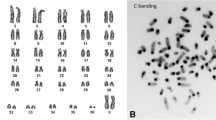
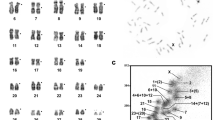
Abstract
We established chromosomal homologies between all chromosomes of the human karyotype and that of an old world monkey (Macaca fuscata) by chromosomal in situ suppression (CISS) hybridization with human chromosome specific DNA libraries. Except for the human chromosome 2 library and limited cross-hybridization of X and Y chromosome libraries all human DNA libraries hybridized to single GTG-banded macaque chromosomes. Only three macaque chromosomes (2, 7, 13) were each hybridized by two separate human libraries (7 and 21, 14 and 15, 20 and 22 respectively). Thus, an unequivocally high degree of synteny between human and macaque chromosomes has been maintained for more than 20 million years. As previously suggested, both Papionini (macaques, baboons, mandrills and cercocebus monkeys, all of which have nearly identical karyotypes) and humans are chromosomally conservative. The results suggest, that CISS hybridization can be expected to become an indispensable tool in comparative chromosome and gene mapping and will help clarify chromosomal phylogenies with speed and accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein R, Pinto M, Morcom G, Bielert C (1980) A reassessment of the karyotype of Papio ursinus: homoeology between human chromosome 15 and 22 and a characteristic submetacentric baboon chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 28: 55–63
Clemente IC, Ponsa M, Garcia M, Egozcue J (1990) Evolution of the Simiiformes and the phylogeny of human chromosomes. Hum Genet 84: 493–506
Collins C, Kuo WL, Segraves R, Pinkel D, Fuscoe J, Gray JW (1991) Construction and characterization of plasmid libraries enriched in sequences from single human chromosomes. Genomics, in press
Créau-Goldberg N, Turleau C, Cochet C, deGrouchy J (1983) New gene assignments in the baboon and new chromosome homoeologies with man. Ann Genet 26: 75–78
Cremer T, Lichter P, Borden J, Ward DC, Manuelidis L (1988) Detection of chromosome aberrations in metaphase and interphase tumor cells by in situ hybridization using chromosome-specific library probes. Hum Genet 80: 235–246
Dutrillaux B (1979) Chromosomal evolution in primates: tentative phylogeny from Microcebus murinus (prosimian) to man. Hum Genet 48: 251–314
Dutrillaux B (1986) Evolution chromosomique chez les primates, les carnivore et les rongeurs. Mammalia, vol 50, numero special
Dutrillaux B, Viegas-Paequignot, Dubos C, Masse R (1978) Complete or almost complete analogy of chromosome banding between the baboon (Papio papio) and man. Hum Genet 43: 37–46
Estop A, Garver JJ, Meera-Khan P, Pearson PL (1979) Rhesus-human chromosome homologies via cytogenetic and gene mapping studies, Human Gene Mapping 5. Cytogenet Cell Genet 25: 150–151
Jauch A, Daumer C, Lichter P, Murken J, Schroeder-Kurth T, Cremer T (1990) Chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization of human gonosomes and autosomes and its use in clinical cytogenetics. Hum Genet 85: 145–150
Klever M, Grond-Ginsbach C, Scherthan H, Schroeder-Kurth T (1991) Chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization after Giemsa banding. Hum Genet 86: 484–486
Lengauer C, Luedecke H-J, Wienberg J, Cremer T, Horsthemke B (1991) Comparative chromosome band mapping in primates by in situ suppression hybridization of band specific DNA microlibraries. Hum Evol 6: 67–71
Lichter P, Cremer T, Borden J, Manuelidis L, Ward DC (1988) Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet 80: 224–234
Lichter P, Chang Tang CJ, Call K, Hermanson G, Evans GA, Housman D, Ward DC (1990) High resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science 247: 64–69
O'Brien SJ, Graves JAM (1990) Human gene mapping 5; report of the committee on comparative gene mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet 55: 406–433
O'Brien SJ, Seuànez HN, Womack JE (1988) Mammalian genome organization: an evolutionary view. Annu Rev Genet 22: 323–351
Pinkel D, Gray JW, Trask B, van denEngh G, Fuscoe J, vanDekken H (1986) Cytogenetic analysis by in situ hybridization with fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 51: 151–157
Pinkel D, Landegent J, Collins C, Fuscoe J, Segraves R, Lucas J, Gray JW (1988) Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome specific libraries: Detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 9138–9142
Ruddle FH (1981) A new era in mammalian gene mapping: somatic cell genetics and recombinant DNA methodologies. Nature 294: 115–119
Seuànez HN (1987) The chromosomes of man: Evolutionary considerations. In: Obe G, Basler A (eds) Cytogenetics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Small M, Stanyon R, Smith DG, Sineo L (1985) High-resolution chromosomes of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Am J Primatol 9: 63–67
Soares MBM, Armada JL, Armada A, daSilva VF, Seuànez HN (1982) Standardization of the karyotype of the rhesus monkey, Macaca mulatta, and interspecific homologies with human chromosomes. J Hum Evol 11: 291–296
Stanyon R, Chiarelli B (1983) Phylogeny of the hominoidea: the chromosome evidence. J Hum Evol 11: 493–504
Stanyon R, Ardito G, Lamberti L, Bigatti P (1983) The banded karyotypes of Macaca fuscata compared with Cerocebus aterrimus. Folia Primatol 41: 137–146
Stanyon R, Romagno D, Wienberg J, Mauer U (1990) Sequence of DNA replication in Macaca fuscata chromosomes: An out-group for phylogenetic comparison between man and apes. Genetica 80: 45–52
Stock AD, Hsu TC (1973) Evolutionary conservatism in arrangement of genetic material: a comparative analysis of chromosome banding between the rhesus macaque (2n=42, 84 arms) and the African green monkey (2n=60, 120 arms). Chromosoma 43: 211–224
Wienberg J, Jauch A, Stanyon R, Cremer T (1990) Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Genomics 8: 347–350
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by E.R. Schmidt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wienberg, J., Stanyon, R., Jauch, A. et al. Homologies in human and Macasa fuscata chromosomes revealed by in situ suppression hybridization with human chromosome specific DNA libraries. Chromosoma 101, 265–270 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346004