. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 23, 775–782 (1970)
Downes, R.W., Hesketh, J.D.: Enhanced photosynthesis at low oxygen concentrations: differential response of temperate and tropical grasses. Planta (Berl.) 78, 79–84 (1968)
Downton, W.J.S.: Preferiental C4-dicarboxylic acid synthesis, the postillumination CO2 burst, carboxyl transfer step, and grana configurations in plants with C4-photosynthesis. Canad. J. Bot. 48, 1795–1890 (1970)
Downton, W.J.S.: Check list of C4 species. In: Photosynthesis and photorespiration (M.D. Hatch, C.B. Osmond, R.O. Slatyer, eds.), pp. 554–558. New York-London-Sydney-Toronto: Wiley 1971
Downton, W.J.S.: The occurrence of C4 photosynthesis among plants. Photosynthetica 9, 96–105 (1975)
Downton, W.J.S., Berry, J., Tregunna, E.B.: Photosynthesis: temperate and tropical characteristics within a single grass genus. Science 163, 78–79 (1969)
Downton, W.J.S., Tregunna, E.B.: Carbon dioxide compensation—its relation to photosynthetic carboxylation reactions, systematics of the Gramineae, and leaf anatomy. Canad. J. Bot. 46, 207–215 (1968)
Ellis, R.P.: The significance of the occurrence of both Kranz and non-Kranz leaf anatomy in the grass species Alloteropsis semialata. S. Afr. J. Sci. 70, 169–173 (1974)
Goldstein, L.D., Ray, T.B., Kestler, D.P., Mayne, B.C., Brown, R.H., Black, C.C.: Biochemical characterization of Panicum species which are intermediate between C3 and C4 photosynthesis plants. Plant Sci. Letters 6, 85–90 (1976)
Haberlandt, G.: Physiologische Pflanzenanatomie. Leipzig: Engelmann 1904
Hatch, M.D., Slack, C.R.: Photosynthetic CO2 fixation pathways. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 21, 141–162 (1970)
Hofstra, J.J., Aksornkoae, S., Atmowidjojo, S., Banaag, Santosa, J.F., Sastrohoetomo, R.A., Thu, L.T.N.: A study on the occurrence of plants with a low CO2 compensation point in different habitats in the tropics. Ann. Bogor. 5, 143–157 (1972)
Holden, M.: Chloroplast pigments in plants with the C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 7, 41–49 (1973)
Kanai, R., Black, C.C.: Biochemical basis for net CO2 assimilation in C4-plants. In: Net carbon dioxide assimilation in higher plants (C.C. Black, ed.), pp. 75–105. Am. Soc. Plant Physiol. (1972)
Kanai, R., Kashiwagi, M.: Panicum milioides, a Gramineae plant having Kranz leaf anatomy without C4-photosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 16, 669–679 (1975)
Kassas, M.: Die Pflanzen der Sahara. In: Sahara (C. Krüger, ed.), pp. 162–181. Wien-München: Schroll 1967
Kortschak, H.P., Hartt, C.E., Burr, G.O.: Carbon dioxide fixation in sugarcane leaves. Plant Physiol. 40, 209–213 (1965)
Krenzer, E.G., Moss, D.N.: Carbon dioxide compensation in grasses. Crop Sci. 9, 619–621 (1969)
Krenzer, E.G., Moss, D.N., Crookston, R.K.: Carbon dioxide compensation points of flowering plants. Plant Physiol. 56, 194–206 (1975)
Laetsch, W.M.: The C4 syndrome: a structural analysis. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25, 27–52 (1974)
Long, S.P., Incoll, L.D., Woolhouse, H.W.: C4 photosynthesis in plants from cool temperate regions, with particular reference to Spartina townsendii. Nature (Lond.) 257, 622–624 (1975)
Maire, R.: Flore de l'Afrique du Nord, Vol. I. Paris: Jouve 1952
Maire, R.: Flore de l'Afrique du Nord, Vol. II. Paris: Jouve 1953
Maire, R.: Flore de l'Afrique du Nord, Vol. III, Paris: Jouve 1955
Mooney, H., Troughton, J.H., Berry, J.A.: Arid climates and photosynthetic systems. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yearb. 73, 793–805 (1974)
Moser, H.: Untersuchungen über die Blattstruktur von Atriplex-Arten und ihre Beziehungen zur Systematik. Beih. Bot. Zbl. 52B, 378–388 (1935)
Moss, D.N., Krenzer, E.G., Brun, W.A.: Carbon dioxide compensation points in related plant species. Science 164, 187–188 (1969)
