Summary
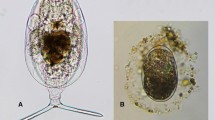
The salt water mite Hyadesia fusca has been recorded from Scandinavia for the first time. It is entirely restricted to the green alga Enteromorpha spp. in the littoral zone or in rockpools. The algae serve as substratum, food and breeding room but they also give rise to violent fluctuations in abiotic environmental parameters. However, oxygen availability and hydrogen-ion activities do not differ very much inside and outside the algal thalli. The fluctuations recorded are between 2 and 12 g O2·10-7 cm-2 min-1 and between pH 8.5 and 10.1.
H. fusca dominates the fauna of many brackish water rockpools. During breeding in June and July more than 900 animals, mostly larvae, may be found on 0.1 g Enteromorpha dry weight. In winter an average of 13 hibernating animals were found per 0.1 g algae. Copulation follows after a long precopula with the male riding on the female. The newborn larvae are often found near the rhizomes inside the algal tubes.
The mite is very tolerant of salinity variations. In laboratory experiments more than 4 weeks of survival, copulation, breeding and larval growth were found to be almost equally successful in salinities between 0.5 and 40‰S.
Hyadesia fusca is a characteristic member of the rockpool ecosystem. It is often very abundant, one of the few Enteromorpha grazers of of the ecosystem and it serves as food for fishes in the system. Together with some better known crustaceans this mite because of its tolerance and survival capabilities must be considered one of the hardiest members of the unstable rockpool ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bénard, F.: Sur deux nouvelles espèces d'Acariens marins, Hyadesia tumida et Hyadesia furcillipes: sous-ordre des Sarcoptiformes, famille des Hyadesidae. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2, 71–96 (1961).
Fox, H. M., Taylor, A. E. R.: The tolerance of oxygen by aquatic invertebrates. Proc. roy. Soc. B 143, 214–225 (1955).
Ganning, B.: Short time fluctuations of the microfauna in a rockpool in the northern Baltic proper. Veröff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh. Sonderbd. 2, 149–154 (1966).
— Laboratory experiments in the ecological work on rockpool animals with special notes on the ostracod Heterocypris salinus. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 15, 27–40 (1967).
—, Wulff, F.: The effects of bird droppings on chemical and biological dynamics in brackish water rockpools. Oikos 20, 274–286 (1969).
Ganning, B., Wulff, F.: Hällkar. Zool. Revy Nr 1–2, 8–10 (1969).
Ganning, B., Wulff, F.: Measurements of community metabolism in some Baltic brackish water rockpools by means of diurnal oxygen curves. Oikos 21 (in press, 1970).
Hagerman, L.: The macro- and microfauna associated with Fucus serratus L., with some ecological remarks. Ophelia 3, 1–43 (1966).
—: Environmental factors affecting Hirschmannia viridis (O. F. Müller) (Ostracoda) in shallow brackish water. Ophelia 7, 79–99 (1966).
Jansson, A. M.: The food-web of the Cladophora-belt fauna. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 15, 574–588 (1967).
Jansson, B.-O.: Salinity resistance and salinity preference of two oligochaetes Aktedrilus monospermatecus Knöllner and Marionina preclitellochaeta n.sp. from the interstitial fauna of marine sandy beaches. Oikos 13, 293–305 (1962).
—: Microdistribution of factors and fauna in marine sandy beaches. Veröff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh., Sonderbd. 2, 77–86 (1966).
—: The availability of oxygen for the interstitial fauna of sandy beaches. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 1, 123–143 (1967).
Lohman, H.: Lentungula fusca nov. spec., eine marine Sarcoptide. Wiss. Meeresuntersuch., N.F. 1, 83–96 (1896).
Ohm, G.: Die Besiedlung der Fucus-zone der Kieler Bucht und der westlichen Ostsee unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Mikrofauna. Kieler Meeresforsch. 20, 30–64 (1964).
Otto, G.: Die Fauna der Enteromorphazone der Kieler Bucht. Kieler Meeresforsch. 1, 1–48 (1936).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganning, B. Population dynamics and salinity tolerance of Hyadesia fusca (Lohman) (Acarina, Sarcoptiformes) from brackish water rockpools, with notes on the microenvironment inside Enteromorpha tubes. Oecologia 5, 127–137 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347626
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347626