Summary
Four genes concerned with the resistance of wild-type Micrococcus radiodurans to the lethal action of mitomycin-C (MTC), mtcA, mtcB, uvsA and uvsB, have been identified by isolating mutants sensitive to MTC.
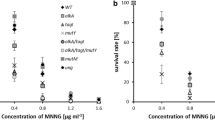
Two strains of M. radiodurans, 302 and 262 carrying mutations in mtcA and mtcB respectively, are between forty and sixty times as sensitive as the wild-type to MTC, only slightly more sensitive than the wild-type to ionizing (λ) radiation and have the same resistance as the wild-type to ultraviolet (u.v.) radiation. Strain 302 can be transformed at a high frequency to wild-type resistance to MTC with DNA from strain 262, and vice versa, indicating that mtcA and mtcB have different genetic locations.
Two further strains of M. radiodurans, 303 and 263 having mutations in uvsA and uvsB respectively are only from four to eight times as sensitive as the wild-type to MTC, seven to thirteen times as sensitive to γ-radiation but between twenty to thirty-three times as sensitive to u.v. radiation. Strain 303 can be transformed with DNA from strain 263, or vice versa, to wild-type resistance to u.v. radiation, implying that uvsA and uvsB also have different genetic locations.
M. radiodurans strain 301 which is mutant in both mtcA and uvsA, and strain 261 which is mutant in mtcB and uvsB are twenty to forty times as sensitive as the wild-type to both MTC and u.v. radiation and seven to ten times as sensitive to γ radiation. Neither mtcA and uvsA nor mtcB and uvsB are closely linked.
None of the mutant strains is deficient in recombination, as measured by transformation. The repair of MTC-induced DNA damage in M. radiodurans must be different from that described for Escherichia coli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A.W., Nordan, H.C., Cain, R.F., Parrish, G., Duggan, D.: Studies on a radioresistant micrococcus. I. Isolation, morphology, cultural characteristics and resistance to gamma radiation. Food Technol., Champaigne 10, 575–578 (1956)
Boling, M.E., Setlow, J.K.: The resistance of Micrococcus radiodurans to ultraviolet radiation. III. A repair mechnism. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 123, 26–33 (1966)
Boyce, R.P., Howard-Flanders, P.: Genetic control of DNA break-down and repair in E. coli K-12 treated with mitomycin-C or ultraviolet light. Z. Vererbungsl. 95, 345–350 (1964)
Cole, R.S.: Inactivation of Escherichia coli, F1 episomes at transfer and bacteriophage lambda by psoralen plus 360-nm light: Significance of deoxyribonucleic acid cross-links. J. Bact. 107, 846–852 (1971)
Cole, R.S.: Repair of DNA containing interstrand crosslinks in Escherichia coli: sequential excision and recombination. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 70, 1064–1068 (1973)
Driedger, A.A.: The DNA content of single cells of Micrococcus radiodurans. Canad. J. Microbiol. 16, 1136–1137 (1970)
Goldmark, P.J., Linn, S.: Purification and properties of the recBC DNase of Escherichia coli K-12. J. biol. Chem. 247, 1849–1860
Marmur, J.: A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J. molec. Biol. 3, 208–218 (1961)
Moseley, B.E.B.: The isolation and some properties of radiation-sensitive mutants of Micrococcus radiodurans. J. gen. Microbiol. 49, 293–300 (1967)
Moseley, B.E.B., Copland, H.J.R.: Isolation and properties of a recombination-deficient mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans. J. Bact. 121, 422–428 (1975)
Moseley, B.E.B., Mattingly, A., Copland, H.J.R.: Sensitization to radiation by loss of recombination ability in a temperature-sensitive DNA mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans held at its restrictive temperature. J. gen. Microbiol. 72, 329–338 (1972)
Moseley, B.E.B., Williams, E.: Repair of damaged DNA in bacteria. In: Advances in Microbial Physiology (A.H. Rose and D.W. Tempest, eds.), Vol. 16, p. 106 London: Academic Press 1977
Sweet, D.M., Moseley, B.E.B.: Accurate repair of ultraviolet-induced damage in Micrococcus radiodurans. Mutation Res. 23, 311–318 (1974)
Sweet, D.M., Moseley, B.E.B.: The resistance of Micrococcus radiodurans to killing and mutation by agents which damage DNA. Mutation Res. 34, 175–186 (1976)
Tempest, P.R., Moseley, B.E.B.: A mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans which is very sensitive to mutagenesis by some monofunctional alkylating agents. Proc. Soc. gen. Microbiol. 4, 137–138 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Ch. Auerbach
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moseley, B.E.B., Copland, H.J.R. Four mutants of Micrococcus radiodurans defective in the ability to repair DNA damaged by mitomycin-C, two of which have wild-type resistance to ultraviolet radiation. Molec. Gen. Genet. 160, 331–337 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332977
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332977