Pilger, R.: Das System der Gramineae. Bot. Jb. 76, 281–384 (1954)
Potztal, E.: Graminales. In: A. Engler's Syllabus der Pflanzenfamilien, Bd. 2 (H. Melchior, Hrsg.). S. 561–578. Berlin: Borntraeger 1964
Quezel, P., Santa, S.: Nouvelle Flore de l'Algérie et des régions désertiques méridionales, Tome I. Paris: Edition du Centre de la Recherche Scientifique 1962
Sabnis, T.S.: The physiological anatomy of the plants of the Indian desert. J. Indian Bot. 2, 217–235 (1921)
Sankhla, N., Ziegler, H., Vyas, O.P., Stichler, W., Trimborn, P.: Eco-physiological studies on Indian arid zone plants. V. A screening of some species for the C4-pathway of photosynthetic CO2-fixation. Oecologia (Berl.) 21, 123–129 (1975)
Shantz, H.L., Piemeisel, L.N.: The water requirements of plants at Akron, Colorado. J. agric. Res. 34, 1093–1189 (1927)
Slatyer, R.O.: Carbon dioxide and water vapour exchange in Atriplex leaves. In: The biology of Atriplex (R. Jones, ed.), pp. 23–29. Canberra: Div. Pl. Ind. CSIRO 1970
Smith, B.N., Benedict, C.R.: Carbon isotopic ratios of chemical constituents of Panicum maximum L. Plant Cell Physiol. 15, 949–951 (1974)
Smith, B.N., Brown, W.V.: The Kranz syndrome in the Gramineae as indicated by carbon isotopic ratios. Amer. J. Bot. 60, 505–513 (1973)
Smith, B.N., Epstein, S.: Two categories of 13C/12C ratios for higher plants. Plant Physiol. 47, 380–384 (1971)
Smith, B.N., Robbins, M.J.: Evolution of C4 photosynthesis: an assessment based on 13C/12C ratios and Kranz anatomy. In: Proceed. Third Int. Cong. Phot. (M. Avron, ed.), pp. 1579–1587. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1974
Stocker, O.: Der Wasser- und Photosynthesehaushalt von Wüstenpflanzen der südalgerischen Sahara. I. Standorte und Versuchspflanzen. Flora 163, 46–88 (1974a)
Stocker, O.: Der Wasser- und Photosynthesehaushalt von Wüstenpflanzen der südalgerischen Sahara. II. Tagesserien. Flora 163, 89–142 (1974b)
Stocker, O.: Der Wasser- und Photosynthesehaushalt von Wüstenpflanzen der südalgerischen Sahara. III. Jahresgang und Konstitutionstypen. Flora 163, 480–529 (1974c)
Stocker, O.: The water-photosynthesis syndrome and the geographical plant distribution in the Saharian deserts. In: Water and plant life — problems and modern approaches, Part 7D (O.L. Lange, L. Kappen, E.D. Schulze, eds.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976 (in press)
Täckholm, G., Drar, M.: Flora of Egypt, Vol. I. Cairo: Fouad I University 1941
Tregunna, E.B., Smith, B.N., Berry, J.A., Downton, W.J.S.: Some methods for studying the photosynthetic taxonomy of the angiosperms. Canad. J. Bot. 48, 1209–1214 (1970)
Troughton, J.H.: Aspects of the evolution of the photosynthetic carboxylation reaction in plants. In: Photosynthesis and photorespiration (M.D. Hatch, C.B. Osmond, R.O. Slatyer, eds.), pp. 124–129. New York-London-Sydney-Toronto: Wiley 1971
Troughton, J.H., Card, K.A., Hendy, C.H.: Photosynthetic pathways and carbon isotope discrimination by plants. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yearb. 73, 768–780 (1974)
Volkens, G.: Die Flora der ägyptisch-arabischen Wüste. Berlin 1887
Welkie, G.W., Caldwell, M.: Leaf anatomy of species in some dicotyledon families as related to the C3 and C4 pathways of carbon fixation. Canad. J. Bot. 48, 2135–2146 (1970)
Winter, K.: Die Rolle des Crassulaceen-Säurestoffwechsels als biochemische Grundlage zur Anpassung von Halophyten an Standorte hoher Salinität. Dissertation. TH Darmstadt (1975)
Zohary, M.: Geobotanical foundations of the Middle East, Vol. I. Stuttgart: Fischer 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winter, K., Troughton, J.H. & Card, K.A. δ13C values of grass species collected in the northern Sahara desert. Oecologia 25, 115–123 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00368848
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00368848