Abstract
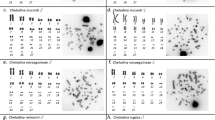
A presumed XY chromosome pair is described fromt estis squashes from the mesopelagic deep-sea fish Bathylagus wesethi, whose 2N chromosome number was determined as 34-“XY”. Although the metacentric “X-chromosome” is the largest in the entire compliment, the “Y” is the smallest and only acrocentric element. The positive heteropycnosis of the sex elements was not easily distinguishable in the nuclei of first meiotic prophase. Tetraploid nuclei were observed in peripheral supporting cells of the testis. Males of at least two other congeners have similar karyotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aida, T.: On the inheritance of colour in a fresh-water fish, Aplocheilus latipes, with special reference to sex-linked inheritance. Genetics 6, 554–573 (1921).
Beçak, W., M. L. Beçak, and H. R. S. Nazareth: Karyotypic studies of two species of South American snakes (Boa constrictor and Bothrops jararaca). Cytogenetics 1, 305–313 (1962).
— and S. Ohno: Close karyological kinship between the reptilian suborder Serpentes and the class Aves. Chromosoma (Berl.) 15, 606–617 (1964).
Bennington, N. L.: Germ cell origin and spermatogenesis in the Siamese fighting fish, Betta splendens. J. Morph. 60, 103–125 (1936).
Brink, J. M. van: L'expression morphologique de la digamétie chez les sauropsidés et les monotrèmes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 10, 1–72 (1959).
Chavin, W., and M. Gordon: Sex-determination in Platypoecilus maculatus. Differentiation of the gonads in members of all male broods. Zoologica (Stuttg.) 36, 135–146 (1951).
Foley, J. O.: The spermatogenesis of Umbra limi with special reference to the behaviour of the spermatogonial chromosomes and the first maturation division. Biol. Bull. 50, 117–147 (1926).
Gordon, M.: Physiological genetics of fishes. In: The physiology of fishes. II. Behavior, p. 431–501, ed. by M. E. Brown. New York: Academic Press 1957.
Huver, C. W.: A quantitative study of DNA in the testis cells of Fundulus diaphanus. Amer. Zool. 4, 320 (1964).
Jörgensen, M.: Zellenstudien. I. Morphologische Beiträge zum Problem des Eiwachstums. Arch. Zellforsch. 10, 1–126 (1913).
Kallman, K. D.: Sex determination in the teleost Xiphophorus milleri. Amer. Zool. 5, 246–247 (1965).
Kobel, H. R.: Heterochromosomen bei Vipera berus L. (Viperidae, Serpentes). Experientia (Basel) 18, 173–174 (1962).
Makino, S.: The chromosomes of the carp (Cyprinus carpio), including those of some related species of Cyprinidae for comparison. Cytologia (Tokyo) 9, 430–440 (1939); - The chromosomal relation between the two allied species of the loach (Cobitidae, Pisces). Cytologia (Tokyo) 12, 79–82 (1941); - A karyological study of gold-fish of Japan. Cytologia (Tokyo) 12, 96–111 (1941).
Matthey, R.: Les chromosomes des Vertébrés. Lausanne: Rouge 1949.
—, and J. M. van Brink: La question des hétérochromosomes chez les Sauropsidés. I. Reptiles. Experientia (Basel) 12, 1–5 (1956); - Sex chromosomes in Amniota. Evolution (Lancaster, Pa.) 11, 163–165 (1957).
Nogusa, S.: Chromosome studies in Pisces IV. The chromosomes of Mogrunda obscura (Gobiidae), with evidence of male heterogamety. Cytologia (Tokyo) 20, 11–18 (1955); - A comparative study of the chromosomes of fishes with particular considerations on taxonomy and evolution. Mem. Hyogo Univ. Agric., Biol. Ser. 3 (I), 62 p. (1960).
Nusbaum-Hilarowicz, J.: Études d'anatomic compareé sur les poissons provenant des campagnes scientifiques de S. A. S. le Prince de Monaco (Deuxieme partie). Rés. Camp. Sci. Monaco 65, 1–100 (1923).
Ralston, E. M.: A study of the chromosomes of Xiphophorus, Platypoecilus, and Xiphophorus X Platypoecilus hybrids during spermatogenesis. J. Morph. 56, 423–432 (1934).
Roberts, F. L.: A chromosome study of twenty species of Centrarchidae. J. Morph. 115, 401–417 (1964).
Simon, R. C.: Chromosome morphology and species evolution in the five North American species of Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus). J. Morph. 112, 77–95 (1963).
—, and A. M. Dollar: Cytological aspects of speciation in two North American teleosts, Salmo gairdneri and Salmo clarki lewisi. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 5, 43–49 (1963).
Svärdson, G.: Chromosome studies on Salmonidae. Rep. Swed. State Inst. F. W. Fish. Res., Drottningholm, Nr. 23, 151 p. (1945).
Vaupel, J.: The spermatogenesis of Lebistes reticulatus. J. Morph. 47, 555–587 (1929).
Weiler, C., and S. Ohno: Cytological confirmation of female heterogamety in the African water frog (Xenopus laevis). Cytogenetics 1, 217–223 (1962).
White, M. J. D.: Animal cytology and evolution, 2nd Ed. Cambridge: The University Press 1954; - The chromosomes, 5th Ed. London: Methuen & Co. 1961.
Winge, Ø.: A peculiar mode of inheritance and its Cytological explanation. J. Genet. 12, 137–144 (1922); - Crossing-over between the X and Y chromosomes in Lebistes. J. Genet. 13, 201–227 (1923).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T.R., Ebeling, A.W. Probable male heterogamety in the deep-sea fish Bathylagus wesethi (Teleostei: Bathylagidae). Chromosoma 18, 88–96 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326446
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326446