Abstract
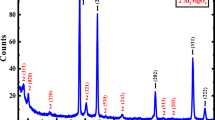
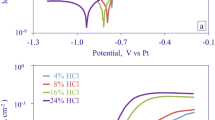
Various experimental studies on a new fast Ag+ ion-conducting composite electrolyte system: (1−x) (0.75Agl∶0.25AgCl)∶xAl2O3 are reported. Undried Al2O3 particles of size <10 Μm were used. The conventional matrix material Agl has been replaced by a new mixed 0.75Agl∶0.25AgCl quenched and/or annealed host compound. Conductivity enhancements ∼10 from the annealed host and ∼3 times from the quenched host obtained for the composition 0.7(0.75Agl∶0.25AgCl)∶0.3Al2O3, can be explained on the basis of the space charge interface mechanism. Direct measurements of ionic mobility Μ as σ function of temperature together with the conductivity σ were carried out for the best composition. Subsequently, the mobile ion concentration n values were calculated from Μ and a data. The value of heat of ion transport q* obtained from the plot of thermoelectric power θ versus 1/T supports Rice and Roth's free ion theory for superionic conductors. Using the best composition as an electrolyte various solid state batteries were fabricated and studied at room temperature with different cathode preparations and load conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Maier, in “Solid state ionics: materials and applications”, edited by B. V. R. Chowdari, S. Chandra, S. Singh and P. C. Srivastava (World Scientific, Singapore, 1992) p. 111.
A. K. Shukla and V. Sharma, ibid.“ p. 91.
J. Maier, in “Superionic solids and solid electrolytes — recent trends”, edited by A. L. Laskar and S. Chandra (Academic Press, New York, 1989) p. 137.
J. B. Wagner, in “High conductivity solid ionic conductors — recent trends and applications”, edited by T. Takahashi (World Scientific, Singapore, 1989) p. 146.
N. J. Dudney, Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 19 (1989) 103.
F. W. Poulsen, in “Transport-structure relations in fast ion and mixed conductors” edited by F. W. Poulsen, N. H. Andersen, K. Clausen, S. Skaarup and O. T. Sorensen (Riso Nat. Lab., Roskilde, Denmark, 1985) p. 67.
T. Jow and J. B. Wagner, Jr, J. Electrochem. Soc. 126 (1979) 1963.
K. Shahi and J. B. Wagner, Jr, ibid. 128 (1981) 6.
C. C. Liang, A. V. Joshi and N. E. Hamilton, J. Appl. Electrochem. 8 (1978) 445.
W. Jander, Angew. Chem. 42 (1929) 462.
C. C. Liang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 120 (1973) 1289.
M. F. Bell, M. Sayer, D. S. Smith and P. S. Nicholson, Solid State Ionics 9/10 (1983) 731.
A. Bunde, W. Dieterich and E. Roman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 55 (1985) 5.
R. Blender and W. Dieterich, J. Phys. C. 20 (1987) 6113.
N. F. Uvarov, V. P. Isupov, V. Sharma and A. K. Shukla, Solid State Ionics 51 (1992) 41.
U. Lauer and J. Maier, Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 96 (1992) 111.
R. C. Agrawal, R. K. Gupta, R. Kumar and A. Kumar, J. Mater. Sci. 29 (1994) 3673.
M. Watanabe, K. Sanui, N. Ogata, T. Kobayashi and Z. Ontaki, J. Appl. Phys. 57 (1985) 123.
S. Chandra, S. K. Tolpadi and S. A. Hashmi, Solid State Ionics 28/30 (1988) 651.
R. C. Agrawal, K. Kathal, R. Chandola and R. K. Gupta, in “Solid state ionics: materials and applications”, edited by B. V. R. Chowdari, S. Chandra, S. Singh and P. C. Srivastava (World Scientific, Singapore, 1992) p. 363.
R. C. Agrawal, K. Kathal and R. K. Gupta, Solid. State Ionics 74 (1994) 137.
R. C. Agrawal and R. Kumar, J. Phys. D. 27 (1994) 2431.
K. M. Shaju and S. Chandra, Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 181 (1994) 301.
K. Shahi, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 41 (1977) 11.
S. M. Girvin, J. Sol. Stat. Chem. 25 (1978) 65.
M. J. Rice and W. L. Roth, ibid. 4 (1972) 294.
S. Chandra and R. C. Agrawal, “Solid state battery — prospects and limitations” (National Academy of Sciences, India: Golden Jubilee Commemoration Volume, 1980) p. 1.
P. HAGENMULLER and W. van GOOL (editors), “Solid electrolytes”, Material Science Series (Academic Press, 1978).
K. Kiukkola and C. Wagner, J. Electrochem. Soc. 104 (1957) 308 & 379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, R.C., Gupta, R.K. Transport property and battery discharge characteristic studies on 1−x(0.75Agl∶0.25AgCl)∶ xAl2O3 composite electrolyte system. JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 30, 3612–3618 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351874
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351874