Abstract
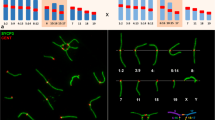
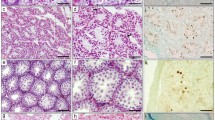
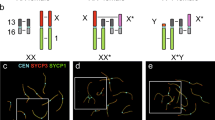
The normal association between the X and Y chromosomes at metaphase I of meiosis, as seen in air-dried light microscope preparations of mouse spermatocytes, is frequently lacking in the spermatocytes of the sterile interspecific hybrid between the laboratory mouse strains C57BL/6 and Mus spretus. The purpose of this work is to determine whether the separate X and Y chromosomes in the hybrid are asynaptic, caused by failure to pair, or desynaptic, caused by precocious dissociation. Unpaired X-Y chromosomes were observed in air-dried preparations at diakinesis, just prior to metaphase I. Furthermore, immunocytology and electron microscopy studies of surface-spread pachytene spermatocytes indicate that the X and Y chromosomes frequently fail to initiate synapsis as judged by the failure to form a synaptonemal complex between the pairing regions of the X and Y Chromosomes. Several additional chromosomal abnormalities were observed in the hybrid. These include fold-backs of the unpaired X or Y cores, associations between the autosome and sex chromosome cores, and autosomal univalents. The occurrence of abnormal autosomal and XY-autosomal associations was also correlated with cell degeneration during meiotic prophase. The primary breakdown in hybrid spermatogenesis occurs at metaphase I (MI), with the appearance of degenerated cells at late MI. In those cells, the X and Y are decondensed rather than condensed as they are in normal mouse MI spermatocytes. These results, in combination with the previous genetic analysis of spermatogenesis in hybrids and backcrosses with fertile female hybrids, suggest that the spermatogenic breakdown in the interspecific hybrid is primarily correlated with the failure of XY pairing at meiotic prophase, asynapsis, followed by the degeneration of spermatocytes at metaphase I. Secondarily, the failure of XY pairing can be accompanied by failure of autosomal pairing, which appears to involve an abnormal sex vesicle and degeneration at pachytene or diplotene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley T, Moses MJ (1980) End association and segregation of the achiasmatic X and Y chromosomes of the sand rat, Psammomys obesus. Chromosoma 78: 203–210
Batanian J, Hulten MA (1987) Electron microscopic investigations of synaptonemal complexes in an infertile human male carrier of a pericentric inversion inv(1)(p32q42). Regular loop formation but defective synapsis including a possible interchromosomal effect. Hum Genet 76: 81–89
Beechey CV (1973) X-Y chromosome dissociation and sterility in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 12: 60–67
Boer Pde, Branje HEB (1979) Association of the extra chromosome of tertiary trisomic male mice with the sex chromosomes during first meiotic prophase, and its significance for impairment of spermatogenesis. Chromosoma 73: 369–379
Boer Pde, Nijhoff JH (1981) Incomplete sex chromosome pairing in oligospermic male hybrids of Mus musculus and M. musculus molossinus in relation to the source of the Y chromosome and the presence or absence of a reciprocal translocation. J Rerod Fertil 62: 235–243
Burgoyne PS, Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U (1985) A reciprocal autosomal translocation which causes male sterility in the mouse also impairs oogenesis. J Reprod Fertil 75: 647–652
Cattanach BM, Pollard CE, Isaacson JH (1968) Ethyl methanesulfonate-induced chromosome breakage in the mouse. Mutat Res 6: 297–307
Chandley AC (1982) A pachytene analysis of two male-fertile paracentric inversions in chromosome 1 of the mouse and in the male-sterile double heterozygote. Chromosoma 85: 127–135
Chandley AC, Speed RM (1987) Cytological evidence that the Srr fragment of XY, Sxr mice pairs homologously at meiotic prophase with the proximal testis-determining region. Chromosoma 95: 345–349
