Abstract
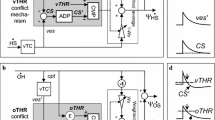
The role of the optokinetic reflex (OKR) is that of cooperating with the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) in the task of image stabilization on the retina during head rotations in a stationary visual surround. Since the dynamics of VOR was already well established, it has been possible to make a broad estimation of what the dynamics of OKR should be in order to obtain the performances observed in normal subjects. A mathematical model of OKR has been presented, and the experimental results obtained by Raphan et al. (1977) in the monkey and by Collins et al. (1970) in man were used to validate the model and to obtain a precise estimation of its parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allum, J.H.J., Graf, W., Dichgans, J., Schmidt, C.L.: Visualvestibular interactions in the vestibular nuclei of the goldfish. Exp. Brain Res. 26, 463–485 (1976)
Barany, R.: Zur Klinik und Theorie des Eisenbahnnystagmus. Arch. Augenheilkd. 88, 139–142 (1921)
Barnes, G.R., Benson, A.J.: A model for the prediction of the nystagmic response to angular and linear acceleration stimuli. In: The use of nystagmography in aviation medicine. NATO AGARD CCP-128, A23, 1–13 (1973)
Benson, A.J., Barnes, G.R.: Vision during angular oscillation: the dynamic interaction of visual and vestibular mechanisms. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 340–345 (1978)
Berthoz, A.: Role of the vestibular nuclei in the control of gaze. A: Vestibular nuclei. In: Control of gaze by brain stem neurons, pp. 279–289. Baker, R., Berthoz, A. (eds.) Amsterdam, New York: Elsevier 1977
Brandt, Th., Dichagans, J., Koenig, E.: Perception of self-rotation induced by optokinetic stimuli. Pflügers Arch. 332, R98 (1972)
Carpenter, R.H.S.: Cerebellectomy and transfer function of the vestibuloocular relfex in the decrebrate cat. Proc. Roy. Soc. (London) 181, 353–374 (1972)
Chun, K.S., Robinson, D.A.: A model of quick phase generation in the vestibulo-ocular reflex. Biol. Cybernetics 28, 209–221 (1978)
Cohen, B., Matsuo, V., Raphan, Th.: Quantitative analysis of the velocity characteristics of optokinetic nystagmus and optokinetic afternystagmus. J. Physiol. 270, 321–344 (1977)
Collewijn, H.: An analog model of the rabbit's optokinetic system. Brain Res. 36, 71–88 (1972)
Collins, W.E., Schroeder, D.J., Rice, N., Mertens, R.A., Kranz, G.: Some characteristics of optokinetic eye movement patterns: a comparative study. AM 70-10. Federal Aviation Administration, 1970
Dichgans, J.: Optokinetic nystagmus as dependent on the retinal periphery via the vestibular nuclei. In: Control of gaze by brain stem neurons, pp. 261–267. Baker, R., Berthoz, A. (eds.) Amsterdam, New York: Elsevier 1977
Dichgans, J.: Smooth pursuit and optokinetic nystagmus in normal and patients. International Symposium on: Reflex control of posture and movements. Pisa 1978
Fernandez, C., Goldberg, J.M.: Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating semicircular canals of the squirrel monkey. II. Response to sinusoidal stimulation and dynamics of peripheral vestibular system. J. Neurophysiol. 82, 661–675 (1971)
Fox, J.E., Holmes, G.: Optic nystagmus and its value in the localization of cerebral lesions. Brain 49, 333–371 (1926)
Henn, V., Young, L.R., Finley, C.: Vestibular nucleus units in alert monkeys are also influenced by moving visual fields. Brain Res. 71, 144–149 (1974)
Honrubia, V., Downey, W., Mitchell, D.P., Ward, P.H.: Experimental studies on optokinetic nystagmus. II. Normal humans. Acta Otolaryng. 65, 441–448 (1968)
Honrubia, V., Jenkins, H., Downey, W., Ward, P.H.: Experimental studies on optokinetic nystagmus. III. Modifications produced by labyrinthectomy and cerebral hemidecortication in cats. Ann. Otol. 80, 97–110 (1971)
Honrubia, V., Scott, B.J., Ward, P.H.: Experimental studies on optokinetic nystagmus. I. Normal cats. Acta Otolaryng. 64, 388–402 (1967)
Hood, J.D.: Observations upon the neurological mechanism of optokinetic nystagmus with special reference to the contribution of peripheral vision. Acta Otolaryng. (Stockh.) 63, 208–215 (1967)
