Summary
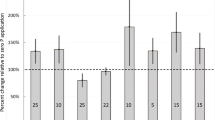
Poultry manure (PM) is commonly applied to cropland as a fertilizer, usually at rates determined by the nitrogen content of the manure. Limited information is available, however, on the volatilization of ammonia from poultry manure-amended soils, despite the effect these losses may have on the fertilizer value of the manure. This study was initiated to determine the influence of incorporation and residue cover on NH3 losses from PM-amended soils. In the first experiment, a dynamic flow technique was used to measure NH3 losses from 18 manures applied to a bare soil surface at a rate of 12 Mg ha-1. In the second experiment, 3 of the 18 manures were incorporated either immediately, 24 h or 72 h after application. The third experiment compared the same three manures applied to a bare soil surface or to corn or soybean residues. Surface application of the manures resulted in the loss of from 4 to 31% of the total N applied in the manures. Incorporation of the PM with soil significantly reduced NH3 loss with the greatest decrease following immediate incorporation. Crop residues either had no effect or slightly reduced NH3 volatilization losses relative to PM application to a bare soil surface. Ammonia volatilization was not well correlated with individual manure properties, but a multiple regression approach using manure pH and total N content offered some promise as a means to segregate manures of the basis of volatilization potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamsen FJ, Sabey BR (1987) Ammonia volatilization from liquid digested sewage sludge as affected by placement in the soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1080–1082
Beauchamp EG, Kidd GE, Thurtell G (1978) Ammonia volatilization from sewage sludge applied in the field. J Environ Qual 7:141–146
Beauchamp EG, Kidd GE, Thurtell G (1982) Ammonia volatilization from liquid dairy manure applied in the field. Can J Soil Sci 62:11–19
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL et al (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, 2nd edn. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 594–624
Donavon WC, Logan TJ (1983) Factors affecting ammonia volatilization from sewage sludge applied to soil in a laboratory study. J Environ Qual 12:584–590
Fenn LB, Hossner LR (1985) Ammonia volatilization from ammonium or ammonium-forming nitrogen fertilizers. Adv Soil Sci 1:123–169
Fenn LB, Kissel DE (1973) Ammonia volatilization from surface application of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils. I. General theory. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 37:855–859
Fenn LB Richards J (1984) Ammonia loss from urea-acid products surface applied to soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:532–539
Gasser JKR (1964) Some factors affecting losses of ammonia from urea and ammonium sulfate applied to soils. J Soil Sci 15:258–272
Hargrove WL (1988) Soil, environmental, and management factors influencing ammonia volatilization under field conditions. In: Bock BR, Kissel DE (eds) Ammonia volatilization from urea fertilizers. Bull Y-206, National Fertilizer Development Center. TVA, Muscle Shoals, Alabama, pp 17–36
Hargrove WL, Kissel DE (1979) Ammonia volatilization from surface applications of urea in the field and laboratory. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:359–363
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In: Page AL et al (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, 2nd edn. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 643–698
King LD (1973) Mineralization and gaseous loss of nitrogen in soil-applied liquid sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 2:356–358
Kirchmann H, Witter E (1989) Ammonia volatilization during aerobic and anaerobic manure decomposition. Plant Soil 115:35–41
Kissel DE, Brewer HL, Arkin GF (1977) Design and test of a field sampler for ammonia volatilization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41:1133–1138
Kolenbrander GJ (1981) Effect of injection of animal waste on ammonia losses by volatilization on arable land and grassland. In: Brogan JC (ed) Nitrogen losses and surface run-off. ECSC, EEC, EAEC; Brussels, Luxembourg, pp 425–439
Lauer DA, Bouldin DR, Klausner SD (1976) Ammonia volatilization from dairy manure spread on the soil surface. J Environ Qual 5:134–141
Marshall VG, Debell DS (1980) Comparison of four methods of measuring volatilization losses of nitrogen following urea fertilization of forest soils. Can J Soil Sci 60:549–563
McInnes KJ, Ferguson RB, Kissel DE, Kanemasu ET (1986) Ammonia loss from applications of urea-ammonium nitrate solution to straw residue. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:969–974
Meyer RD, Olson RA, Rhoades HP (1961) Ammonia losses from fertilized Nebraska soils. Agron J 53:241–244
Nelson KE, Turgeon AJ, Street RJ (1980) Thatch influence on mobility and transformation of nitrogen carriers applied to turf. Agron J 72:487–492
Overcash MR, Humenik FJ, Miner JR (1983) Overview of livestock production. In: CRC Livestock waste management, vol 2. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 114–182
Ryan JA, Keeney DR (1975) Ammonia volatilization from surface applied wastewater sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed 47:386–393
Sims JT, Palmer D, Scarborough J, Graeber R (1989) Poultry manure management. Coop Bull 27. Dept Nat Res Environ Cont, Dover, Delaware
Terman GL (1979) Volatilization losses of nitrogen as ammonia from surface-applied fertilizers, organic amendments, and crop residues. Adv Agron 31:189–223
Terry RE, Nelson DW, Sommers LE, Meyers GJ (1978) Ammonia volatilization volatilization from wastewater sludge applied to soils. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50:2657–2665
Wolf DC, May ML, Phillips JM, Gale PM (1987) Ammonia volatilization from soil amended with hen manure. Agronomy Abstr. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisconsin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schilke-Gartley, K.L., Sims, J.T. Ammonia volatilization from poultry manure-amended soil. Biol Fertil Soils 16, 5–10 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336507
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336507