Abstract
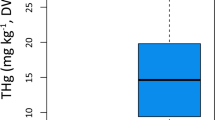
Trace metals were analyzed in the muscle and other organs from several species of deep-water sharks (particularly Centrophorus granulosus and Galeus melastomus) from 1280 to 1500 m depth in the eastern Mediterranean between 1985 and 1991. As has been shown with other pelagic fish, there was a significant correlation between specimen size and the mercury concentration in the muscle as well as in the liver and kidneys. For a given size, the level of mercury in sharks from the eastern Mediterranean was considerably higher compared with the same species caught off the west coast of Italy. There was no significant correlation between the concentrations of Cd, Cu, Zn and Fe in the muscle (or other organs) and body size. The overall trace metal content was considerably higher in the specimens from the eastern Mediterranean compared with the same species from the N. E. Atlantic. It is suggested that these higher-than-expected trace metal levels might be due to a relatively high trace metal content in the waters of the region or to the unusual physiology of these fish, possibly related to the extreme oligotrophic conditions in the area.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Arima, S., Marchaud, M., Martin, J. L. M. (1980). Pollutants in deep sea organisms and sediments. Ambio spec. Rep. 6: 97–100. Rec. Tray. Centre Oceanologique de Bretagne (COB) 615:669–672
Baldi, F. (1986). The biogeochemical cycle of mercury in the Tyrrhenian Sea. In: Papers presented at the FAO/UNEP/WHO/IOC/IAEA Meetings on the biogeochemical cycle of mercury in the Mediterranean, Siena, 27–31 Aug. 1984. F. A. O. Fish. Rep. No. 325 (Suppl.), Rome, p. 29–43
Barber, R. T., Vijayakumar, A., Cross, F. A. (1972). Mercury concentrations in recent and ninety-year-old benthopelagic fish. Science, N. Y. 178 (4061): 636–639
Bernhard, M. (1988). Mercury in the Mediterranean. UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies No. 98, UNEP
Bernhard, M., Andreae, M. O. (1984). Transport of trace metals in marine food chains. In: Nriagu, J. O. (ed.). Changing metal cycles and human health. Dahlem Konferenzen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 143–168
Bernhard M., Renzoni, A. (1977). Mercury concentration in Mediterranean marine organisms and their environment: natural or anthropogenic origin. Thalassia jugosl. 13: 265–300
Bruland, K. W., Franks, R. P. (1983). Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn and Cd in the Western North Atlantic. In: Wong, C. S., Boyle, E., Bruland, K. W., Burton, J. D., Goldberg, E. D. (eds.). Trace metals in sea water. Plenum Press, New York, p. 395–414
Cross, F. A., Hardy, L. H., Jones, N. Y., Barber, R. T. (1973). Relation between total body weight and concentrations of Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Hg in white muscle of bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix) and bathyl-demersal fish (Antimora rostrata). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 30: 1287–1291
Csanaday, G., Flierl, G., Karl, D., Kester, D., O'Connor, T., Ortner, P., Philpot, W. (1979). Deep water dumpsite 106. In: Goldberg, E. D. (ed.). Assimilative capacity of U. S. coastal waters for pollutants. U. S. Dept. of Commerce, NOAA, Washington D. C., p. 123–147
Denton, G. R. W., Burdon-Jones, C. (1986). Trace metals in fish from the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 17(5): 201–209
Eisler, R. (1981). Trace metal concentrations in marine organisms. Pergamon Press, New York
Forrester, C. R., Ketchen, K. S., Wong, C. C. (1972). Mercury content of spring dogfish (Squalus acanthias) in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29: 1487–1490
Forstner, U., Wittmann, G. T. W. (1979). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Gilat, E., Gelman, A. (1984). On the sharks and fishes observed using underwater photography during a deep water cruise in the eastern Mediterranean. Fish. Res. 2: 257–271
Golani, D. (1986/1987). On deep water sharks caught off the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Israel J. Zool. 34: 23–31
Gordon, J. D. M., Duncan, J. A. R. (1985). The ecology of the deep sea benthic and benthopelagic fish on the slopes of the Rockall trough, northeastern Atlantic. Prog. Oceanogr. 15: 37–69
