Summary
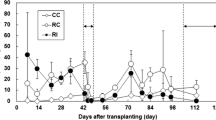
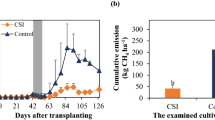
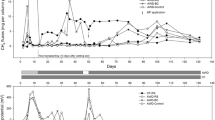
A field experiment was conducted to determine whether selected nitrification inhibitors (encapsulated calcium carbide and dicyandiamide) and SO sup-2inf4 -containing compounds [(NH4)2SO4 and Na2SO4] had mitigating effects on CH4 emissions from flooded rice. Microplots were established within a rice bay drill-seeded with the Texmont rice cultivar and CH4 fluxes were measured over the main rice cropping season. Methane emissions over the 77-day sampling period were approximately 230, 240, 260, 290, 310, and 360 kg CH4 ha-1 from the calcium carbide, Na2SO4-rate II, Na2SO4-rate I, (NH4)2SO4, dicyandiamide, and urea (control) treatments, respectively. Reductions in CH4 evolution, compared to the control, ranged from 14 to 35%, depending on treatment. The selected inhibitors and SO sup-2inf4 -containing compounds appear to be effective in reducing the CH4 emitted from flooded rice fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blake DR, Rowland FS (1988) Continuing worldwide increase in tropospheric methane, 1978–1987. Science 239:1129–1131
Bouwman AF (1991) Agronomic aspects of wetland rice cultivation and associated methane emissions. Biogeochemistry 15:65–88
Bronson KF, Mosier AR (1991) Effect of encapsulated calcium carbide on dinitrogen, nitrous oxide, methane, and carbon dioxide emissions from flooded rice. Biol Fertil Soils 11:116–120
Bronson KF, Touchton JT, Hauck RD (1989) Decomposition rate of dicyandiamide and nitrification inhibition. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 20:2067–2078
Cicerone RJ, Shetter JD, Delwiche CC (1983) Seasonal variations of methane flux from a California rice paddy. J Geophy Res 88:11022–11024
De Bont JAM, Lee KK, Bouldin DF (1978) Bacterial oxidation of methane in a rice paddy. Ecol Bull 26:91–96
Freney JR, Jacq VA, Baldensperger JF (1982) The significance of the biological sulfur cycle in rice production. Dev Plant Soil Sci 5:271–317
Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Seiler W (1986) Methane emission during a cultivation period from an Italian rice paddy. J Geophys Res 91:11803–11814
Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Seiler W (1985) Production, oxidation and emission of methane in rice paddies. FEMS Microbial Ecol 31:343–351
Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Seiler W (1986) Effects of vegetation on the emission of methane from submerged paddy soils. Plant and Soil 92:223–233
International Rice Research Institute (1988) Worldwide rice statistics 1987. IRRI, Los Baños, Philippines
Knowles R (1979) Denitrification, acetylene reduction, and methane metabolism in lake sediment exposed to acetylene. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:486–493
Kristjansson JK, Schonheit P, Thauer RK (1982) Different K s values for hydrogen and methanogenic and sulfate-reducing bacteria: An explanation for the apparent inhibition of methanogenesis by sulfate. Arch Microbiol 131:278–282
Lindau CW, Bollich PK, DeLaune RD, Patrick WH Jr, Law VJ (1991) Effect of urea fertilizer and environmental factors on CH4 emission from a Louisiana, USA rice field. Plant and Soil 136:195–203
Patrick WH Jr, DeLaune RD (1977) Chemical and biological redox systems affecting mutrient availability in coastal wetlands. Geosci Manage 18:131–137
Reddy KR, Patrick WH Jr (1984) Nitrogen transformations and loss in flooded soils and sediments. CRC Crit Rev Environ Control 13:274–309
Ryden JC, Rolston DE (1983) The measurement of denitrification. In: Freney JR, Sampson JR (eds) Gaseous loss of nitrogen from plant—soil systems. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W Junk publishers, The Hague, pp 91–132
SAS Institute (1988) SAS/STAT User's Guide, Release 6.03 edn. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, North Carolina
Sass RL, Fisher FM, Harcombe PA (1990) Methane production and emission in a Texas rice field. Global Biogeochem Cycles 4:47–68
Schutz H, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Rennenberg H, Seiler W (1989) A 3-year continuous record on the influence of daytime, season, and fertilizer treatment on methane emission rates from an Italian rice paddy. J Geophy Res 94:16405–16416
Seiler W, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Scharffe D (1984) Methane emission from rice paddies. J Atmos Chem 1:241–268
United States Envrionmental Protection Agency (1990) Overview of methane's contribution to global warming. In: Methane emissions and opportunities for control. USEPA/Air and Radiation, EPA/400/9-90-007, Washington, DC, pp 2–24
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1991) Introduction. In: Braatz BV, Hogan KB (eds) Substainable rice productivity and methane reduction research plan. USEPA/Office of Air and Radiation, Washington, DC, pp 12–18
Van Breeman N, Feijtel TCJ (1990) Soil processes and properties involved in the production of greenhouse gases, with special relevance to soil taxonomic systems. In: Bouwmann AF (ed) Soils and the greenhouse effect. John Wiley, Chichester, pp 195–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindau, C.W., Bollich, P.K., DeLaune, R.D. et al. Methane mitigation in flooded Louisiana rice fields. Biol Fertil Soils 15, 174–178 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361607
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361607