Abstract
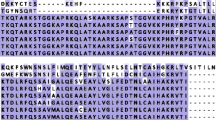
Two clones that encode variants (HCc1 and HCc2) of the major basic nuclear protein of the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii, were identified by immunoscreening of a cDNA expression library. The first clone carries a full-length cDNA with an open reading frame (HCc1) encoding 113 amino acids. The cDNA from the second clone lacks some of the 5′ end, and the coding sequence is only 102 residues. The two proteins display 77% sequence similarity and their NH2-ends are homologous to the NH2-peptide of the HCc protein determined by P. Rizzo. The amino acid composition, which confirms the basic nature of lysine-rich HCc proteins, differs markedly from other known DNA-binding proteins such as histones, HMGs or prokaryotic histone-like proteins. No convincing homology was found with other proteins. HCc antigens were localized on C. cohnii by immunofluorescence, and by electron microscopy (EM) with immunogold labelling. HCc proteins are mainly detected at the periphery of the permanently condensed chromosomes, where active chromatin is located, as well as in the nucleolar organizing region (NOR). This suggests that these basic, non-histone proteins, with a moderate affinity for DNA, are involved at some level in the regulation of gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Herzog M, Grahber A (1991) Separation of coding sequences from structural DNA in the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Mar Mol Biol Biotechnol (in press)
Bodansky, S, Mintz, LB, Holmes, DS (1979) The mesocaryote Gyrodinium cohnii lacks nucleosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 88:1329–1336
Caput, D, Beutler, B, Hartog, K, Thayer, R, Brown-Shimer, S, Cerami, A (1986) Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3′-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1670–1674
Cavalier-Smith, T (1981) The origin and early evolution of the eukaryotic cell. Soc Gen Microbiol Symp 32:33–84
Chartier, F, Laine, B, Bélaïche, D, Sautière, P (1989) Primary structure of the chromosomal proteins MC1a, MC1b and MC1c from the archaebacterium Methanothrix soehngenii. J Biol Chem 264:17006–17015
Crevel, G, Laine, B, Sautière, P, Galleron, C (1989) Isolation and characterization of DNA-binding proteins from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 and from spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1007:36–43
DeLange, RJ, Green, GR, Searcy, DG (1981 a) A histone-like protein (HTa) from Thermoplasma acidophilum. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem 256:900–904
DeLange, RJ, Williams, LC, Searcy, DG (1981 b) A histone-like protein (HTa) from Thermoplasma acidophilum. II. Complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem 256:905–911
Dodge, JD (1965) Chromosome structure in the dinoflagellates and the problem of the mesocaryotic cell. Excerpta Med Int Congr Ser 91:339–341
Doenecke, D, Toenjes, R (1984) Conserved dyad symmetry structures at the 3′ end of H5 histone genes: Analysis of the duck H5 gene. J Mol Biol 178:121–135
Drlica, K, Rouvière-Yaniv, J (1987) Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev 51:301–319
Dumas, JP, Ninio, J (1882) Efficient algorithm for folding and comparing nucleic acids sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 10:197–206
Garnier, J, Ogsthorpe, DJ, Robson, B (1978) Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol 120:97–120
Géraud ML, Sala-Rovira M, Herzog M, Soyer-Gobillard MO (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of the DNA-binding protein HCc during the cell cycle of the histone-less dinoflagellate protoctist Crypthecodinium cohnii B. Biol Cell 71, in press
Giesbrecht, P (1965) Uber das Ordnungsprinzip in den Chromosomes von Dinoflagellaten und Bakterien. Zentralbl Bakteriol Abt Orig 196:516–519
Goad, W, Kanehisha, MI (1982) Pattern recognition in nucleic acids sequences: I A general method for finding local homologies and symmetries. Nucleic Acids Res 10:247–264
Goodwin GH, Nicolas RH, Wright CA, Zavou S (1985) The structures and functions of the low molecular weight HMG proteins. In: Reeck GR, Goodwin GH, Puigdomènech P (eds) Chromosomal proteins and gene expression. (NATO ASI Series, Life Sciences vol 101) pp 221–238
Gourret, JP (1978) Description et interpretation des nucleoïdes structurés observés dans des bactéroïdes de Rhizobium. Biol Cell 32:299–306
Hamkalo, BA, Rattner, JC (1977) The structure of a mesokaryote chromosome. Chromosoma 60:39–47
Herzog, M, Maroteaux, L (1986) Dinoflagellate 17 S ribosomal sequence inferred from the gene sequence; Evolutionary implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8644–8648
