Summary
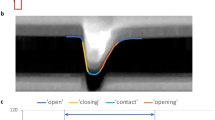
The purpose of this paper is to examine blink kinematics and the neural basis of blinks evoked reflexively by different kinds of stimuli. The kinematics of the upper lid movement and the electromyographic response of lid muscles levator palpebrae and orbicularis oculi were recorded in the rabbit during trigeminally and visually-evoked blinks. We find that there is a basic, kinematic difference between blinks. A blink in response to an airpuff is more rapidly accomplished and achieves a higher velocity than does an equal amplitude blink in response to a flash of light. The two forms of the reflex blink result from differences in the nature and timing of activity in antagonistic lid muscle motoneurons. Nevertheless, most characteristics of blink neural control are common to both reflex blinks. Most importantly, it appears that blinks are produced by two-stage neural control, an early component that is preprogrammed and a late component that is under stimulus control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collewjin H, Van Der Steen J, Steinman RM (1985) Human eye movements associated with blinks and prolonged eyelid closure. J Neurophysiol 54: 11–27
Doane MG (1980) Interaction of eyelids and tears in corneal wetting and the dynamics of the normal human eyeblink. Am J Ophthalmol 89: 507–516
Evinger C, Manning KA (1985) Adaptive plasticity of reflex blinks. Neuroscience Abstr 11: 1040
Evinger C, Shaw MD, Peck CK, Manning KA, Baker R (1984) Blinking and associated eye movements in humans, guinea pigs, and rabbits. J Neurophysiol 52: 323–339
Hall RD, Hicks BL (1973) Two somatic eyelid reflexes in the albino rat. Physiol Behav 11: 167–176
Hiraoka M, Shimamura M (1977) Neural mechanisms of the corneal blinking reflex in cats. Brain Res 125: 265–275
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle. I. Some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 87: 175–189
Hopf HC, Bier J, Breuer B, Scheerer W (1973) The blink reflex induced by photic stimuli. In: Desmedt JE (ed) New developments in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, Vol III. Karger, Basel, pp 666–672
Hung G, Hsu F, Stark L (1978) Dynamics of the human eyeblink. Am J Optom Physiol Opt 54: 678–690
Keller EL (1974) Participation of medial pontine reticular formation in eye movement generation in monkey. J Neurophysiol 37: 316–332
Kennard DW, Glaser GH (1964) An analysis of eyelid movements. J Nerv Ment Dis 139: 31–48
King WM, Fuchs AF (1979) Reticular control of vertical saccadic eye movements by mesencephalic burst neurons. J Neurophysiol 42: 861–876
Kugelberg E (1952) Facial reflexes. Brain 75: 385–396
Lindquist C, Martensson A (1970) Mechanisms involved in the cat's blink reflex. Acta Physiol Scand 80: 149–159
Lisberger SG (1984) The latency of pathways containing the site of motor learning in the monkey vestibulo-ocular reflex. Science 225: 74–76
Lisberger SG, Westbrook LE (1985) Properties of visual inputs that initiate horizontal smooth pursuit eye movements in monkeys. J Neurosci 5: 1662–1673
Manning KA, Riggs LA, Komenda JK (1983) Reflex eyeblinks and visual suppression. Percept Psychophys 34: 250–256
McCormick DA, Thompson RF (1984) Cerebellum: essential involvement in the classically conditioned eyelid response. Science 223: 296–299
Mortin LI, Keifer J, Stein PSG (1985) Three forms of the scratch reflex in the spinal turtle: movement analyses. J Neurophysiol 53: 1501–1516
Nashner LM, McCollum G (1985) The organization of human postural movements: a formal basis and experimental synthesis. Behav Brain Sci 8: 135–172
Ongerboer de Visser BW (1980) The corneal reflex: electrophysiological data in man. Prog Neurobiol 15: 71–83
Ongerboer de Visser BW, Mechelse K, Megens PH (1977) Corneal reflex latency in trigeminal nerve lesions. Neurol (Minneap) 27: 1164–1167
Riggs LA, Volkmann FC, Moore RK (1981) Suppression of the blackout due to blinks. Vision Res 21: 1075–1079
Robertson GA, Mortin LI, Keifer J, Stein PSG (1985) Three forms of the scratch reflex in the spinal turtle: central generation of motor patterns. J Neurophysiol 53: 1517–1534
Rushworth G (1962) Observations on blink reflexes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 25: 93–108
Shahani B (1970) The human blink reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 33: 792–800
Shahani BT, Young RR (1973) Blink reflexes in orbicularis oculi. In: Desmedt JE (ed) New developments in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, Vol III. Karger, Basel, pp 641–648
Shaw MD, Alley KA (1982) Generation of motoneurons in the rabbit brainstem. J Comp Neurol 207: 203–207
Sherrington C (1948) The integrative action of the nervous system. Yale University Press, New Haven (1st ed 1906, Scribner's) pp 70–77, 230–235
Uhlrich DJ, Blough PM, Blough DS, Lehmkuhle S (1983) Inhibition of the human blink reflex by visual form stimuli. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (Suppl) 24: 188
Yates SK, Brown WF (1981) Light-stimulus-evoked blink reflex: methods, normal values, relation to other blink reflexes, and observations in multiple sclerosis. Neurol (NY) 31: 272–281
Yeo CH, Hardiman MJ, Glickstein M (1985) Classical conditioning of the nictitating membrane response of the rabbit. I. Lesions of the cerebellar nuclei. Exp Brain Res 60: 87–98
Zametkin AJ, Stevens JR, Pittman R (1979) Ontogeny of spontaneous blinking and of habituation of the blink reflex. Ann Neurol 5: 453–457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manning, K.A., Evinger, C. Different forms of blinks and their two-stage control. Exp Brain Res 64, 579–588 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340495