Summary
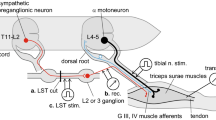
Studies were carried out to determine the cause of 20–30 msec difference in latency of reflex discharges elicited by electrical stimulation of A fibres of tibial nerve and recorded in inferior cardiac and kidney nerves in anaesthetized cats. Conduction velocity of tonic and reflex induced impulses was measured in these nerves with the cross-correlation method. Cross-correlograms of potentials of both nerves have one maximum corresponding to the mean velocity of approximately 0.6 m/sec. There's no significant activity corresponding to conduction through preganglionic B fibres even after suppressing the C fibres activity with tetraethylammonium. If the recording electrodes on the inferior cardiac nerve are placed 12–18 mm nearer to the ganglion stellatum than the electrodes on the kidney nerve to the aorticorenal ganglion the reflex discharge in the former nerve appears 20–30 msec earlier than in the latter. As this difference depends on non-equal recording conditions it cannot be quoted as an argument of bulbar mediation of spinal afferent impulses to so called cardiovascular neurones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon, P., W. Raule, and H. Schaefer: Zur Physiologie eines sympathischen Ganglions und zur Frage der Vasodilatatoren und des sympathischen Tonus. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 260, 116–136 (1954).
Casby, J. U., R. Siminoff, and T. R. Houseknecht: An analogue cross-correlator to study naturally induced activity in intact nerve trunks. J. Neurophysiol. 26 432–448 (1963).
Coote, J. H., and C. B. B. Downman: Central pathways of some autonomic reflex discharges. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 183, 714–729 (1966).
Dittmar, C.: Ein neuer Beweis für die Reizbarkeit der centripetalen Fasern des Rückenmarks. Ber. Sächs. Ges. Wiss., mat.-phys. Kl. 22, 18 (1870).
— Über die Lage des sogenannten Gefäßzentrums in der Medulla oblongata. Ber. Sächs. Ges. Wiss. 25, 449 (1873).
Downman, C. B. B., A. F. Goggio, B. A. McSwiney, and M. H. C. Young: Reflex vaso-motor responses of the paw of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 102, 216–227 (1943).
Erlanger, J., and H. S. Gasser: Electrical signs of nervous activity, p. 194. Philadelphia: Univ. of Pennsylvania Press 1937.
Fernandez de Molina, A., and E. R. Perl: Sympathetic activity and the systemic circulation in the spinal cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 181, 82–102 (1965).
Holmes, R., and R. W. Torrance: Afferent fibres of the stellate ganglion. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 44, 271–281 (1959).
Iggo, A., and M. Vogt: Preganglionic sympathetic activity in normal and in reserpine-treated cats. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 1950, 114–133 (1960).
Khayutin, V. M.: The vasomotor reflexes, pp. 1–376. „Nauka“, Moscow 1964 (in Russian).
Konradi, G. P.: On the bulbar vasomotor centre. Bull. exp. Biol. Med. 17, 39–42 (1944) (in Russian).
Langley, J. N.: Vasomotor centers. Part. III. Spinal vascular (and other autonomic) reflexes and the effect of strychnine on them. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 59, 231–258 (1924).
Mukherjee, S. R.: Effect of bladder distension on arterial blood pressure and renal circulation in acute spinal cats. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 138, 300–306 (1957).
Owsjannikow, F.: Die tonischen und reflektorischen Zentren der Gefäßnerven. Ber. Sächs. Ges. Wiss., math.-phys. Kl. 23, 135–147 (1871).
Page, J. H., and J. W. McCubbin: Renal vascular and systemic arterial pressure responses to nervous and chemical stimulation of the kidney. Amer. J. Physiol. 173, 411–420 (1953).
Pawloff, I. P.: On the vasomotor centres in the spinal cord. Voenno-medizinskii Zh. 129, 17–44 (1877) (in Russian).
Person, R. S., and L. N. Mishin: Auto- and cross-correlation analysis of the muscular electrical activity. Fiziol Zh. (Lening.) 49 (1963) (in Russian).
Sell, R., A. Erdelyi u. H. Schaefer: Untersuchungen über den Einfluß peripherer Nervenreizung auf die sympathische Aktivität. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 267, 566–581 (1958).
Skock, V. I.: Electrical reactions of the cats stellate ganglion; Proc. of Kiev University v. 16, pp. 203–209 (1957) (in Russian).
Sonina, R. S.: Vasomotor reflexes from small intestine receptive zone after acute brain anemization. Fiziol. Zh. (Lening.) (in press) (1967).
Szentivanyi, M., and A. Juhasz Nagy: A new aspect of the nervous control of the coronary blood vessels. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 44, 67–79 (1959).
Weidinger, H., L. Fedina, H. Kehrel u. H. Schaefer: Über die Lokalisation des „bulbären, sympathischen Zentrums“ und seine Beeinflussung durch Atmung und Blutdruck. Kreisl.-Forsch. 50, 229–241 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katunsky, A.Y., Khayutin, V.M. The reflex latency and the level of mediation of spinal afferent impulses to the cardiovascular sympathetic neurones. Pflügers Archiv 298, 294–304 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363870
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363870