Abstract
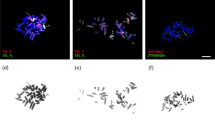
The synaptonemal complexes of three amphimictic (meiotic) strains of Meloidogyne are examined in this study. M. microtyla (n = 19) has a tripartite synaptonemal complex (SC) comprised of two lateral elements and one central region with a distinct central element. The central region of the SC in both M. carolinensis (n = 18) and M. megatyla (n = 18) lack a distinct central element. The evolutionary history is different in the strains since M. microtyla has arisen by a mechanism involving an increase in chromosome number (from an ancestral stock of n = 18) while both M. carolinensis and M. megatyla have maintained the number of chromosomes of the ancestral stock. The structure of the SCs of the latter two strains are identical to the structure of the SC of the meiotic parthenogenetic M. hapla. Thus, the pachytene karyotype of M. carolinensis was reconstructed to establish the pairing pattern and identify any changes that may be related to the different morphology of the SC in an amphimictic stock. Although recombination nodules (RN) have been observed in the parthenogenetic M. hapla, none of the three amphimictic strains had any SC associated structures that resembled a RN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdanov, Yu. F.: Formation of cytoplasmic synaptonemal-like polycomplexes at zygotene in Ascaris suum male meiosis. Chromosoma (Berl.) 61, 1–21 (1977)
Braten, T., Nordby, O.: Ultrastructure of meiosis and centriole behavior in Ulva mutabilis. J. Cell Sci. 13, 69–81 (1973)
Gillies, C. B.: Synaptonemal complex and chromosome structure. Ann. Rev. Genet. 9, 91–109 (1975)
Goldstein, P.: Sex determination in nematodes. In: Plant parasitic nematodes (B. Zuckerman, R. Rhode, edit.), Vol. III, New York; Academic Press 1981
Goldstein, P.: Synaptonemal complexes of Caenorhabditis elegans: Pachytene karyotype analysis of male and hermaphrodite wild-type and him mutants. Chromosoma (Berl.) 86, 577–593 (1982)
Goldstein, P., Moens, P. B.: Karyotype analysis of Ascaris suum male and female pachytene nuclei by 3-D reconstruction from electron microscopy of serial sections. Chromosoma (Berl.) 58, 101–111 (1976)
Goldstein, P., Slaton, D. E.: The Synaptonemal complexes of Caenorhabditis elegans: Comparison of wild-type and mutant strains and pachytene karyotype analysis of wildtype. Chromosoma (Berl.) 84, 585–597 (1982)
Goldstein, P., Triantaphyllou, A. C.: Occurrence of synaptonemal complexes and recombination nodules in a meiotic race of Meloidogyne hapla and their absence in a mitotic race. Chromosoma (Berl.) 68, 91–100 (1978a)
Goldstein, P., Triantaphyllou, A. C.: Karyotype analysis of Meloidogyne hapla by 3-D reconstruction of synaptonemal complexes from electron microscopy of serial sections. Chromosoma (Berl.) 70, 131–139 (1978b)
Goldstein, P., Triantaphyllou, A. C.: Karyotype analysis of the plant-parasitic nematode Heterodera glycines by electron microscopy. I. The diploid. J. Cell Sci. 40, 171–179 (1979)
Goldstein, P., Triantaphyllou, A. C.: Karyotype analysis of the plant-parasitic nematode Heterodera glycines by electron microscopy. II. The tetraploid and an aneuploid hybrid. J. Cell Sci. 43, 225–237 (1980)
Goldstein, P., Triantophyllou, A. C.: Pachytene karyotype analysis of tetraploid Meloidogyne hapla females by electron microscopy. Chromosoma (Berl.) 84, 405–412 (1981)
Maguire, M.: A possible role for the synaptonemal complex in chiasma maintenance. Exp. Cell Res. 112, 297–308 (1978)
Moens, P. B.: The structure and function of the synaptonemal complex in Lilium longiflorum sporocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 23, 418–451 (1968)
Rasmussen, S. W.: The transformation of the synaptonemal complex into the “elimination chromatin” in Bombyx mori oocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 60, 205–221 (1977)
Storms, R., Hastings, P. J.: A fine structure analysis of meiotic pairing in Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Exp. Cell Res. 104, 39–46 (1977)
Triantaphyllou, A. C.: Genetics and Cytology. In: Plant parasitic nematodes, Vol. II, (B. Zuckerman, W. Mai, R. Rhode, edit.), New York; Academic Press 1971
Triantaphyllou, A. C.: Cytogenetics of root-knot nematodes. In: Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne species), (ed. Lamberti, F., Taylor, C. E.) London: Academic Press 1979
Westergaard, M., Wettstein, D. von: The synaptonemal complex. Ann. Rev. Genet. 6, 71–100 (1972)
Zickler, D., Sage, J.: Synaptonemal complexes with modified lateral elements in Sordaria humana: Development of and relationship to the recombination nodules. Chromosoma (Berl.) 84, 305–318 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldstein, P., Triantaphyllou, A.C. The synaptonemal complexes of Meloidogyne: relationship of structure and evolution of parthenogenesis. Chromosoma 87, 117–124 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333513
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333513