Summary
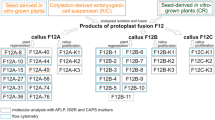
A Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cell strain carrying a positive (dominant) trait, resistance to azetidine-2-carboxylate (A2C), was selected in strain NX1 which lacked nitrate reductase activity (a negative or recessive trait). This universal hybridizer strain, denoted NXAr, was fused with dextran to a Daucus carota strain, PR, which carried glyphosate (GLP) resistance. A large number of hybrids were selected in a medium with NO -3 as the sole nitrogen source and A2C as inhibitor, conditions which prevent the growth of both parents. When the selected colonies were then tested for GLP resistance, 93% carried this trait. In addition the hybrid nature was indicated by additive chromosome numbers, both A2C and GLP resistance in suspension cultures, intermediate nitrate reductase activity and the presence of banding patterns for three isozymes which match those of the parents. Southern hybridization analysis using an enolpyruvylshikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) probe, pMON 6145, also showed the presence of the gene from both parents in the hybrid strains based on restriction length polymorphisms. The PR strain contains increased levels of EPSPS which confers GLPr due to gene amplification. Since the universal hybridizer can be used as a fusion partner with any wild-type line many protoplast fusion studies can be carried out easily.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A2C:
-
azetidine-2-carboxylate
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- EPSPS:
-
5-enolpyruvylshikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase
- GLP:
-
glyphosate
- HAT:
-
hypoxanthine, aminopterin, glycine and thymidine medium
- IDH:
-
isocitrate dehydrogenase
- MDH:
-
malate dehydrogenase
- 5MT:
-
5-methyltryptophan
- NBT:
-
nitroblue tetrazolium
- PGI:
-
phosphoglucoisomerase
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecylsulfate
References
Brown AHD, Nevo E, Zohary D, Dagan O (1978) Genetic variation in natural populations of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum). Genetica 49:97–108
Cella R, Parisi B, Nielsen E (1982) Characterization of a carrot cell line resistant to azetidine-2-carboxylic acid. Plant Sci Lett 24:125–135
Donn G, Tischer E, Smith JA, Goodman HM (1984) Herbicideresistant alfalfa cells: an example of gene amplification in plants. J Mol Appl Genet 2:621–635
Fedoroff NJ, Mauvais J, Chaleff D (1983) Molecular studies on mutations at the shrunken locus in maize caused by the controlling element Ds. J Mol Appl Genet 2:11–29
Feinberg AP, Volgelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Fine IH, Costello LA (1963) The use of starch electrophoresis in dehydrogenase studies. Methods Enzymol VI:958–972
Glimelius K, Eriksson T, Grafe R, Muller AJ (1978) Somatic hybridization of nitrate-deficient mutants of Nicotiana tabacum by protoplast fusion. Physiol Plant 44:273–277
Hamill JD, Pental D, Cocking EC, Muller AJ (1983) Production of a nitrate reductase deficient streptomycin resistant mutant of Nicotiana tabacum for somatic hybridization studies. Heredity 50:197–200
Hauptmann RM, Widholm JM (1982) Cryostorage of cloned amino acid analog-resistant carrot and tobacco suspension cultures. Plant Physiol 70:30–34
Kameya T, Horn ME, Widholm JM (1981) Hybrid shoot formation from fused Daucus carota and D. capillifolius protoplasts. Z Pflanzenphysiol 104:459–466
Kao KO (1975) A chromosomal staining method for cultured cells. In: Gamborg OL, Wetter LR (eds) Plant tissue culture methods. National Research Council of Canada, Saskatoon, pp 63–64
Lo Schiavo F, Giovinazzo G, Terzi M (1983) 8-azaguanine resistant carrot cell mutants and their use as universal hybridizers. Mol Gen Genet 192:326–329
Marton L, Dung TM, Mendel RR, Maliga P (1982) Nitrate reductase deficient cell lines from haploid protoplast culture of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Mol Gen Genet 186:301–304
Muller AJ, Grafe R (1978) Isolation and characterization of cell lines of Nicotiana tabacum lacking nitrate reductase. Mol Gen Genet 161:67–76
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nafziger ED, Widholm JM, Steinrucken HC, Killmer JL (1984) Selection and characterization of a carrot cell line tolerant to glyphosate. Plant Physiol 76:571–574
Nagy JJ, Maliga P (1976) Callus induction and plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts of Nicotiana sylvestris. Z Pflanzenphysiol 78:453–455
Pental D, Hamill JD, Cocking EC (1984) Somatic hybridization using a double mutant of Nicotiana tabacum. Heredity 53:79–83
Rigby PWJ, Dieckmann M, Rhodes C, Berg P (1977) Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol 113:237–251
Shah DM, Horsch RB, Klee HJ, Kishore GM, Winter JA, Tumer NE, Hironaka CM, Sanders PR, Gasser CS, Aykent S, Siegel NR, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1986) Engineering herbicide tolerance in transgenic plants. Science 233:478–481
Shure M, Wessler S, Fedoroff N (1983) Molecular identification and isolation of the waxy locus in maize. Cell 35:225–233
Sidorov VA, Menczel L, Nagy F, Maliga P (1981) Chloroplast transfer in Nicotiana based on metabolic complementation between irradiated and iodoacetate treated protoplasts. Planta 152:341–345
Tanksley SD (1980) Pgi-1 a single gene in tomato responsible for a variable number of isozymes. Can J Genet Cytol 22:271–278
Widholm JM (1976) Selection and characterization of cultured carrot and tobacco cells resistant to lysine, methionine and proline analogs. Can J Bot 54:1523–1529
Widholm JM (1982) Selection of protoplast fusion hybrids. In: Fujiwara A (ed) Plant tissue culture 1982. Maruzen, Tokyo, pp 609–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Melchers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, J., Hauptmann, R.M., Smith, A.G. et al. Selection of a Nicotiana plumbaginifolia universal hybridizer and its use in intergeneric somatic hybrid formation. Mol Gen Genet 208, 474–480 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328142
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328142