Herzog, M, Soyer, MO (1981) Distinctive features of dinoflagellate chromatin. Absence of nucleosomes in a primitive species Prorocentrum micans E. Eur J Cell Biol 27:151–155
Herzog, M, vonBoletzky, S, Soyer, MO (1984) Ultrastructural and biochemical nuclear aspects of eukaryote classification: Independent evolution of the dinoflagellates as a sister group of the actual eukaryotes? Orig Life 13:205–215
Lenaers, G, Maroteaux, L, Michot, B, Herzog, M (1989) Dinoflagellates in evolution. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of largesubunit ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol 29:40–51
Lenaers G, Scholin C, Bhaud Y, Saint-Hilaire D, Herzog M (1991) A molecular phylogeny of dinoflagellate protists (Pyrrhophyta) inferred from the sequence of 24S rRNA divergent domains D1 and D8. J Mol Evol (in press)
Lipman, DJ, Wilbur, WJ, Smith, JF, Waterman, MS (1984) On the statistical significance of nucleic acid similarities. Nucleic Acids Res 12:215–226
Mayes, ELV (1984) Immunoaffinity purification of protein antigens. In: Walker, JM (ed) Methods in molecular biology. 1. Proteins, Humana Press, Clifton, pp 13–20
Mead, DA, Szczesna-Skorupa, E, Kemper, B (1986) Single-stranded DNA “blue” T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng 1:67–74
Pettijohn, DE (1988) Histone-like proteins and bacterial chromosome structure. J Biol Chem 263:12793–12796
Rizzo, PJ, Nooden, LD (1974) Partial characterization of dinoflagellate chromosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 349:415–427
Rizzo, PJ, Burghardt, RC (1980) Chromatin structure in the unicellular algae Olithodiscus luteus, Crypthecodinium cohnii and Peridinium balticum. Chromosoma 76:91–99
Rizzo, PJ (1981) Comparative aspects of basic nuclear proteins in dinoflagellates. BioSystems 14:433–443
Rizzo, PJ, Burghardt, RC (1982) Histone-like proteins and chromatin structure in the wall-less dinoflagellate Gymnodinium nelsoni. BioSystems 15:27–34
Rizzo, PJ, Morris, RL (1984) Some properties of the histone-like protein from Crypthecodinium cohnii (HCc). BioSystems 16:211–216
Rizzo, PJ, Choi, J, Morris, RL (1984) The major histone-like protein from the nonphotosynthetic dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii (Pyrrhophyta) is present in stationary phase. J Phycol 20:95–100
Rizzo PJ (1987) Biochemistry of the dinoflagellate nucleus. In: Taylor FJR (ed) The biology of dinoflagellates. (Botanical monographs, vol 21) Blackwell, pp 143–173
Rizzo, PJ, Morris, RL, Zweidler, A (1988) The histones of the endosymbiont alga of Peridinium balticum (Dinophyceae). BioSystems 21:231–238
Sambrook, J, Fritsch, EF, Maniatis, T (1989) Molecular cloning, A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY
Sigee, DC (1984) Structural DNA and genetically active DNA in dinoflagellate chromosomes. BioSystems 16:203–210
Sommerville, J (1985) Organizing the nucleolus. Nature 318:410–411
Sommerville, J (1986) Nucleolar structure and ribosome biogenesis. TIBS 11:438–442
Soyer, MO, Haapala, OK (1974a) Structural changes of Dinoflagellate chromosomes by pronase and ribonuclease. Chromosoma 47:179–192
Soyer, MO, Haapala, OK (1974b) Division and function of dinoflagellate chromosomes. J Microsc 19:137–146
Soyer-Gobillard, MO, Géraud, ML, Coulaud, D, Barray, M, Théveny, B, Révet, B, Delain, E (1990) Location of B- and Z-DNA in the chromosome of a primitive eukaryote dinoflagellate. J Cell Biol 111:293–308
Spiker, S, Key, JL, Wakim, B (1976) Identification and fractionation of plant histones. Arch Biochem Biophys 176:510–518
Steele RE (1980) Aspects of the composition and organization of dinoflagellate DNA. PhD thesis dissertation, Yale University
Taylor, FJR (1978) Problems in the development of an explicit hypothetical phylogeny of the lower eukaryotes. BioSystems 10:67–89
Tokuyasu, KT (1989) Use of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and poly(vinyl alcohol) for cryoultramicrotomy. Histochem J 21:163–171
Tuttle, R, Loeblich, AR (1975) An optimal growth medium for the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Phycologia 14:1–8
Vernet, G, Sala-Rovira, M, Maeder, M, Jacques, F, Herzog, M (1990) Basic nuclear proteins of the histone-less eukaryote Crypthecodinium cohnii (Pyrrhophyta): two-dimensional electrophoresis and DNA-binding properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 1048:281–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by M. Trendelenburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sala-Rovira, M., Geraud, M.L., Caput, D. et al. Molecular cloning and immunolocalization of two variants of the major basic nuclear protein (HCc) from the histone-less eukaryote Crypthecodinium cohnii (Pyrrhophyta). Chromosoma 100, 510–518 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352201
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352201