Abstract
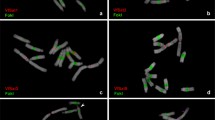
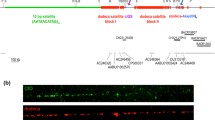
We have investigated the organisation, nucleotide sequence, and chromosomal distribution of a tandemly repeated, satellite DNA from Allium cepa (Liliaceae). The satellite, which constitutes about 4% of the A. cepa genome, may be resolved from main-band DNA in antibiotic-CsCl density gradients, and has a repeat length of about 375 base pairs (bp). A cloned member of the repeat family hybridises exclusively to chromosome telomeres and has a non-random distribution in interphase nuclei. We present the nucleotide sequences of three repeats, which differ at a large number of positions. In addition to arrays made up of 375-bp repeats, homologous sequences are found in units with a greater repeat length. This divergence between repeats reflects the heterogeneity of the satellite determined using other criteria. Possible constraints on the interchromosomal exchange of repeated sequences are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnheim N (1983) Concerted evolution of multigene families. In: Nei M, Kohn RK (eds) Evolution of genes and proteins. Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass, pp 38–61
Barnes SR, Webb DA, Dover G (1978) The distribution of satellite and main-band DNA components in the melanogaster species subgroup of Drosophila. I. Fractionation of DNA in actinomycin D and distamycin A density gradients. Chromosoma 67:341–363
Beauchamp RS, Mitchell AR, Buckland RA, Bostock CJ (1979) Specific arrangements of human satellite III DNA sequences in human chromosomes. Chromosoma 71:153–166
Bedbrook JR, Jones J, O'Dell M, Thompson RD, Flavell RB (1980) A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin in Secale species. Cell 19:545–560
Bennett MD (1982) Nucleotypic basis of the spatial ordering of chromosomes in eukaryotes and the implications of the order for genome evolution and phenotypic variation. In: Dover GA, Flavell RB (eds) Genome evolution. Academic Press, London, pp 239–261
Bennett MD, Gustafson JP, Smith JB (1977) Variation in nuclear DNA in the genus Secale. Chromosoma 61:149–176
Biggin MD, Gibson TJ, Hong GF (1983) Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:3963–3965
Bonner TI, Brenner DJ, Neufeld BR, Britten RJ (1973) Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol 81:123–135
Brahic CM, Haase L (1978) Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridisation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:6125–6129
Cooke HJ, McKay RDG (1978) Evolution of a human Y chromosome-specific repeated sequence. Cell 13:453–460
Deumling B, Greilhuber J (1982) Characterisation of heterochromatin in different species of the Scilla sibirica group (Liliaceae) by in situ hybridisation of satellite DNAs and fluorochrome banding. Chromosoma 84:535–555
Dover G (1982) Molecular drive: A cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Evans IJ, James AM, Barnes SR (1983) Organisation and evolution of repeated DNA sequences in closely related plant genomes. J Mol Biol 170:803–826
Flavell RB (1982) Sequence amplification, deletion and rearrangement: Major sources of variation during species divergence. In: Dover GA, Flavell RB (eds) Genome evolution. Academic, London, pp 301–323
Flavell RB, O'Dell M, Hutchinson J (1981) Nucleotide sequence organisation in plant chromosomes and evidence for sequence translocation during evolution. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 45:501–508
Fussell CP (1975) The position of interphase chromosomes and late replicating DNA in centromere and telomere regions of Allium cepa L. Chromosoma 50:201–210
Grunstein M, Hogness DS (1975) Colony hybridisation: A method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:3961–3965
Horz W, Zachau HG (1977) Characterisation of distinct segments in mouse satellite DNA by restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem 73:383–392
Ingle J, Pearson GG, Sinclair J (1973) Species distribution and properties of nuclear satellite DNA in higher plants. Nature New Biol 242:193–197
Jamieson G, Evans IJ, Barnes SR (1985) An enzymic method of preparing plant chromosomes for in situ hybridisation. Stain Technol (in press)
Jones JDG, Flavell RB (1982) The structure, amount and chromosomal localisation of defined repeated DNA sequences in species of the genus Secale. Chromosoma 86:613–641
Kirk JTO, Rees H, Evans G (1970) Base composition of nuclear DNA within the genus Allium. Heredity 25:507–512
Lam BS, Carroll D (1983) Tandemly repeated DNA sequences from Xenopus laevis. I. Studies on sequence organization and variation in satellite I DNA (741 base-pair repeat). J Mol Biol 165:567–585
Manuelidis L (1977) A simplified method for preparation of mouse satellite DNA. Anal Biochem 78:561–568
Miklos GLG (1982) Sequencing and manipulating highly repeated DNA. In: Dover GA, Flavell RB (eds) Genome evolution. Academic, London, pp 41–68
Miklos GLG, Gill AC (1981) The DNA sequences of cloned complex satellite DNAs from Hawaiian Drosophila and their bearing on satellite DNA sequence conservation. Chromosoma 82:409–427
Pardue ML, Gall JG (1975) Nucleic acid hybridisation to the DNA of cytological preparations. In: Prescott DM (ed) Methods in cell biology, Vol X. Academic, New York, pp 1–16
Rogers AW (1979) Techniques of autoradiography 3rd edn. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulsen AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Singer MF (1982) Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol 76:67–112
Smith GP (1976) Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossovers. Science 191:528–535
Sobell HM (1973) The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA and its implications in molecular biology. Progr Nucleic Acids Res Mol Biol 13:153–190
Stack SM, Clarke CR (1973) Differential Giemsa staining of the telomeres of Allium cepa chromosomes: Observations related to chromosome pairing. Can J Genet Cytol 15:619–624
Stack SM, Comings DE (1979) The chromosomes and DNA of Allium cepa. Chromosoma 70:161–181
Strachan T, Coen E, Webb D, Dover G (1982) Modes and rates of change of complex DNA families of Drosophila. J Mol Biol 158:37–54
Twigg AJ, Sherratt D (1980) Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid Col E1. Nature 283:216–218
Vosa CG (1976) Heterochromatic patterns in Allium. I. The relationship between the species of the cepa group and its allies. Heredity 36:383–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, S.R., James, A.M. & Jamieson, G. The organisation, nucleotide sequence, and chromosomal distribution of a satellite DNA from Allium cepa . Chromosoma 92, 185–192 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348692
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348692