Summary
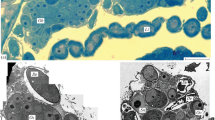
Ultrastructural evidence is presented for the manufacture, storage, and release of a distinctive cellular product in the corpus allatum of the insect Leucophaea. This product (C body material) originates in the Golgi zone and acquires a characteristic, regularly structured appearance of exceptionally high electron density.
The differential distribution of this easily identified product in various sites in the organ permits the reconstruction of a sequence of dynamic events involving transport from the intra- to the extracellular compartment which affords access to the circulation. A small amount of (surplus ?) C body material becomes incorporated in multivesicular bodies.
The variability in the occurrence, distribution, and fate of the C body material during various periods of the animal's life cycle, and under experimentally altered conditions, suggests a relationship with the glandular function of the corpus allatum. Conspicuous deposits of C body material, especially in the extracellular stroma, parallel situations in which the hormonal activity of the organ seems to be low or temporarily suspended. Thus the ultrastructural manifestations of intermittent sluggishness in the system, as observed in Leucophaea, provide valuable cues for the existence of a periodically changing production line involving a specific glandular material. The precise relationship with the comparable cyclicity of juvenile hormone activity remains to be ascertained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akert, K., Sandri, C.: An electron-microscopic study of zinc iodide-osmium impregnation of neurons. I. Staining of synaptic vesicles at cholinergic junctions. Brain Res. 7, 286–295 (1968).
Alexander, N. J., Fahrenbach, W. H.: Fine structure of endocrine hindgut cells of a lepidopteran, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübn.). Z. Zellforsch. 94, 337–345 (1969).
Farquhar, M. G.: Lysosome function in regulating secretion: disposal of secretory granules in cells of the anterior pituitary gland. In: Lysosomes in biology and pathology (J. T. Dingle and H. B. Fell, eds.), vol. 2, p. 462–482. Amsterdam-London: North-Holland Pub. Co. 1969.
Fawcett, D. W., Long, J. A., Jones, A. L.: The ultrastructure of endocrine glands. In: Recent Progr. Hormone Res. (E. B. Astwood, ed.) 25, 315–380 (1969).
Fell, H. B.: The experimental study of keratinization in organ culture. In: The epidermis (W. Montagna and W. C. Lobitz, Jr., eds.), p. 61–81. New York and London: Academic Press. 1964.
Jensen, H. M., Mottet, N. K.: Ultrastructural features of defective in vitro keratinization of chick embryonic skin. J. Cell Sci. 6, 485–509 (1970a).
—: Ultrastructural changes in keratinizing epithelium following trypsinization, epidermal detachment and apposition to mesenchymes. J. Cell Sci. 6, 511–535 (1970b).
Karnovsky, M. J.: The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J. Cell Biol. 35, 213–236 (1967).
Martin, R., Barlow, J., Miralto, A.: Application of the zinc iodide-osmium tetroxide impregnation of synaptic vesicles in cephalopod nerves. Brain Res. 15, 1–16 (1969).
Meyer, A. S., Schneiderman, H. A., Hanzmann, E., Ko, J. H.: The two juvenile hormones from the cecropia silk moth. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 60, 853–860 (1968).
Mottet, N. K., Jensen, H. M.: The differentiation of chick embryonic skin. An electron microscopic study with a description of a peculiar epidermal cytoplasmic ultrastructure. Exp. Cell Res. 52, 261–283 (1968).
Parakkal, P. F., Matoltsy, A. G.: An electron microscopic study of developing chick skin. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 403–416 (1968).
Richardson, K. C.: Electron microscopic identification of autonomic nerve endings. Nature (Lond.) 210, 756 (1966).
Rodríguez, E. M.: Fixation of the central nervous system by perfusion of the cerebral ventricles with a threefold aldehyde mixture. Brain Res. 15, 396–412 (1969).
Roller, H., Dahm, K. H., Sweely, C. C., Trost, B. M.: The structure of the juvenile hormone. Angew. Chem. 6, 179–180 (1967).
Scharrer, B.: Histophysiological studies on the corpus allatum of Leucophaea maderae. IV. Ultrastructure during normal activity cycle. Z. Zellforsch. 62, 125–148 (1964).
—: Ultrastructural study of the sites of origin and release of a cellular product in the corpus allatum of insects. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 66, 244–245 (1970).
Smith, R. E., Farquhar, M. G.: Lysosome function in the regulation of the secretory process in cells of the anterior pituitary gland. J. Cell Biol. 31, 319–347 (1966).
Steinbrecht, R. A.: Op-art-bodies. A new class of periodically layered cell inclusions observed in crayfish epidermis cells. Electron microscopy II, p. 221–222. Fourth European Regional Conference (D. S. Bocciarelli, ed.). Rome: Tipografia Poliglotta Vaticana 1968.
Thomsen, E., Thomsen, M.: Fine structure of the corpus allatum of the female blow-fly Calliphora erythrocephala. Z. Zellforsch. 110, 40–60 (1970).
Tombes, A. S., Smith, D. S.: Ultrastructural studies on the corpora cardiaca-allata complex of the adult alfalfa weevil, Hypera postica. J. Morph. 132, 137–147 (1970).
Waku, Y., Gilbert, L. I.: The corpora allata of the silkmoth, Hyalophora cecropia: an ultrastructural study. J. Morph. 115, 69–96 (1964).
Wang, N. S., Huang, S. N., Sheldon, H., Thurlbeck, W. M.: Ultrastructural changes of Clara and type II alveolar cells in adrenalin-induced pulmonary edema in mice. Amer. J. Path. 62, 237–252 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by research grants NB-05219, NB-00840, and 5P01 NS-07512 from the U.S.P. H.S.
I wish to express my thanks to Mrs. Sarah Wurzelmann, Mrs. Cynthia Jones, and Mr. Stanley Brown for excellent technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scharrer, B. Histophysiological studies on the corpus allatum of Leucophaea maderae . Z. Zellforsch. 120, 1–16 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331240
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331240