Summary
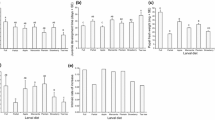
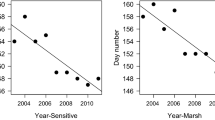
Densities were examined in natural populations consisting of horsenettle (Solanum carolinense), larvae of a horsenettle-specific phytophagous moth (Frumenta nundinella), and a polyphagous parasitoid wasp (Scambus pterophori), that parasitized the moth. Herbivore and parasitoid densities were both positively associated with fruit density, but moth larval density was linear while parasitoid density increased parabolically; thus, optimum moth survivorship was at intermediate moth densities. There was no evidence of escape from herbivory in time by plant populations due to either mean flowering date or a spread of flowering in seasonal time. However, one plant population and one moth population apparently escaped in space due to isolated location. Although plant reproductive success is reduced whether or not moth larvae are parasitized, both presence of a numerical herbivore refuge and parasitoid attack at high fruit and moth densities would be expected to stabilize long-term temporal dynamics of this simple food chain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bateman, M.A.: Determinants of abundance in a population of the Queensland fruit fly. In: Insect abundance (T.R.E. Southwood, ed.), pp. 119–131. London: Roy. Entomol. Soc. 1968
Black, J.N.: Competition between plants of different initial seed sizes in swards of subterranean clover (T. subterraneum L.) with particular reference to leaf area and light micro-climate. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 9, 299–318 (1958)
Britton, N., Brown, A.: An illustrated flora of the northern United States and Canada, 2nd ed. Vol. 3. New York: Dover 1970
Burnett, T.: Effects of temperature and host density on the rate of increase of an insect parasite. Amer. Natur. 85, 337–352 (1951)
Cavers, P.B., Harper, J.L.: Studies in the dynamics of plant populations I. The fate of seed and transplants introduced into various habitats. J. Ecol. 55, 59–72 (1967)
Cheke, R.A.: Experiments on the effect of host spatial distribution on the numerical response of parasitoids. J. Anim. Ecol. 43, 107–113 (1974)
Cockerell, T.D.A.: “Mimicry” among insects. Nature 133, 329–330 (1934)
Cottam, G., Curtis, J.T.: The use of distance measures in phytosociological sampling. Ecology 37, 451–460 (1956)
Cromartie, W.J.: The effect of stand size and vegetational background on the colonization of cruciferous plants by herbivorous insects. J. Appl. Ecol. 12, 517–533 (1975)
DeBach, P., Smith, H.S.: The effect of host density on the rate of reproduction of entomophagous parasites. J. Econ. Entomol. 34, 741–745 (1941)
Ehrlich, P.R., Birch, L.C.: The “balance of nature” and “population control”. Amer. Natur. 101, 97–107 (1967)
Eisenberg, R.M.: The regulation of density in a natural population of the pond snail, Lymnaea elodes. Ecology 47, 889–906 (1966)
Flanders, S.E.: Effect of host density on parasitism. J. Econ. Entomol. 28, 898–900 (1935)
Foott, W.H.: Occurrence of Frumenta nundinella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in Canada. Can. Entomol. 99, 443–444 (1967)
Hardin, J.W., Doerksen, G., Herndon, H., Hobson, M., Thomas, F.: Pollination ecology and floral biology of four weedy genera in southern Oklahoma. Southwest. Nat. 16, 403–412 (1972)
Hassell, M.P., Varley, G.C.: New inductive population model for insect parasites and its bearing on biological control. Nature 223, 1133–1137 (1969)
Holling, C.S.: Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 91, 385–398 (1959)
Ilnicki, R.D., Tisdell, T.F., Fertig, S.N., Furrer, A.H.Jr.: Life history studies as related to weed control in the northeast. 3. Horse nettle. Bull. no. 368. Kingston RI: Rhode Island Agric. Exp. Sta. 1962
Janzen, D.H.: Association of a rainforest palm and seed-eating beetles in Puerto Rico. Ecology 53, 258–261 (1972a)
Janzen, D.H.: Escape in space by Sterculia apetala seeds from the bug Dysdercus fasciatus in a Costa Rican deciduous forest. Ecology 53, 350–361 (1972b)
Linsley, E.G., Cazier, M.A.: Further observations on bees which take pollen from plants of the genus Solanum. Pan-Pac Entomol. 39, 1–18 (1963)
Liu, H.J., MacFarlane, R.P., Pengelly, D.H.: Relationships between flowering plants and four species of Bombus (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in southern Ontario. Can. Entomol. 107, 577–588 (1975)
Montgomery, B.E.: Preliminary studies of insect parasites in Indiana. Can. Entomol. 65, 185–190 (1933)
Murdoch, W.W.: Switching in general predators: experiments on predator specificity and stability of prey populations. Ecol. Monogr. 39, 335–354 (1969)
Murfeldt, M.E.: New species of Tineidae. Can. Entomol. 13, 242–246 (1881)
Nicholson, A.J., Bailey, V.A.: The balance of animal populations. Part. 1. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1935, 551–598 (1935)
Price, P.W.: Niche breadth and dominance of parasitic insects sharing the same host species. Ecology 52, 587–596 (1971)
Price, P.W.: Behavior of the parasitoid Pleolophus basizonus (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) in response to changes in host and parasitoid density. Can. Entomol. 104, 129–140 (1972)
Price, P.W., Tripp, H.A.: Activity patterns of parasitoids on the swaine jack pine sawfly Neodiprion swainei (Hymenoptera: Diprionidae), and parasitoid impact on the host. Can. Entomol. 104, 1003–1016 (1972)
Ralph, C.P.: Effect of host plant density on populations of a specialized, seed-sucking bug, Oncopeltus fasciatus. Ecology 58, 799–809 (1977)
Robertson, C.: Flowers and insects: lists of visitors of four hundred and fifty-three flowers. Carlinville Il: Science Press 1928
Root, R.B.: Organization of a plant-arthropod association in simple and diverse habitats: the fauna of collards (Brassica oleracea) Ecol. Monogr. 43, 95–124 (1973)
Shahjahan, M., Streams, F.: Plant effects of host-finding by Leiophron pseudopallipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of the tarnished plant bug. Environ. Entomol. 2, 921–925 (1973)
Sokal, R.R., Rohlf, F.J.: Biometry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman 1969
Steel, R.G.D., Torrie, J.H.: Principles and procedures of statistics. New York: McGraw-Hill 1960
Tisdell, T.F.: A life cycle study of horse nettle (Solanum carolinense). Ph. D. dissertation: Rutgers University 1961
Townes, H., Townes, M.: Ichneumon-flies of America north of Mexico. U.S. Nat. Mus. Bull., no. 216, part 2, p. 28, 1960
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solomon, B.P., McNaughton, S.J. Numerical and temporal relationships in a three-level food chain. Oecologia 42, 47–56 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347617
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347617