Greig, R. A., Wenzloff, D. R., Pearce, J. B. (1976). Distribution and abundance of heavy metals in finfish, invertebrates and sediments collected at a deep water disposal site. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 7(10): 185–187
Hornung, H., Kress, N. (1991). Trace metals in offshore and inshore fish from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Toxic. envirl Chem. 31/32: 135–145
Hornung, H., Krom, M. D., Cohen, Y. (1989). Trace metals in sediments and benthic organisms from Haifa Bay, Israel. Estuar. cstl Shelf Sci. 29: 43–56
Hornung, H., Krumgalz, B. S., Cohen, Y. (1984). Mercury pollution in sediments, benthic organisms and inshore fishes of Haifa Bay, Israel. Mar. envirl Res. 12: 191–208
Hornung, H., Oren, O. H. (1980/1981). Heavy metals in Donax trunculus L. (Bivalvia) in Haifa Bay, Mediterranean (Israel). Mar. envirol Res. 4: 195–201
Kress, N., Galil, B., Hornung, H. (1991). Monitoring of the disposal of fly ash in the sea. Israel Oceanographic & Limnological Research Reports, No. 18, Haifa (in Hebrew)
Kress, N., Krom, M. D., Galil, B. (1990). Monitoring of the disposal of fly ash in the sea. Israel Oceanographic & Limnological Research Reports, No. 18, Haifa (in Hebrew)
Lyle, J. M. (1986). Mercury and selenium concentrations in sharks from northern Australian waters. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 37: 309–321
Mauchline, J., Gordon, J. D. M. (1983). Diets of the sharks and chimaeroids of the Rockall trough, northeastern Atlantic. Mar. Biol. 75: 269–278
Miller, G. E., Grant, P. M., Kishore, R., Steinkruger, F. J., Rowland, F. S., Guinn, V. P. (1972). Mercury concentrations in museum specimens of tuna and swordfish. Science, N. Y. 175: 1121–1122
Najdek, M., Bazulic, D. (1986). Preliminary investigation on methylmercury content in bivalves of different sizes. In: Papers presented at the FAO/UNEP/WHO/IOC/IAEA meeting on the biogeochemical cycle of mercury in the Mediterranean, Siena, 27–31 Aug. 1984. F.A.O. Fish. Rep. No. 325 (Suppl.), Rome, p. 122–124
Peterson, C. L., Klawe, W. L., Sharp, G. D. (1973). Mercury in tuna: a review. Fish. Bull. U.S. 71(3): 603–613
Ramelow, G., Hornung, H. (1978). An investigation into possible mercury losses during lyophilization of marine biological samples. Atom. Absorp. Newsl. 17: 59–60
Renzoni, A., Baldi, F. (1975). Osservazioni sulla distribuzione di mercurio della fauna del Mar Ligure e del Mar Tirreno. Acqua Aria 8: 597–602
Roether, W., Schlitzer, P. (1991). Eastern Mediterranean deep water renewal on the basis of chlorofluoromethane and tritium data. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 15: 333–354
Shultz, C. D., Crear, D., Pearson, J. E., Rivers, J. B., Hylin, J. W. (1976) Total and organic mercury in the Pacific blue marlin. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 15: 230–234
Stoeppler, M., Bernhard, M., Backhaus, F., Schulte, E. (1979). Comparative studies on trace metal levels in marine biota. I. Mercury in marine organisms from western Italian coast, the Strait of Gibraltar and the North Sea. Sci. total Envir. 3: 209–223
Turekian, K. K., Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth's crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 72: 175–192
UNEP/FAO/WHO (1987). Assessment of the state of pollution in the Mediterranean Sea by mercury and mercury compounds. MAP Tech. Rep. Ser. 18. UNEP, Athens
Vas, P. (1991). Trace metal levels in sharks from British and Atlantic waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 22: 67–72
Vas, P., Gordon, J. D. M. (1988). Trace metal concentrations in the scyliorhinid shark Galeus melastomus from the Rockall trough. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 19(8): 396–398
Windom, H., Stein, D., Sheldon, R., Smith, R. Jr. (1987). Comparison of trace metal concentrations in muscle tissue of a benthopelagic fish (Coryphaenoides armatus) from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Deep-Sea Res. 54(2): 213–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hornung, H., Krom, M.D., Cohen, Y. et al. Trace metal content in deep-water sharks from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Marine Biology 115, 331–338 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346351
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346351