Abstract
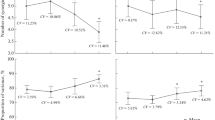
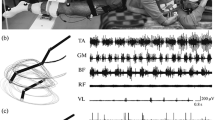
By using a suitable experimental and mathematical procedure variables characterising motor coordination in human locomotion have been obtained for different subjects and correlations between them have been analysed.—1. The comparison between the EMG signals and the torques at joints point out the complex coordination of muscle activation with particular reference to the function of biarticular muscles.—1. The comparison between the EMG signals and the instantaneous length of the eleven muscles considered suggests a relevant influence of the reflex regulation from Ia afferents.—It appears that locomotion cannot be considered to be a completely stereotiped function. In fact, despite the similar kinematics, the torque time courses of different subjects present significant differences in agreement with different temporal sequence of muscle activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein, M.A.: The coordination and regulation of movements. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1967
Bizzi, E., Kalil, R.E., Tagliasco, V.: Eye-head coordination in monkeys: evidence for controlly patterned organization. Science 173, 452–454 (1971)
Bresler,B., Berry,F.R.: Energy and power in the leg during normal level walking. Prosthetic Devices Research Project. Inst. of Engineering Research. U.C.B. Ser. II Issue 15, 1951
Cappozzo, A., Leo, T., Pedotti, A.: A general computing method for the analysis of human locomotion. J. Biomech. 8, 307–320 (1975)
Cappozzo, A., Figura, F., Marchetti, M., Pedotti, A.: The interplay of muscular and external forces in human ambulation. J. Biomech., 9, 35–43 (1976)
De Luca, C.: A model for a motor unit train recorded during constant force isometric contractions. Biol. Cybernetics 19, 159–167 (1975)
Drillis, R., Contini, R.: Body segment parameters. Tech. Rept. 116.03, N.Y.U., School of Eng. and Science, New York, 1966
Eberhart, H.D., Inman, V.T.: An evaluation of experimental procedures used in a foundamental study of human locomotion. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 51, 1213–1228 (1951)
Elftman, H.: the function of the muscles in locomotion. Amer. J. Physiol. 125, 357–366 (1939)
Engberg, I., Lundberg, A.: an electromiographic analysis of muscular activity in the hindlimb of the cat during unrestrained locomotion. Acta Physiol. Scand. 75, 614–630 (1969)
Gelfand, I.M., Tselin, M.: Mathematical modeling of mechanisms of the central nervous system. In: Models of the structural-functional organization of certain biological systems, pp. 1–22. Gelfand, I.M., Gurfinkel, V.S., Fomin, S.V., Tsetlin, M.L., eds. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press 1971
Goslow, G.E., Reinking, R.M., Stuart, D.G.: The cat step cycle: Hindlimb joint angles and muscle length during unrestrained locomotion. J. Morph. 141, 1–42 (1973)
Granit, R.: The basis of motor control, London-New York: Academic Press 1970
Grillner, S.: Locomotion in vertebrates: central mechanisms and reflex interaction. Physiol. Rev. 55, 247–304 (1975)
Kostyuk, P.G.: Interneural mechanism of interaction between descending and afferents signals in the spinal cord. In: Proc. of Golgi Centennial Symp., pp. 247–259. Santini, M., Ed. New York: Raven Press 1974
Gurfinkel, V.S., Kostyuk, P.G., Shik, M.L.: On some possible modes of descending control of the spinal cord activity in connection with the problem of motor control. In: Proc. Symp. Intern. Biophys. Congr. 4th, Moscow, 1973
Lamoureux, L.M.: Kinematic measurements in the study of human walking. Bull. Prostet. Res. BPR. 10–15: 1–84 (1971)
Mac Conail, M.A., Basmajian, J.V.: Muscles and movements. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins Comp. 1969
Manter, J.T.: The dynamics of quadrupedal walking. J. Exp. Biol. 15, 522–540 (1938)
Morrison, J.B.: The mechanics of muscle function in locomotion. J. Biomech. 3, 431–451 (1970)
Paul, J.P.: Forces transmitted by joints in the human body. Proc. Mech. Engng. 181, 3 (1967)
Ralston, H.J.: Energy-sped relation and optimal speed during level walking. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. 17, 277–283 (1958)
Severin, F.V., Orlowsky, G.N., Shik, M.L.: Work of the muscle receptors during controlled locomotion. Biofizika 12, 575–586 (1967) (Engl. Transl.)
Stark, L.: Neurological control system: Studies in bioengineering. New York: Plenum Press 1968
Sutherland, D.H., Hagy, J.L.: Measurement of gait movements from motion picture film. J. Bone J. Surg. 54, 787–797 (1972)
Fundamental studies of human locomotion and other information relating to design of artificial limbs, 2 Vol., Eberhart, H.D. (Ed.): University of California (1947)
The pattern of muscular activity in the lower extremety during walking: a presentation of summarized data. Tech. Rep. Sect. II, Iss. 25; Prosth. devices research project. Inst. Engng. Res. Berkeley, University of California (1953)
Wetzel, M.L., Stuart, D.G.: Activation and coordination of vertebrate Locomotion. In: McNeil-Alexander, R., Goldspink, G. (Eds.): Mechanics, energetics of animal locomotion. London: Chapman Haw (in press) 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedotti, A. A study of motor coordination and neuromuscular activities in human locomotion. Biol. Cybernetics 26, 53–62 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363992
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363992