Jeannerod, M., Magnin, M., Schmid, R., Stefanelli, M.: Vestibular habituation to angular velocity steps in the cat. Biol. Cybernetics 22, 39–48 (1976)
Melvill Jones, G., Milsum, J.H.: Spatial and dynamic aspects of visual fixation. IEEE Trans. Bio-med. Eng. BME-12, 54–62 (1965)
Melvill Jones, G., Milsum, J.H.: Frequency response analysis of central vestibular unit activity resulting from rotational stimulation of the semi-circular canals. J. Physiol. 219, 191–215 (1971)
Mevio, E.: Ricerca comparativa del nistagmo in soggetti normali e patologici. Thesis, University of Pavia 1978
Precht, W., Shimazu, H., Markham, C.H.: A mechanism of central compensation of vestibular function following hemilabyrinthectomy. J. Neurophysiol. 29, 996–1010 (1966)
Rademaker, G.G.J., ter Braak, J.W.G.: On the central mechanism of some optic reaction. Brain 71, 48–77 (1948)
Raphan, Th., Cohen, B., Matsuo, V.: A velocity-storage mechanism responsible for optokinetic nystagmus (OKN), optokinetic after-nystagmus (OKAN), and vestibular nystagmus. In: Control of gaze by brain stem neurons, pp. 37–47. Baker, R., Berthoz, A. (eds.) Amsterdam, New York: Elsevier 1977
Robinson, D.A.: Models of the saccadic eye movement control system. Kybernetic 14, 71–83 (1973)
Robinson, D.A.: Oculomotor control signals. In: Basic mechanisms of ocular motility and their clinical implications, pp. 337–374. Lennerstrand, G., Bach-y-Rita, P. (eds.) Oxford: Pergamon Press 1975
Robinson, D.A.: Adaptive gain control of the vestibulo-ocular reflex by the cerebellum. J. Neurophysiol. 39, 954–969 (1976)
Robinson, D.A.: Vestibular and optokinetic symbiosis: an example of explaining by modelling. In: Control of gaze by brain stem Neurons, pp. 49–58. Baker, R., Berthoz, A. (eds.) Amsterdam, New York: Elsevier 1977a
Robinson, D.A.: Linear addition of optokinetic and vestibular signals in the vestibular nuclei. Exp. Brain Res. 30, 447–450 (1977b)
Schmid, R., Lardini, F.: On the predominance of anti-compensatory eye movements in vestibular nystagmus. Biol. Cybernetics 23, 135–148 (1976)
Schmid, R., Zambarbieri, D.: Model of visual-vestibular interaction (in preparation)
Steinhausen, W.: Über den Nachweis der Bewegung der Cupola in der intakten Bogengangsampulle des Labyrinthes bei der natürlichen rotatorischen und calorischen Reizung. Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol. 228, 322–328 (1931)
Tauber, E.S., Koffler, S.: Optomotor responses in human infants in apparent motion: evidence of innateness. Science 152, 382–383 (1966)
ter Braak, J.W.C.: Untersuchungen über optokinetischen Nystagmus. Arch. Neurol. Physiol. 21, 309–376 (1936)
Waespe, W., Henn, V.: Neuronal activity in the vestibular nuclei of the alert monkey during vestibular and optokinetic stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 27, 523–539 (1977a)
Waespe, W., Henn, V.: Vestibular nuclei activity during optokinetic after-nystagmus (OKAN) in the alert monkey. Exp. Brain Res. 30, 323–330 (1977b)
Waespe, W., Henn, V.: The convergence ov vestibular and visual information onto neurons of the vestibular nuclei in alert monkey (macaca mulatta). Proc. of IFAC Symp. on Control Mechanisms in Bio and Eco-systems, 3, 143–152 (1977c)
Waespe, W., Henn, V.: Motion information in the vestibular nuclei of alert monkeys: visual and vestibular input versus optomotor output. International Symposium on: Reflex control of posture and movements. Pisa 1978
Waespe, W., Henn, V., Miles, T.S.: Activity in the vestibular nuclei of the alert monkey during spontaneous eye movements and vestibular or optokinetic stimulation. In: Control of gaze by brain stem neurons, pp. 269–278. Baker, R., Berthoz, A. (eds.) Amsterdam, New York: Elsevier 1977
Wolpert, E.M.: Der Einfluß der peripheren Retina-Reizfeldgröße-auf den Geschwindigkeitsgang des optokinetischen Nystagmus. Med. Diss., Freiburg 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported by CNR, Special Project on Biomedical Engineering, grant No. 78.00512.86
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmid, R., Zambarbieri, D. & Sardi, R. A mathematical model of the optokinetic reflex. Biol. Cybernetics 34, 215–225 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337428
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337428