Abstract
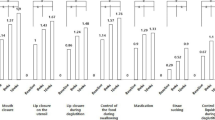
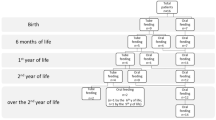
The purpose of this study was to determine the efficacy of oral sensorimotor treatment in moderately eating-impaired children with cerebral palsy and to examine the effects of treatment on measures of growth. Six domains of feeding were examined in 35 children 4.3–13.3 years of age. Weight and skinfold measures were taken. Children were observed at lunch time, and spoon-feeding, biting, chewing, cup drinking, straw drinking, swallowing, and drooling were examined. Children underwent 20 weeks of sensorimotor treatment, 5–7 min/day, 5 days/week. Limited improvement was observed in the following eating domains: spoon-feeding, biting, and chewing, but not in drinking. Children as a group maintained the pretreatment weight-age percentile. To meet the increasing growth demands of the teenage years, oralmotor therapy may need to be combined with oral caloric supplementation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosma JF: Development and impairments of feeding in infancy and childhood. In: Groher M (ed.): Dysphagia: Diagnosis and Management, 2nd ed. Stoneham, MA: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1992, pp 107–141
Thomessen M, Kase BF, Riis G, Heiberg A: The impact of feeding problems on growth and energy intake in children with cerebral palsy. Eur J Clin Health 45:479–487, 1991
Gisel EG, Patrick J: Identification of children with cerebral palsy, unable to maintain a normal nutritional state. Lancet 1:283–286, 1988
Charney EB, Su R, Davies JC, Stallings VA: Nutritional status and nutritional intake of children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol (Suppl 64) 33:14, 1991
Reilly S, Skuse D: Characteristics and management of feeding problems of young children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:379–388, 1992
Patrick J, Gisel EG: Nutrition for the feeding impaired child. J Neurol Rehab 4:115–119, 1990
Patrick J, Boland M, Stoski D, Murray GE: Rapid correction of wasting in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 28:734–739, 1986
Campbell PH: Assessig oral-motor skills in severely handicapped persons: an analysis of normal and abnormal patterns of movement. In: York R, Edgar E (eds.). Teaching the Severely Handicapped. Seattle, WA: Association for the Severely Handicapped, 1979, pp 39–63
Krick J, Van Duyn MS: The relationship between oral-motor development and growth: a pilot study in a pediatric population with cerebral palsy. J Am Diet Assoc 84:555–569, 1984
Karle IP, Bleiler RE, Ohlson MA: Nutritional status of cerebral palsied children. J Am Diet Assoc 38:22–26, 1961
Sanders KD, Cox K, Cannon R, Blanchard D, Pither J, Papatakis P, Varella L, Maughan R: Growth response to enteral feeding by children with cerebral palsy. J Parent Ent Nutr 14:23–26, 1990
Young JA, Craig MA: Transient diplegia in children who fail to thrive. Child Care Health Dev 17:173–182, 1991
Martin HP: Nutrition: its relationship to children's physical, mental and emotional development. Am J Clin Nutr 26:766–775, 1973
Johnson CB, Deitz JC: Time use of mothers with pre-school children: a pilot study. Am J Occup Ther 39:578–583, 1985
Edebol-Tysk K: Evaluation of care-load for individuals with spastic tetraplagia. Dev Med Child Neurol 31:737–745, 1989
Alexander R: Oral-motor treatment for infants and young children with cerebral palsy. Semin Speech Lang 8:98–100, 1987
Sobsey R, Orelove FP: Neurophysiological facilitation of eating skills in children with severe handicaps. J Assoc Sev Hand 9:98–110, 1984
Ottenbacher K, Scoggins A, Wayland J: The effectiveness of oral sensory-motor therapy with the severely and profoundly developmentally disabled. Occup Ther J Res 1:147–160, 1981
Ottenbacher K, Hicks J, Roark A, Swinea J: Oral-sensorimotor therapy in the developmentally disabled: a multiple baseline study. Am J Occup Ther 37:541–547, 1983
Riordan MM, Iwata BA, Wohl MK, Finney JW: Behavioral treatment of food refusal and selectivity in developmentally disabled children. Appl Res Ment Ret 1:95–112, 1980
Riordan MM, Iwata BA, Finney JW, Wohl MK, Stanley AE: Behavioral assessment and treatment of chronic food refusal in handicapped children. J Appl Behav Anal 17:327–341, 1984
Kenny DJ, Koheil RM, Greenberg J, Reid D, Milner M, Moran R, Judd PL: Development of a multidisciplinary feeding profile for children who are dependent feeders. Dysphagia 4:16–28, 1989
Gisel EG: Chewing cycles in 2 to 8-year-old normal children: a developmental profile. Am J Occup Ther 42:40–46, 1988
Gisel EG: Effect of food texture on the development of chewing of children between 6 months and 2 years of age. Dev Med Child Neurol 33:69–79, 1991
Tobis J, Saturen P, Larios G, Posniak A: Study of growth patterns in cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehab 42:475–481, 1961
Sterling H: Height and weight of children with cerebral palsy and acquired brain damage. Arch Phys Med 41:131–135, 1960
Galler JR, Ramsey F, Solimano G, Kucharski LT, Harrison R: The influence of early malnutrition on subsequent behavioral development. IV. Soft neurologic signs. Pediatr Res 18:826–832, 1984
Galler JR, Ramsey F, Solimano G: A follow-up study of the effects of early malnutrition on subsequent development. II. Fine motor skills in adolescence. Pediatr Res 19:524–527, 1985
Stolovitz P, Gisel EG: Circumoral movements in response to three different food textures in children 6 months to 2 years of age. Dysphagia 6:17–25, 1991
Parrot LC, Selley WG, Brooks WA, Lethbridge PC, Cole JJ, Flack FC, Ellis RE, Tripp JH: Dysphagia in cerebral palsy: a comparative study of the Exeter Dysphagia Assessment Technique and a multidisciplinary assessment. Dysphagia 7:209–219 1992
Gisel EG: Effect of oral sensorimotor treatment on measures of growth and efficiency of eating in the moderately eating impaired child with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia (in press)
McPherson KA, Kenny DA, Koheil R, Bablich K, Sochaniwskyi A, Milner M. Ventilation and swallowing interactions in normal children and children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:577–588, 1992
Schwartz JL, Niman C, Gisel EG: Tongue movements in normal pre-school children during eating. Am J Occup Ther 38:87–93, 1984
Haberfellner H, Rossiwall B: Appliances for treatment of oral sensorimotor disorders. Am J Phys Med 56:241–248, 1977
Haberfellner H, Richter M: Zur Apparativen Therapie orofazialer Dyskinesien bei zerebral bewegungsgestörten Patienten. Fort Kieferorthop 46:224–232, 1985
Sochaniwskyj AE, Koheil RM, Bablich K, Milner M, Kenny DJ: Oral motor functioning, frequency of swallowing and drooling in normal children and in children with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 67:866–874, 1986
Monahan P, Shapiro B, Fox C: Effect of tube-feeding on oral function. Dev Med Child Neurol (Suppl 57) 30:7, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gisel, E.G. Oral-motor skills following sensorimotor intervention in the moderately eating-impaired child with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia 9, 180–192 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341263
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341263