Abstract
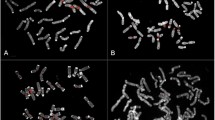
We describe a cloned 2.7 kb alpha satellite sequence, Pan-3, from the pygmy chimpanzee (Pan paniscus) that specifically hybridizes in situ to chromosome 19 in the pygmy chimpanzee and to the homeologous human chromosome, no. 17. Using high stringency conditions of hybridization on Southern blots, this sequence hybridized to DNA from both species of chimpanzee (P. paniscus and P. troglodytes) and from human but not to DNA from gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) or orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus). Partial sequence analysis showed that Pan-3 and a previously described human chromosome 17-specific clone have up to 91% sequence identity. To our knowledge this is the highest sequence similarity reported between alphoid subsets from human and any other primate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BaldiniA, SmithDI, RocchiM, MillerOJ, MillerDA (1989) A human alphoid DNA clone from the EcoRI family: Genomic and internal organization and chromosomal assignment. Genomics 5:822–828
ChooKH, VisselB, EarleE (1989) Evolution of alpha-satellite DNA on human acrocentric chromosomes. Genomics 5:332–344
DoverGA (1986) Molecular drive in multigene families: how biological novelties arise, spread and are assembled. Trends Genet 2:159–165
HarperME, SaundersGF (1981) Localization of single copy DNA sequences on G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 83:431–439
HattoriM, SakakiY (1986) Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem 152:232–238
ISCN 1985 (1985) An international system of cytogenetics nomenclature. Karger, Basel, p 99
JorgensenAL, BostockCJ, BakAL (1987a) Homologous subfamilies of human alphoid repetitive DNA on different nucleolus organizing chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1075–1079
JorgensenAL, JonesC, BostockCJ, BakAL (1987b) Different subfamilies of alphoid repetitive DNA are presented on the human and chimpanzee homologous chromosomes 21 and 22. EMBO J 6:1691–1696
JorgensenAL, KolvraaS, JonesC, BakAL (1988) A subfamily of alphoid repetitive DNA shared by the NOR-bearing human chromosomes 14 and 22. Genomics 3:100–109
KiyamaR, MatsuiH, OishiM (1986) A repetitive DNA family (Sau3A family) in human chromosomes: extrachromosomal DNA and DNA polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4665–4669
KiyamaR, OishiM, KandaN (1988) Chromosomal localization of Sau3A repetitive DNA revealed by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 96:372–375
KoopFB, GoodmanM, XuP, ChanK, SlightomJL (1986) Primate-globin DNA sequences and man's place among the great apes. Nature 319:234–238
KurnitDM, MaioJJ (1973) Subnuclear distribution of DNA species in confluent and growing mammalian cells. Chromosoma 42:23–36
LinCC, AlitaloK, SchwabM, GeorgeD, VarmusHE, BishopJM (1985) Evolution of karyotypic abnormalities and c-myc oncogene amplification in human colonic carcinoma cell lines. Chromosoma 92:11–15
MaioJJ (1971) DNA strand reassociation and polyribonucleotide binding in the African green monkey, Cercopithecus aethiops. J Mol Biol 56:579–595
MaioJJ, BrownFL, MusichPR (1981) Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. The HindIII and EcoRI dimer families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma 83:103–127
MillerDA, SharmaV, MitchellAR (1988) A human-derived probe, p82H, hybridizes to the centromeres of gorilla, chimpanzee, and orangutan. Chromosoma 96:270–274
MitchellAR, GosdenJR, MillerDA (1985) A cloned sequence, p82H, of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromosomes. Chromosoma 92:369–377
PearsonWR, LipmanDJ (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2444–2448
RiabowolK, Shmookler ReisRJ, GoldsteinS (1985) Interspersed repetitive and tandemly repetitive sequences are differentially represented in extrachromosomal covalently closed circular DNA of human diploid fibroblasts. Nucleic Acids Res 13:5563–5584
RigbyPWJ, DieckmanMRC, BergP (1977) Labelling deoxyribonucleic acid to a high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol 113:237–251
RosenbergH, SingerM, RosenbergM (1978) Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIAN. Science 200:394–402
SmithGP (1976) Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science 191:528–535
SmithHO, BirnsteilML (1976) A simple method for DNA restriction map site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res 3:2387–2398
SouthernEM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
WayeJS, WillardHF (1986) Structure, organization, and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Mol Cell Biol 6:3156–3165
WayeJS, WillardHF (1989) Concerted evolution of alpha satellite DNA: Evidence for species specificity and a general lack of sequence conservation among alphoid sequences of higher primates. Chromosoma 98:273–279
WayeJS, MitchellAR, WillardHF (1988) Organization and genomic distribution of “82H” alpha satellite DNA: evidence for a low-copy or single-copy alphoid domain located on human chromosome 14. Hum Genet 78:27–32
WillardHF, WayeJS (1987a) Hierarchical order in chromosome-specific human alpha satellite DNA. Trends Genet 3:192–198
WillardHF, WayeJS (1987b) Chromosome-specific subsets of human alpha satellite DNA: Analysis of sequence divergence within and between chromosomal subsets and evidence for an ancestral pentameric repeat. J Mol Evol 25:207–214
YurovYB, MitkevichSP, AlexandrovIA (1987) Application of cloned satellite DNA sequences to molecular-cytogenetic analysis of constitutive heterochromatin heteromorphisms in man. Hum Genet 76:157–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by T.C. Hsu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldini, A., Miller, D.A., Miller, O.J. et al. A chimpanzee-derived chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA sequence conserved between chimpanzee and human. Chromosoma 100, 156–161 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337244
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337244