Abstract
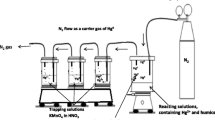
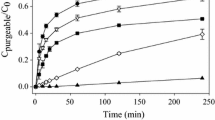
The potential ability of humic substances to reduce Hg(II) to Hg(0) in aqueous systems and, consequently, strongly influence Hg speciation and mobility in the environment is known but has not been studied in detail. A demonstration of the redox behavior of Hg in the presence of humic substances is made in the present work. Calculations show that the reduction is thermodynamically possible. The effects of some chemical parameters (pH, aerobic/anaerobic conditions, presence of chloride) on the process were studied experimentally. Hg(0) production was highest in O2-free systems in the absence of chloride at pH ca 4.5, when ca 25% of initially 2x10−6 M Hg(II) was reduced to Hg(0) in 50 hr. The presence of a competing ion (10−4 M Eu) in the system as well as methylation of the carboxyl groups in the humic substance considerably reduced the Hg(0) production. The practical importance of the abiotic reduction of Hg in the environment is pointed out.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts, J. J., Schindler, J. E., Miller, R. W. and Nutter, D. E. Jr: 1974, Science 184, 895.
Arsenie, I., Borén, H., Johnsson, S. and Allard, B.: 1990, unpublished.
Cheam, V. and Gamble, D. S.: 1974, Canadian J. Soil Sci. 54, 413.
Clarkson, T. W. and Greenwood, M. R.: 1970, Anal. Biochem. 37, 236.
Ephraim, J., Borén, H., Pettersson, C., Arsenie, I. and Allard, B.: 1989, Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 356.
Frimmel, F. H., Immerz, A. and Niedennann, H.: 1984, in C. J. M. Kramer and J. C. Duinker (eds), Complexation of Trace Metals in Natural Waters, Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W. Junk Publ., The Hague, p. 329.
Gilmour, J.T.: 1971, Environ. Lett. 2, 143.
Goodman, B. A. and Chesire, M. V.: 1975, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 39, 1711.
Hahne, H. C. H. and Kroontje, B.: 1973, J. Environ. Qual. 2, 444.
Huffman, E. W. D. Jr. and Stuber, H. A.: 1985, in G. R. Aiken, D. M. Mcknight, and R. L. Wershaw (eds), Humic Substances in Soil, Sediment and Water, John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 447
Langford, C. H., Kay, R., Quance, G. W. and Khan, T. R.: 1977, Anal. Lett. 10, 1249.
Lu, J. I., Li, C. S., Wang, W. H. and Peng, A.: 1983, Proc. Int. Conf. Heavy Metals in the Environment, Heidelberg, 1983, CEP Consultants Ltd, Edinburgh, p. 780.
Lövgren, L. and Sjöberg, S.: 1989, priv. comm.
Mantoura, R. F. C., Dickson, A. and Riley, J. P.: 1978, Estuarine Coastal Marine Sci. 6, 387.
Miles, C. J. and Brezonik, P. L.: 1981, Environ. Sci. Techn. 15, 1089.
Miller, R. W.: 1975, Verh. Int. Verein. Limnol. 19, 2082.
Miller, R. W., Schindler, J. and Alberts, J. J.: 1975, in F. G. Howel (ed.), ‘Mineral Cycling in South-Eastern Ecosystems’, p. 445.
Nash, K., Fried, S., Friedman, A. M. and Sullivan, J. C.: 1981, Environ. Sci. Techn. 16, 834.
Pang, S. W., Qui, Q., and Sun, J.: 1983, Kexue Xuebao 1, 234.
Senesi, N., Chen, Y. and Schnitzer, M.: 1977, Soil Biol. Biochem. 9, 397.
Skogerboe, R. K. and Wilson, S. A.: 1981, Anal. Chem. 53, 228.
Strohal, P. and Huljev, D.: 1971, in Nuclear Techniques in Environmental Pollution, IAEA, Vienna, p. 439.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.: 1981, Aquatic Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Szalay, A. and Szilágyi, M.: 1967, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 31, l.
Szilágyi, M.: 1967, Geokhimiya 12, 1489.
Szilágyi, M.: 1971, Soil Sci. 111, 233.
Turner, R. R., VandenBrook, A. J., Barkay, T. and Elwood, J. W.: 1989, Proc. Int. Conf. Heavy Metals in the Environment, Geneva 1989, CEP Consultants Ltd, Edinburgh, p. 353.
Wilson, S. A. and Weber, J. H.: 1979, Chem. Geol. 26, 345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allard, B., Arsenie, I. Abiotic reduction of mercury by humic substances in aquatic system — an important process for the mercury cycle. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 56, 457–464 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342291
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342291