Abstract
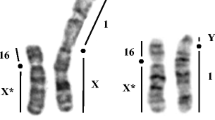
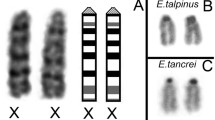
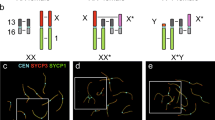
Blastocysts and late gestation stages of the marsupial mouse, Antechinus stuartii, were examined cytologically and electrophoretically to investigate X chromosome activity during embryogenesis. A late replicating X chromosome was identified in the protoderm cells of female unilaminar blastocysts and in the cells of embryonic and extra-embryonic regions of older blastocysts. Sex chromatin bodies were also observed in female bilaminar and trilaminar blastocysts. The X linked enzyme α-galactosidase showed no evidence of paternal allele expression in the extra-embryonic region of bilaminar blastocysts or in the yolk sac and embryonic tissue of known heterozygotes. It is concluded that the late replicating X chromosome is paternal in origin and that unlike the laboratory mouse, X inactivation is not correlated with cell differentiation in Antechinus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper DW, Wooley PA, Maynes GM, Sherman FS, Poole WE (1983) Studies on metatherian sex chromosomes. XII. Sexlinked inheritance and probable paternal X-inactivation of αgalactosidase A in Australian marsupials. Aust J Biol Sci 36:511–517
Epstein CJ (1983) The X chromosome in development. In: Sandberg AA (ed) Cytogenetics of the mammalian X chromosome. Part A. Basic mechanisms of X chromosome behaviour. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 51–65
Grzeschik KH, Grzeschik AM, Benoff S, Romeo G, Siniscalco M, Van Someren H, Khan PM, Westerveld A, Bootsma D (1972) X-linkage of human α-galactosidase. Nature New Biol 240:48–50
Ho MW, Beutler S, Tennant L, O'Brien JS (1972) Fabry's disease: evidence for a physically altered α-galactosidase. Am J Hum Genet 24:256–266
Johnston PG, Robinson ES (1985) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in heterozygous kangaroo embryos and extra-embryonic membranes. Genet Res 45:205–208
Johnston PG, Robinson ES (1986) Lack of correlation between Gpd expression and X chromosome late replication in cultured fibroblasts of the kangaroo Macropus robustus. Aust J Biol Sci 39:39–45
McMahon A, Fosten M, Monk M (1983) X-chromosome inactivation mosaicism in the three germ layers and the germ line of the mouse embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol 74:207–220
Monk M, Harper MI (1979) Sequential X chromosome inactivation coupled with cellular differentiation in early mouse embryos. Nature 281:311–313
Rebourcet R, Weil D, Van Cong N, Frézal J (1975) α-Galactosidase: a dimeric enzyme dependent on a structural locus on the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 14:406–408
Selwood L (1980) A timetable of embryonic development of the dasyurid marsupial Antechinus stuartii (Macleay). Aust J Zool 28:649–668
Selwood L (1986) The marsupial blastocyst — a study of the blastocysts in the Hill Collection. Aust J Zool 34:177–187
Selwood L, Young GJ (1983) Cleavage in vivo and in culture in the dasyurid marsupial Antechinus stuartii (Macleay). J Morphol 176:43–60
Sugawara O, Takagi N, Sasaki M (1985) Correlation between X-chromosome inactivation and cell differentiation in female preimplantation mouse embryos. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39:210–219
Takagi N, Sasaki M (1975) Preferential inactivation of the paternally derived X-chromosome in the extra-embryonic membranes of the mouse. Nature 256:640–642
VandeBerg JL, Johnston PG, Cooper DW, Robinson ES (1983) X-chromosome inactivation and evolution in marsupials and other mammals. In: Rattazzi MC, Scandalios JG, Whitt GS (eds) Isozymes: Current topics in biological and medical research, vol. 9. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 201–218
VandeBerg JL, Robinson ES, Samollow PB, Johnston PG (1987) X-linked gene expression and X-chromosome inactivation: Marsupials, mouse and man compared. In: Isozymes: Current topics in biological and medical research, vol. 15. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 225–253
Wake N, Takagi N, Sasaki M (1976) Non-random inactivation of X chromosome in the rat yolk sac. Nature 262:580–581
West JD (1982) X chromosome expression during mouse embryogenesis. In: Genetic control of gamete production. Proceedings of the Serono Clinical Colloquia on Reproduction No 3. Academic Press, London, pp 49–92
West JD, Frels WI, Chapman VM, Papaioannou VE (1977) Preferential expression of the maternally derived X chromosome in the mouse yolk sac. Cell 12:873–882
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, P.G., Robinson, E.S. X chromosome inactivation in female embryos of a marsupial mouse (Antechinus stuartii). Chromosoma 95, 419–423 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333993
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333993