Abstract
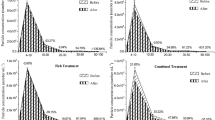
Experiments on the edible mussel Mytilus edulis, the American oyster Crassostrea virginica, and the hard clam Mercenaria mercenaria, using flowing systems, showed that the feeding and biodeposition rates were affected by food concentration. At all levels of food concentration, the order of increasing feeding rate (both the percent of available particulate carbon and the actual amount of carbon removed) was: clam < oyster < mussel. All bivalves exhibited lower feeding rates (both precent and actual) at low food concentrations. However, the precent of available food removed quickly increased to a maximum at food concentrations typical for the natural environment. This maximum remained constant for the mussel and oyster, but declined with increasing food concentration for the clam. However, because this percentage was for increasing levels, the actual carbon removed continued to increase up to the highest food level for all three bivalves. In increasing order of biodeposition rate, the bivalves were: clam < oyster < mussel. The biodeposition rates of the three bivalves increased logarithmically with increased food concentration as a result of the production of pseudofeces. The feeding and biodeposition data were used to calculate assimilation rates, and this pointed out the higher efficiency of the oyster compared to the mussel and clam.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Davids, C.: The influence of suspensions of micro-organisms of different concentrations on the pumping and retention of food by the mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). Neth. J. Sea Res. 2, 233–249 (1964).
Dean, D.: The experimental feeding of oysters. Unpublished Ph. D. Thesis, Rutgers University 1957.
Dodgson, R. W.: Report on mussel purification. Rep. Bd Agric. Fish., Lond. (Section II) 10, 1–498 (1928).
Dunstan, W. M. and K. R. Tenore: Intensive outdoor culture of marine phytoplankton enriched with treated sewage effluent. J. Aquacult. 1, 181–192 (1973).
Galtsoff, P. S.: The American oyster. Fishery Bull. 64, 1–480 (1964).
Guillard, R. R. L. and J. H. Ryther: Studies on marine planktonic diatoms. Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–239 (1962).
Haven, D. and R. Morales-Alamo: Aspects of biodeposition by oysters and other invertebrate filter feeders. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 487–498 (1966).
—: Filtration of partieles from suspension by the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 139, 248–264 (1970).
Jørgensen, C. B.: Biology of suspension feeding, 367 pp. New York: Pergamon Press 1966.
Loosanoff, V. L. and J. B. Engle: Effect of different concentrations of micro-organisms on the feeding of oysters, (C. virginica). Fishery Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. U.S. 51 (42), 31–57 (1947).
Lund, E. J.: A quantitative study of ciearance of a turbid medium and feeding by the oyster. Publs Inst. mar. Sci. Univ. Tex. 4, 296–312 (1957).
Riley, G. A.: Theory of food-chain relations in the ocean. In: The sea, Vol. II. pp 438–455. Ed. by M. N. Hill. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1959.
Ryther, J. H., W. M. Dunstan, K. R. Tenore and J. E. Huguenin: Controlled eutrophication-increasing food production from the sea by recycling human wastes. Bioscience 22, 144–152 (1972).
Tammes, P. M. and A. D. Dral: Observations on the straining of suspensions by mussels. Archs néerl. Zool. 11, 87–112 (1955).
Winter, J.: Filter feeding and food utilization in Arctica islandica L. and Modiolus modiolus L. at different food concentrations. In: Marine food chains, pp 196–206. Ed. by J. H. Steele. Berkeley: University of California Press 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Bunt, Miami
Contribution No. 2993 from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tenore, K.R., Dunstan, W.M. Comparison of feeding and biodeposition of three bivalves at different food levels. Marine Biology 21, 190–195 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355249
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355249