Chandley AC, Speed RM, McBeath S, Hargreave TB (1986) A human 9;20 reciprocal translocation associated with male infertility analyzed at prophase and metaphase I of meiosis. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41: 145–153
Chapman VM, Kratzer PG, Quarantillo BA (1983) Electrophoretic variation for X chromosome-linked hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT) in wild-derived mice. Genetics 103: 785–795
Chapman VM, Keitz BT, Disteche CM, Lau EC, Snead ML (1991) Linkage of Amelogenin (Amel) to the distal protion of the mouse X chromosome. Genomics 10: 23–28
Counce SJ, Meyer GF (1973) Differentiation of the synaptonemal complex and the kinetochore in Locusta spermatocytes studied by whole mount electron microscopy. Chromosoma 44: 231–253
Dresser ME, Moses MJ (1980) Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus). IV. Light and electron microscopy of synapsis and nucleolar development by silver staining. Chromosoma 76: 1–22
Forejt J (1974) Nonrandom association between a specific autosome and the X chromosome in meiosis of the male mouse: possible consequence of the homologous centromeres' separation. Cytogenet Cell Genet 13: 369–383
Forejt J (1979) Meiotic studies of translocations causing male sterility in the mouse. II. Double heterozygotes for Robertsonian translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet 23: 163–170
Forejt J, Gregorova S (1977) Meiotic studies of translocations causing male sterility in the mouse. I. Autosomal reciprocal translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet 19: 159–179
Forejt J, Gregorova S, Goetz P (1981) XY pair associates with the synaptonemal complex of autosomal male-sterile translocations in pachytene spermatocytes of the mouse (Mus musculus). Chromosoma 82: 41–53
Gabriel-Robez O, Ratomponirina C, Dutrillaux B, Carre-Pigeon F, Rumpler Y (1986) Melotic association between the XY chromosomes and the autosomal quadrivalent of a reciprocal translocation in two infertile men, 46,XY,t(12;22) and 46,XY,t(17;21). Cytogenet Cell Genet 43: 154–160
Gabriel-Robez O, Rumpler Y, Ratomponirina C, Petit C, Levilliers J, Croqueme MF, Couturier J (1990) Deletion of the pseudoautosomal region and lack of sex-chromosome pairing at pachytene in two infertile men carrying an X;Y translocation. Cytogenet Cell Genet 54: 38–42
Haldane JBS (1922) Sex ratio and unisexual sterility in hybrid animals. J Genet 12: 101–109
Heyting C, Moens PB, Raamsdonk Wvan, Dietrich AJJ, Vink ACG, Redeker EJW (1987) Identification of two major components of the lateral elements of synaptonemal complexes of the rat. Eur J Cell Biol 43: 148–154
Hotta Y, Chandley AC (1982) Activities of X-linked enzymes in spermatocytes of mice rendered sterile by chromosomal alterations. Gamete Res 6: 65–72
Imai HT, Matsuda Y, Shiroishi T, Moriwaki K (1981) High frequency of X-Y chromosome dissociation in primary spermatocytes of F1 hybrids between Japanese wild mice (Mus musculus molossinus) and inbred laboratory mice. Cytogenet Cell Genet 29: 166–175
Imai HT, Wada MY, Moriwaki K (1990) The sex chromosome association (Sxa) gene is located on the X-chromosome in mice. Jpn J Genet 65: 65–69
Jaafar H, Gabriel-Robez O, Rumpler Y (1989) Pattern of ribonucleic acid synthesis in vitro in primary spermatocytes from mouse testis carrying an X-autosome translocation. Chromosoma 98: 330–334
Johannisson R, Gropp A, Winking H, Coerdt W, Rehder H, Schwinger E (1983) Down's syndrome in the male. Reproductive pathology and meiotic studies. Hum Genet 63: 132–138
Johannisson R, Lohrs U, Wolf HH, Schwinger E (1987) Two different XY-quadrivalent associations and impairment of fertility in men. Cytogenet Cell Genet 45: 222–230
Lifschytz E, Lindsley DL (1972) The role of X-chromosome inactivation during spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69: 182–186
Luciani JM, Guichaoua MR, Mattei A, Morazzani MR (1984) Pachytene analysis of a man with a 13q;14q translocation and infertility. Behavior of the trivalent and nonrandom association with the sex vesicle. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38: 14–32
Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U (1986) Synaptonemal complex analysis in spermatocytes and oocytes of tertiary trisomic Ts(512)31H mice with male sterility. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41: 169–176
Matsuda Y, Imai HT, Moriwaki K, Kondo K, Bonhomme F (1982) X-Y chromosome dissociation in wild derived Mus musculus subspecies, laboratory mice, and their F1 hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet 34: 241–252
Matsuda Y, Imai HT, Moriwaki K, Kondo K (1983) Modes of inheritance of X-Y dissociation in inter-subspecies hybrids between BALB/c mice and Mus musculus molossinus. Cytogenet Cell Genet 35: 209–215
Matsuda Y, Hirobe T, Chapman VM (1991) Genetic basis of X-Y chromosome dissociation and male sterility in interspecific hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 4850–4854
Matsuda Y, Chapman VM (1992) Analysis of sex-chromosome aneuploidy in interspecific backcross progeny between the laboratory mouse strain C57BL/6 and Mus spretus. Cytogenet Cell Genet (in press)
Miklos GLG (1974) Sex-chromosome pairing and male fertility. Cytogenet Cell Genet 13: 558–577
Moens PB, Heyting C, Dietrich AJJ, Raamsdonk Wvan, Chen Q (1987) Synaptonemal complex antigen location and conservation. J Cell Biol 105: 93–103
Moses MJ (1977) Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus). I. Morphology of autosomal complement in spread preparations. Chromosoma 60: 90–125
Pathak S, Elder FFB, Maxwell BL (1980) Asynaptic behavior of X and Y chromosomes in the Virginia opossum and the southern pygmy mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 26: 142–149
Purnell DJ (1973) Spontaneous univalence at male meiosis in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 12: 327–335
Rathenberg R, Muller D (1973) X and Y chromosome pairing and disjunction in a male mouse with an XYY sex-chromosome constitution. Cytogenet Cell Genet 12: 87–92
Rosenmann A, Wahrman J, Richler C, Voss R, Persitz A, Goldman B (1985) Meiotic association between the XY chromosomes and unpaired autosomal elements as a cause of human male sterility. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39: 19–29
Rosenmann A, Wahrman J, Richler C, Madgar I, Weissenberg R, Chaki R (1987) Under what circumstances is the human XY bivalent tangled? A note on chromosomally-derived sterility. Cytogenet Cell Genet 45: 58–61
Saadallah N, Hulten M (1985) A complex three breakpoint translocation involving chromosomes 2, 4, and 9 identified by meiotic investigations of a human male ascertained for subfertility. Hum Genet 71: 312–320
Setterfield LA, Mittwoch U (1986) Reduced oocyte numbers in tertiary trisomic mice with male sterility. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41: 177–180
Setterfield LA, Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U (1988a) Chromosome pairing and germ cell loss in male and female mice carrying a reciprocal translocation. J Reprod Fertil 82: 369–379
Setterfield LA, Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U (1988b) Pachytene pairing in relation to sperm and oocyte numbers in a malefertile reciprocal translocation in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 49: 293–299
Solari AJ, Ashley T (1977) Ultrastructure and behavior of the achiasmatic, telosynaptic XY pair of the sand rat (Psammomys obesus). Chromosoma 62: 319–336
Speed RM (1986a) Abnormal RNA synthesis in sex vesicles of tertiary trisomic male mice. Chromosoma 93: 267–270
Speed RM (1986b) Oocyte development in XO foetuses of man and mouse: The possible role of heterologous X-chromosome pairing in germ cell survival. Chromosoma 94: 115–124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by C. Heyting
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuda, Y., Moens, P.B. & Chapman, V.M. Deficiency of X and Y chromosomal pairing at meiotic prophase in spermatocytes of sterile interspecific hybrids between laboratory mice (Mus domesticus) and Mus spretus . Chromosoma 101, 483–492 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352471
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352471