Summary
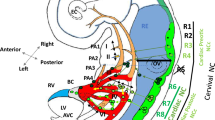
The existence of a neural crest cell migration pathway from occipital levels of the hindbrain into the heart was suspected in mammalian embryos because it had previously been identified in avian embryos and because the Di George anomaly, an association between craniofacial and cardiac malformations, is most easily explained on the basis of abnormal neural crest cell migration to all of the affected structures. In order to demonstrate the existence of this pathway, neural crest cells were labelled in situ in rat embryos with the fluorescent dye DiI, and the embryos cultured for up to 48 h. Cells labelled between occipital somites 1 and 2 or 3 and 4 migrated within and dorsal to the third and fourth pharyngeal arches and into the outflow tract of the heart (conus cordis and truncus arteriosus). The cardiac labelling was in individually visible cells, in contrast to the mass of fluorescence seen in the pharyngeal and dorsal mesenchyme. Within the outflow tract wall, the labelled cells were enmeshed by strands of alcian blue-stained extracellular matrix. There was no labelling of cardiac cells following injections just rostral to, or just caudal to, somites one and four. This study establishes the existence and precise levels of origin of the ‘cardiac’ neural crest in a mammalian embryo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockman DE, Kirby ML (1984) Dependence of thymus development on derivatives of the neural crest. Science 223:498–500
Bockman DE, Kirby ML (1988) Neural crest function in thymus development. In: Reif AE, Schlesinger (eds) Th-1: immunology, neurology and therapeutic applications. Dekker, New York, pp 451–467
Bockman DE, Redmond ME, Kirby ML (1989) Alteration of early vascular development after ablation of cranial neural crest. Anat Rec 225:209–217
Buckley SKL, Steele CE, New DAT (1978) In vitro development of early postimplantation rat embryos Dev Biol 63:396–403
Dencker L, d'Argy R, Danielsson BRG, Ghantous H, Serber GO (1987) Saturable accumulation of retinoic acid in neural and neural crest derived cells in early embryonic development. Dev Pharmacol Ther 10:212–223
Dencker L, Annerwall E, Busch C, Eriksson U (1990) Localization of specific retinoid binding sites and expression of cellular retinoid binding sites and expression of cellular retinoic acid binding protein (CRABP) in the early mouse embryo. Development 110:343–352
DiGeorge AM (1968) Congenital absence of the thymus and its immunologic consequences: concurrence with congenital hypoparathyroidism. March of Dimes-Birth Defects Foundation: BD: OAS IV(1) White Plains, New York, pp 116–121
Godement P, Vanselow J, Thanos J, Bonhoeffer F (1987) A study in developing visual systems with a new method of staining neurones and their processes in fixed tissue. Development 101:697–713
Goulding EH, Pratt RM (1986) Isotretinoin teratogenicity in mouse whole embryo culture. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 6:99–112
Honig MG, Hume RI (1986) Fluorescent carbocyanine dyes allow living neurons of identified origin to be studied in long-term cultures. J Cell Biol 103: 171–187
Honig MG, Hume RI (1989) DiI and DiO: versatile fluorescent dyes for neuronal labelling and pathway tracing. Trends Neurosci 12:333–336
Jarvis BL, Johnston MC, Webster WS, Sulik KK (1985) Isotretinoin-induced ear malformations in mice (abstract). Teratology 31:27A
Kirby ML (1987) Cardiac morphogenesis—recent research advances. Pediatr Res 21:219–224
Kirby ML (1989) Plasticity and predetermination of mesencephalic and trunk neural crest transplanted into the region of the cardiac neural crest. Dev Biol 134:402–412
Kirby ML, Stewart DE (1983) Neural crest origin of cardiac ganglion cells in the chick embryo: identification and extirpation. Dev Biol 97:433–443
Kirby ML, Gale TF, Stewart DE (1983) Neural crest cells contribute to aorticopulmonary septation. Science 220:1059–1061
Lammer EJ, Opitz JM (1986) The DiGeorge Anomaly as a developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet Suppl 2:113–127
Lammer EJ, Chen DT, Hoar RM, Agnisti ND, Benke PJ, Braun JT, Curry CJ, Ferbhoff PM, Grix AW Jr, Lott IT, Richard JM, Sun SC (1985) Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Eng J Med 313:837–841
Le Douarin NM (1982) The neural crest. Cambridge University Press
Le Lievre CS, Le Douarin NM (1975) Mesenchymal derivatives of the neural crest: Analysis of chimaeric quail and chick embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 34:123–154
Lumsden A, Keynes R (1989) Segmental patterns of neuronal development in the chick hindbrain. Nature 337:424–428
Maden M, Ong DE, Chytil F (1990) Retinoid binding protein distribution in the developing mammalian nervous system. Development 109:75–80
Morriss-Kay GM, Tan SS (1987) Mapping cranial neural crest cell migration pathways in mammalian embryo. Trends Genet 3:257–261
New DAT, Coppola PT, Cockroft DL (1976) Comparison of growth in vitro and in vivo of post-implantation embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 36:133–144
Noden DM (1980) The migration and cytodifferentiation of cranial neural crest cells. In: Pratt P, Christiansen P (eds) Current trends in prenatal craniofacial development. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 3–25
Noden DM (1988) Interactions and fates of avian craniofacial mesenchyme. Development 108[Suppl]:121–140
Ruberte E, Dollé P, Chambon P, Morriss-Kay G (1991) Retinoic acid receptors and cellular binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development 111:45–60
Selleck MAJ, Stern CD (1991) Fate mapping and cell lineage analysis of Hensen's node in the chick embryo. Development 112:615–626
Serbedzija GN, Bronner-Fraser M, Fraser SE (1989) A vital dye analysis of the timing and pathways of avian neural crest cell migration. Development 106:806–819
Serbedzija GN, Fraser SE, Bronner-Fraser M (1990) Pathways of trunk neural crest cell migration in the mouse embryo as revealed by vital dye labelling. Development 108:605–612
Sims PJ, Waggoner AS, Wary LH, Hoffman JF (1974) Studies on the mechanisms by which cyanine dyes measure membrane potential in red blood cells in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry 13:3315–3330
Tan SS, Morriss-Kay GM (1985) The development and distribution of the cranial neural crest in the rat embryo. Cell Tissue Res 240:403–416
Tan SS, Morriss-Kay GM (1986) Analysis of cranial neural crest cell migration and early fates in postimplantation rat chimaeras. J Embryol Exp Morphol 98:21–58
Tucker GC, Delarue M, Zada S, Boucaut JC, Thiery JP (1988) Expression of the HNK-1/NC-1 epitope in early vertebrate neurogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 251:457–465
Vincent M, Thiery JP (1984) A cell surface marker for neural crest and placodal cells: Further evolution in peripheral and central nervous system. Dev Biol 103:468–481
Webster WS, Johnston MC, Lammer EJ, Sulik KK (1986) Isotretinoin embryopathy and the cranial neural crest: an in vivo and in vitro study. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 6:211–222
Wilkinson DG (1990) Segmental gene expression in the developing mouse hindbrain. Semin Dev Biol 1:127–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukiishi, Y., Morriss-Kay, G.M. Migration of cranial neural crest cells to the pharyngeal arches and heart in rat embryos. Cell Tissue Res 268, 1–8 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00338048
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00338048