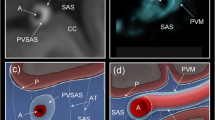
Summary
125I labelled Amipaque (metrizamide) was introduced by cisternal puncture into six rabbits and perfused at various pressures. The torcular was exposed, frozen rapidly, and excised intact. Sections of arachnoid proliferations were made from the frozen specimen and either freeze dried or sandwiched directly for autoradiography. Some specimens were freeze dried en bloc prior to sectioning and sandwiching. All sections were exposed for 2–3 weeks at-80°C prior to development of the autoradiographs.
On microscopic examinations of the autoradiographs most of the activity was in the tubules or between cells suggesting intercellular passage. Some label was also present within the brain. The significance of this is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alksne, J. F., White, L. E., Jr.: Electron-microscope study of the effect of increased intracranial pressure on the arachnoid villus. J. Neurosurg. 22, 481–488 (1965)
Alksne, J. F., Lovings, E. T.: Functional ultrastructure of the arachnoid villus. Arch. Neurol. 27, 371–377 (1972)
Appleton, T. C.: Autoradiography of soluble labelled compounds. J. R. Microscop. Soc. 83, 277–281 (1964)
Brown, D. A. et al. Assessment of autoradiographic resolution using soluble extracellular fluid indicators, In: Autoradiography of diffusible substance, pp. 161–182. (eds. L. J. Roth and W. E. Stumpf) New York: Acad. Press 1969
Golman, K., Dahl, S. G.: Absorption of labelled metrizamide, diatrizoate, inulin and water from cerebrospinal fluid to blood. Acta Radiol. [Suppl.] (Stockh.) 335, 276–285 (1973)
Gomez, D. G., Potts, D. G.: The surface characteristics of arachnoid granulations. Arch. Neurol. 31, 88–93 (1974)
Gomez, D. G., Potts, D. G., Effects of pressure on the arachnoid villus. Exp. Eye Res. [Suppl.] 25, 117–125 (1977)
Gomez, D. G., Potts, D. G., Deonarine, V.: Arachnoid granulations of the sheep. Arch. Neurol. 30, 169–175 (1974)
Gomez, D. G., Potts, D. G., Deonarine, V.: Effects of pressure gradient changes on the morphology of arachnoid villi and granulations of the monkey. Lab. Invest. 28, 648–657 (1973)
Haughton, V. M., Ho, K. C., Larson, S. J., Unger, G. F., Paz, F. C.: Experimental production of arachnoiditis with water soluble myelographic media. Radiology 123, 681–685 (1977)
Holterman, H.: Acta Radiol. [Suppl.] (Stockh.) 335, 1–3 (1973)
Horowitz, S. B.: The ultra-low temperature autoradiography of water and its solutes. In: Methods in cell biol. Vol. III, pp. 249–275, (ed. D. M. Prescott) New York: Academic Press 1974
Jayatilaka, A. D. P.: Arachnoid granulations in sheep. J. Anat. 99, 315–327 (1965)
Jayatilaka, A. D. P.: An electron microscopic study of sheep arachnoid granulations. J. Anat. 99, 635–649 (1965)
Kinter, W. B., Wilson, T. H.: Autoradiographic study of sugar and amino acid absorption by inverted sacs of hamster intestine. J. Cell Biol. 25, 19–39 (1965)
Meryman, H. T.: Aspects of freezing injury relevant to autoradiography, In: Autoradiography of diffusible substances, pp. 201–209. (eds. L. J. Roth and W. S. Stumpf) New York: Academic Press 1969
Potts, D. G., Gomez, D. G. In: Radiology of the skull and brain, pp. 2915–2937 (eds. T. H. Newton and D. G. Potts) St. Louis: Mosby 1977
Potts, D. G., Deonarine, V., Wooster, W.: Perfusion studies of the cerebrospinal fluid absorptive pathways in the dog. Radiology 104, 320–325 (1972)
Potts, D. G., Gomez, D. G., Abbott, G. F.: Possible causes of complications of myelography with water-soluble contrast medium. Acta Radiol. [Suppl.] (Stockh.) 355, 390–402 (1977)
Potts, D. G., Reilly, K. F., Deonarine, V.: Morphology of the arachnoid villi and granulations. Radiology 105, 333–341 (1972)
Rogers, A. W.: Techniques of autoradiography. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1973
Seaforth, R.: (Nuclides and Sources Division, New England Nuclear Corp., Boston, MA 02118) Personal communication
Shabo, A. L., Abbott, M. M., Maxwell, D. S.: The response of the arachnoid villus to intracisternal injection of autogenous brain tissue. Neurology 19, 724–734 (1969)
Shabo, A. L., Maxwell, D. S.: The morphology of the arachnoid villi. A light and electron microscopic study in the monkey. J. Neurosurg. 29, 451–463 (1968)
Shabo, A. L., Maxwell, D. S.: The subarachnoid space following the introduction of a foreign protein: an electron microscopic study with peroxidase. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 30, 506–541 (1971)
Sharp, R. F.: Relative cerebral glucose uptake of neuronal perikarya and neutrophil determined with 2-deoxyglucose in resting and swimming rat. Brain Res. 110, 127–139 (1976)
Stirling, C. E., Kinter, W. B.: High-resolution radiography of galactose accumulation in rings of hamster intestine. J. Cell Biol. 35, 585–604 (1967)
Stumpf, W. E.: Techniques for the autoradiography of diffusible compounds. In: Methods in cell biology XIII, pp. 171–192 (ed. D. M. Prescott). New York: Academic Press 1976
Tripathi, R. C.: Ultrastructure of the arachnoid mater in relation to outflow of cerebrospianl fluid. Lancet 1973 II 8–11
Tripathi, R.: Tracing the bulk outflow route of cerebrospinal fluid by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Brain Res. 80, 503–506 (1974)
Tripathi, B. J., Tripathi, R. C.: Vacuolar transcellular channels as a drainage pathway for cerebrospinal fluid. J. Physiol. 239, 195–206 (1974)
Trump, B. F.: Effects of freezing and thawing on cells and tissue. In: Autoradiography of diffusible substances, pp. 211–240. (eds. L. J. Roth and W. E. Stumpf) New York and London: Academic Press 1969
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by NIH research grant NS09198
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.C.P., Gomez, D.G., Potts, D.G. et al. Passage of Amipaque (metrizamide) through the arachnoid granulations. Neuroradiology 17, 185–190 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342745
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342745