Abstract
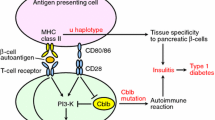
H-2 haplotype differences distinguish the related C57BL/KsJ (BKs) and C57BL/6J (B6) inbred strains. BKs mice are more susceptible to diabetes induction by a recessive obesity gene, diabetes (db), or by multi-dose streptozotocin (MSZ) administration. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether the H-2 differences were the important genetic background modifiers determining inbred strain susceptibility or resistance to these diabetogenic stresses. Diabetes susceptibility of BKs.B6-H-2 b congenic mice was compared with that of the parental BKs and B6 stocks. In addition, diabetes severity was studied in (B6 × BKs)F1 and F2 db/db mice and an H-2 segregation analysis was performed. BKs susceptibility genes expressed in a dominant fashion in the F1 generation, and were transmitted to F2 db/db males without apparent segregation. No association between H-2 b haplotype and B6-type diabetes resistance was found in response to either the db mutation or to MSZ. Insulitis, associated with development of hyperglycemia in BKs males, also occurred in the H-2 b congenic stock. However, an apparent interaction between H-2 b haplotype, the db mutation (on chromosome 4), and male gender (Y chromosome?) was indicated by a segregation ratio distortion in recovery of this genotype. A more moderate diabetes in some F2 db/db females suggested that non-MHC-linked genes controlling sex steroid metabolism were the important determinants of diabetogenic sensitivities in the C57BL stocks. In support of the latter, strain differences were demonstrated in activity levels of steroid sulfatase, which is regulated by a sex-linked gene likely expressed on both the X and Y chromosome, and which may control tissue levels of active androgens and estrogens. We show that the diabetes-susceptible F1 hybrids exhibit the higher activity associated with the BKs strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, D. W.: How pure are inbred strains of mice? Immunol. Today 3: 210–214, 1982
Bailey, C. J. and Many, C. J.: Glucose tolerance and plasma insulin in the rat in relation to the oestrus cycle and sex hormones. Horm. Metab. Res. 4: 266–270, 1972
Cohn, J. A. and Cerami, A.: The influence of genetic background on the susceptibility of mice to diabetes induced by alloxan and on recovery from alloxan diabetes. Diabetologia 17: 187–189, 1979
Coleman, D. L. and Hummel, K. P.: The influence of genetic background on the expression of the obese (ob) gene in the mouse. Diabetologia 9: 287–293, 1973
Coleman, D. L. and Hummel, K. P.: The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. II. Studies on background modifiers. Isr. J. Med. 11: 708–713, 1975
Craig, I. W. and Tolley, E.: Steroid sulphatase and the conservation of mammalian X chromosomes. Trends Genet. 2: 201–204, 1986
Debray-Sachs, M., Dardenne, M., Sai, P., Savino, W., Quiniou, M.C., Boillot, D., Gepts, W., and Assan, R.: Anti-islet immunity and thymic dysfunction in the mutant diabetic C57BL/KsJ db/db mouse. Diabetes 30: 1048–1054, 1983
Eisenbarth, G. S.: Type 1 diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 314: 1360–1368, 1986
Erickon, R. P., Harper, K., and Kramer, J. M.: Identification of an autosomal locus affecting steroid sulfatase activity among inbred strains of mice. Genetics 105: 181–189, 1983
Hayes, C. E., Klyczek, K. K., Krum, D. P., Whitcomb, R. M., Hullet, D. A., and Cantor, H.: Chromosome 4 Jt gene controls murine T cell surface I-J surface expression. Science 223: 559–563, 1984
Hobkirk, R.: Steroid sulfotransferases and steroid sulfate sulfatases. Characteristics and biological roles. Can. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 63: 1127–1144, 1985
Hobkirk, R., Cardy, C. A., Saidi, F., Kennedy, T. G., and Girard, L. R.: Development and characteristics of an oestrogen sulfotransferase in placenta and uterus of the pregnant mouse. Biochem. J. 216: 451–457, 1983
Hummel, K. P., Dickie, M. M., and Coleman, D. L.: Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science 153 : 1127–1128, 1966
Hummel, K. P., Coleman, D. L., and Lane, P. W.: The influence of genetic background on expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. I. C57BL/KsJ and C57BL/6J strains. Biochem. Genet. 7: 1–13, 1972
Karn, R. C.: Sex-limited genetic variation in a mouse salivary protein. Biochem. Genet. 20: 493–504, 1982
Kiesel, U. and Kolb, H.: Low dose streptozotocin-induced autoimmune diabetes is under the genetic control of the major histocompatibility complex in mice. Diabetologia 23: 69–71, 1982
Kiesel, U. and Kolb, H.: Genetic control of low-dose streptozotocin-induced autoimmune diabetes in mice. J. Immunol. 130: 1719–1722, 1983
