Summary
-
1
Novomessor cockerelli and N. albisetosus have been considered by previous authors to be individual foragers. This investigation, however, has demonstrated that workers of both species employ recruitment techniques when they encounter large prey.
-
2.
Novomessor workers usually carry large food items in a cooperative action directly to the nest.
-
3.
The chemical communication system employed during foraging was investigated in laboratory and field experiments. Secretions released from the poison gland proved to be the most effective recruitment signal.
-
4.
In order to summon nestmates to large food objects, Novomessor employs the following two different recruitment techniques.
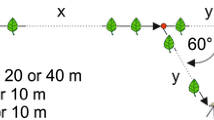
Short-range recruitment: After discovering the prey, the scout releases poison gland secretion into the air. Nestmates already in the vicinity are attracted from as far away as 2 m and move upwind toward the prey.
Long-range recruitment: If short-range recruitment does not attract enough foragers, a scout lays a chemical trail with poison gland secretion from the prey to the nest. Nestmates are stimulated by the pheromone alone to leave the nest and follow the trail toward the prey.
-
5.
The trail pheromone is short-lived, and trail laying consequently does not lead to mass communication. Instead, the pheromone releases a short pulse of outrushing ants, usually numerous enough to subdue the prey and to carry it home when the ants act jointly.
In several field experiments, we demonstrated that these recruitment and prey-retrieving techniques enable Novomessor to counteract interference competition by mass-recruiting ant species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein R.A.: Foraging strategies of ants in response to variable food density. Ecology 56, 213–219 (1975)
Blum, M.S.: Myrmicine trail pheromone: specificity, source and significance. J. NY Entomol. Soc. 82, 141–147 (1974)
Brown, W.L.: Novomessor manni a synonym of Aphaenogaster ensifera (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomol. News 85, 45–53 (1974)
Creighton, W.S.: The ants of North America. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv. Univ. 104, 1–585 (1950)
Creighton, W.S.: Studies on the distribution of the genus Novomessor (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Psyche (Cambridge, Massachusetts) 62, 89–97 (1955)
Davidson, D.W.: Foraging ecology and community organization in desert seed-eating ants. Ecology 58, 725–737 (1977)
Hölldobler, B.: Recruitment behavior in Camponotus socius (Hym. Fromicidae). Z. vergl. Physiol. 75, 123–142 (1971)
Hölldobler, B.: Homing in the harvester ant Pogonomyrmex badius. Science 171, 1149–1151 (1971b)
Hölldobler, B.: Chemische Strategie beim Nahrungserwerb der Diebsameise (Solenopsis fugax LATR.) und der Pharaoameis (Monomorium pharaonis L.). Oecologia (Berlin) 11, 371–380 (1973)
Hölldobler, B.: Recruitment behavior, home range orientation and territoriality in harvester ants, Pogonomyrmex. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1, 3–44 (1976a)
Hölldobler, B.: The behavioral ecology of mating in harvester ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Pogonomyrmex). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1, 405–523 (1976b)
Hölldobler, B., Wilson, E.O.: Recruitment trails in the harvester ant Pogonomyrmex badius. Psyche 77, 385–399 (1970)
Hölldobler, B., Stanton, R., Engel, H.: A new exocrine gland in Novomessor (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and its possible significance as a taxonomic character. Psyche 83, 32–41 (1976)
Kannowski, P.B.: Notes on the ant Novomessor manni (Wheeler and Creighton). Occas. Pap. Mus. Zool. Univ. Mich. 556, 1–6 (1954)
Markl, H., Hölldobler, B.: Recruitment and food-retrieving behavior in Novomessor (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). II. Vibrational signals. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 4, 183–216 (1978)
Moser, J.C., Silverstein, R.M.: Volatility of trail marking substance of the town ant. Nature 215, 206–207 (1967)
Oster, G., Wilson, E.O.: Caste and ecology in the social insects. Princeton: Princeton University Press (in press) (1978)
Wheeler, W.M., Creighton, W.S.: A study of the ant genera Novomessor and Veromessor. Proc. Am. Acad. Arts Sci. 69, 341–387 (1934)
Whitford, W.G.: Foraging behavior in Chihuahuan desert harvester ants. Am. Midl. Nat. 95, 455–458 (1976)
Whitford, W.G.: Foraging by seed-harvesting ants. In: Production ecology of ants and termites. Brian M.V., (ed.), pp. 107–110. London: Cambridge University Press 1978
Whitford, W.G., Ettershank, G.: Factors affecting foraging activity in Chihuahuan desert harvester ants. Environ. Entomol. 4, 689–696 (1975)
Wilson, E.O.: Chemical communication among workers of the fire ant Solenopsis saevissima (Fr. Smith). Anim. Behav. 10, 134–164 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. M. Lindauer on the occasion of his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hölldobler, B., Stanton, R.C. & Markl, H. Recruitment and food-retrieving behavior in Novomessor (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 4, 163–181 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354978
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354978