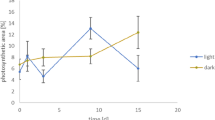
Abstract
The carbon-fixation patterns of freshly isolated zooxanthellae from the hermatypic coral Acropora formosa were examined during a 15 min exposure to sodium mosa were examined during a 15 min exposure to sodium [14C]bicarbonate. The labelling pattern during the first 60 s exposure showed that the C3 carbon-fixation pathway is the major route for photosynthetic carbon fixation in Symbiodinium sp. 3-Phosphoglyceric acid, which constituted >50% of the label after 5 s, steadily decreased over the first 60 s. Hexose phosphates, aspartate, malate and glucose were the other main products during the first 60 s. Over longer periods, significant amounts of the organic acids succinate, aspartate and glutamate were found in the extract along with glucose; but no glycerol.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Barnes, D. J., Chalker, B. E. (1990). Calcification and photosynthesis in reef-building corals and algae. In: Dubinsky, Z. (ed.) Coral reefs. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p. 109–131
Beardall, J., Bukerjii, D., Glover, H. E., Morris, I. (1976). The path of carbon in photosynthesis by marine phytoplankton. J. Phycol. 12: 409–417
Black, C. C., Bender, M. M. (1976). 13C values in marine organisms from the Great Barrier Reef. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol. 3: 25–32
Blank, R. J., Trench, R. K. (1988). Immunogold localisation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase in Symbiodinium kawagutii Trench et Blank, an endosymbiotic dinoflagellate. Endocytobiosis Cell Res. 5: 75–82
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantiation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Analyt. Biochem. 72: 248–254
Crossland, C. J., Barnes, D. J. (1977). Gas-exchange studies with the staghorn coral Acropora acuminata and its zooxanthellae. Mar. Biol. 40: 185–194
D'Aoust, B. G., White, R., Wells, J. M., Olsen, D. A. (1976). Coralalgal associations: capacity for producing and sustaining elevated oxygen tensions in situ. Undersea biomed. Res. 3: 35–40
Downton, W. J. S., Bishop, D. G., Larkum, A. W. D., Osmond, C. B. (1976). Oxygen inhibition of photosynthetic oxygen evolution in marine plants. Oxygen inhibition of photosynthetic oxygen evolution in marine plants. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol. 3: 73–79
Giersch, C. (1979). Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of 14C-labelled photosynthetic intermediates in isolated intact chloroplasts. J. Chromat. 172: 153–161
Heldt, H. W. (1980). Measurement of metabolite movement across the envelope and of the pH in the stroma and the thylakoid space in intact chloroplasts. Meth. Enzym. 69: 604–613
Jeffrey, S. W., Haxo, F. T. (1968). Photosynthetic pigments of symbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae) from corals and clams. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 135: 149–165
Jeffrey, S. W., Humphrey, G. F. (1975). New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pfl. 167: 191–194
Loeblich III, A. R. (1984). Dinoflagellate physiology and biochemistry. In: Spector, D. L. (ed.). Dinoflagellates. Academic Press, London, p. 299–342
McEvoy-Bowe, E. (1985). Cooling plate for cellulose thin-layer electrophoresis and its application to amino acid analysis. J. Chromat. 347: 199–208
Morris, I., Darley, M. (1982). Physiology and biochemistry of algae: introduction and bibliography. In: Rosowski, J. R., Parker, B. C. (eds.) Selected papers in phycology. II. Phycological Society of America, Kansas, p. 278–287
Mukerji, D., Glover, H. E., Morris, I. (1978). Diversity in the mechanism of carbon dioxide fixation in Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 14: 137–142
Muscatine, L. (1990). The role of symbiotic algae in carbon and energy flux in reef corals. In: Dubinsky, Z. (ed.) Coral reefs. Elservier, Amsterdam, p. 75–87
Muscatine, L., Falkowski, P. G., Porter, J. W., Dubinsky, Z. (1984). Fate of photosynthetic-fixed carbon in light- and shade-adapted colonies of the symbiotic coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B). 222: 181–202
Muscatine, L., Pool, R. R., Cernichiari, E. (1972). Some factors influencing selective release of soluble organic material by zoox-anthellae from reef corals. Mar. Biol. 13: 298–308
Porter, J. W., Muscatine, L., Dubinsky, Z., Falkowski, P. G. (1984) Primary production and photoadaptation in light- and shadeadapted colonies of the symbiotic coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 222: 161–180
Schmitz, K., Kremer, B. P. (1977). Carbon fixation and analysis of assimilates in a coral — dinoflagellate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 42 305–313
Streamer, M., McNeil, Y., Yellowlees, D. (1986). The short-term partitioning of carbon-14 assimilate between zooxanthellae and polyp tissue in Acropora formosa. Mar. Biol. 90: 565–573
Ting, I. P. (1976). Malate dehydrogenase and other enzymes of C4 acid metabolism in marine plants. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol. 3: 121–127
Trench, R. K. (1971). The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. III. The effect of homogenates of host tissues on the excretion of photosynthetic products in vitro by zooxanthellae from two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177: 250–264
Trench, R. K., (1979). The cell biology of plant — animal symbiosis. A. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 30: 485–531
Trench, R. K. (1987). Dinoflagellates in non-parasitic symbioses. In: Taylor, F. G. H. (ed.) The biology of dinoflagellates. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p. 530–570
Tytler, E. M., Trench, R. K. (1986). Activities of enzymes in β-carboxylations and of catalase in cell free preparations from the symbiotic dinoflagellates Symbiodinium spp. from a coral, a clam, and a zoanthid and two sea anemones. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 228: 483–492
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Streamer, M., McNeil, Y.R. & Yellowlees, D. Photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation in zooxanthellae. Marine Biology 115, 195–198 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346335
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346335