Le, P. H., Leiter, E. H., and Leyendecker, J. R.: Genetic control of susceptibility to streptozotocin diabetes in inbred mice: Effect of testosterone and H-2 haplotype. Endocrinology 116: 2450–2455, 1985
Leiter, E. H.: The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. IV. Male lethal syndrome in CBA/Lt. Diabetes 30: 1035–1044, 1981
Leiter, E. H.: Multiple low dose streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia and insulitis in C57BL mice: Influence of inbred background, sex, and thymus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79: 630–634, 1982
Leiter, E. H.: Genetic control of pathogenesis of diabetes in C3H mice. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex. Diabetes 33: 1068–1071, 1984
Leiter, E. H.: Differential susceptibility of BALB/c sublines to diabetes induction by multi-dose streptozotocin treatment. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 122: 78–85, 1985a
Leiter, E. H.: Type C retrovirus production by pancreatic beta cells. Association with accelerated pathogenesis in C3H-db/dg (“diabetes”) mice. Am. J. Pathol. 119: 22–32, 1985b
Leiter, E. H., Coleman, D. L., and Hummel, K. P.: The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. III. Effect of H-2 haplotype and sex. Diabetes 30: 1029–1034, 1981a
Leiter, E. H., Simon, D., Cherry, M., and Phillips, C. A.: Induction in C57BL/KsJ mice of complement-dependent antibody cytotoxic to cultured beta cells. Diabetes 30: 30–39, 1981b
Leiter, E. H., Prochazka, M., and Shultz, L. D.: Effect of immunodeficiency on diabetogenesis in genetically diabetic mice. J. Immunol. 138: 3224–3229, 1987
Loria, R. M., Montgomery, B., Corey, L. A., and Chinchilli, V. M.: Influence of diabetes mellitus heredity on susceptibility to Cox-sackie B4. Arch. Virol. 81: 251–262, 1984
Nestler, J. E., Clore, J. N., Strauss, J. F., and Blackard, W. G.: The effects of hyperinsulinemia on serum testosterone, progesterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and cortisol levels in normal women and in a woman with hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 64: 180–184, 1987
Oschilewski, M., Schwab, E., Kiesel, U., Opitz, U., Stunkel, K., Kolb-Bachofen, V., and Kolb, H.: Administration of silica or monoclonal antibody to Thy-1 prevents low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice. Immunol. Lett. 12: 289–294, 1986
Paik, S.-G., Michelis, M. A., Kim, Y. T., and Shin, S.: Induction of insulin dependent diabetes by streptozotocin. Inhibition by estrogens and potentiation by androgens. Diabetes 31: 724–729, 1982
Prochazka, M., Premdas, F. H., Leiter, E. H., and Lipson, L. G.: Estrone treatment dissociates primary versus secondary consequences of “diabetes” (db) gene expression in mice. Diabetes 35: 725–728, 1986
Rossini, A. A., Appel, M. C., Williams, R. M., and Like, A. A.: Genetic influence of the streptozotocin induced insulitis and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 26: 916–920, 1977
Rozhin, J., Corombos, J. D. Horwitz, J. P., and Brooks, S. C.: Endocrine steroid sulfotransferases: steroid alchohol sulfotransferase from human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7. J. Steroid Biochem. 25: 973–979, 1986
Singer, S. S.: The properties and the endocrine control of the production of the steroid sulfotransferases. In G. Litwack (ed.): Biochemical Actions of Hormones. IX, pp. 271–303, Academic press, New York, 1982
Snell, G. D., Demant, P., and Cherry, M.: Hemagglutination and cytotoxic studies of H-2.1 and related specificities in the EK crossover regions. Transplantation 11: 210–237, 1971
Szymura, J. M. and Klein, J.: Mapping of the mouse Upg-1 locus. Immunogenetics 16: 89–90, 1982
Vadheim, C., Rotter, J. I., MacLaren, N. K., Riley, W. J., and Anderson, C. E.: Preferential transmission of diabetic alleles within the HLA gene complex. N. Engl. J. Med. 315: 1314–1320, 1986
Washburn, L. and Eicher, E. M.: Sex reversal in XY mice caused by dominant mutation on chromosome 17. Nature 303: 338–340, 1983
White, P. C., Chaplin, D. D., Weis, J. H., Dumont, B., New, M. I., and Seidman, J. G.: Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. Nature 312: 465–467, 1984
Wolf, J., Lilly, F., and Shin, S.: The influence of genetic background on the susceptibility of inbred mice to streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes 33: 567–571, 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leiter, E.H., Le, P.H. & Coleman, D.L. Susceptibility to db gene and streptozotocin-induced diabetes in C57BL mice: control by gender-associated, MHC-unlinked traits. Immunogenetics 26, 6–13 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345448
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345448