Summary
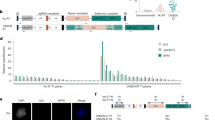
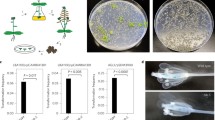
We present a detailed analysis of the function of the right and left T-DNA border regions of the nopaline Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. An avirulent deletion of the right border of the nopaline Ti plasmid (pGV3852) was used as an acceptor for 14 different T-DNA border constructs. The functional activities of these constructs were assayed by their ability to restore virulence, i.e. transformation on inoculated plants. Tumorigenicities were measured in several independent experiments over a 2 year period and the statistical significance of their relative levels was evaluated. The data indicate: (i) the entire sequence of the 25 bp direct repeat of the T-DNA is required to provide an efficient substrate for mediating T-DNA transfer events; deletion derivatives of either the conserved or the vaiable domain of the repeat are defective in T-DNA transfer; (ii) while the 25 bp direct repeat alone can promote the T-DNA transfer, the flanking sequences of the repeats enhance (on the right) or attenuate (on the left) their activity; and (iii) tumorigenicity measurements vary depending on the plant assay system: potato discs are more sensitive than wounded tobacco leaves in detecting differences in T-DNA border activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright LM, Yanofsky MF, Leroux B, Ma S, Nester EW (1987) Processing of the T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens generates border nicks and linear, single-stranded T-DNA. J Bacteriol 169:1046–1055
Barker RF, Idler KB, Thompson DV, Kemp JD (1983) Nucleotide sequence of the T-DNA region from the Agrobacterium tumefaciens octopine Ti plasmid pTi15955. Plant Mol Biol 2:335–350
Bolivar F, Rodriguez R, Greene P, Betlach M, Heynecker H, Boyer H, Crosa J, Falkow S (1977) Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2:95–113
Casadaban MJ, Cohen SN (1980) Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 138:179–207
Chilton M-D, Currier TC, Farrand SK, Bendich AJ, Gordon MP, Nester EW (1974) Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA and PS8 bacteriophage DNA not detected in crown gall tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:3672–3676
Depicker A, De Wilde M, De Vos G, De Vos R, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1980) Molecular cloning of overlapping segments of the nopaline Ti-plasmid pTiC58 as a means to restriction endonuclease mapping. Plasmid 3:193–211
De Vos G, De Beuckeleer M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1981) Restriction endonuclease mapping of the octopine tumor inducing pTiAch5 of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid 6:249–253
Douglas CJ, Staneloni RJ, Rubin RA, Nester EW (1985) Identification and genetic analysis of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosomal virulence region. J Bacteriol 161:850–860
Gheysen G, Dhaese P, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1985) DNA flux across genetic barriers: the crown gall phenomenon. In: Hohn B, Dennis ES (eds) Genetic flux in plants. Advances in plant gene research, vol. 2. Springer, Wien, Heidelberg, Berlin, New York, pp 11–47
Gielen J, De Beuceleer M, Seurinck J, Deboeck F, De Greve H, Lemmers M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1984) The complete nucleotide sequence of the TL-DNA of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiAch5. EMBO J 3:835–846
Holsters M, Villarroel R, Gielen J, Seurinck J, De Greve H, De Greve H, Schell J (1983) An analysis of the boundaries of the octopine TL-DNA in tumors induced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet 190:35–41
Jen GC, Chilton M-D (1986) The right border region of pTiT37 T-DNA is intrinsically more active than the left border region in promoting T-DNA transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3895–3899
Joos H, Inzé D, Caplan A, Sormann M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1983) Genetic analysis of T-DNA transcripts in nopaline crown galls. Cell 32:1057–1067
Leong SA, Ditta GS, Helinski DR (1982) Heme biosynthesis in Rhizobium: identification of a cloned gene coding for δ-aminolevulinic acid synthetase from Rhizobium meliloti. J Biol Chem 257:8724–8730
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Maxam A, Gilbert W (1977) A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:560–564
Nagy JI, Maliga P (1976) Callus induction and plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts of Nicotiana sylvestris. Z Pflanzenphysiol 78:453–455
Nomura N, Yamagishi H, Oka A (1978) Isolation and characterization of transducing coliphage fd carrying a kanamycin resistance gene. Gene 3:39–51
Peralta EG, Ream LW (1985) T-DNA border sequences required for crown gall tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:5112–5116
Peralta EG, Hellmiss R, Ream W (1986) Overdrive, a T-DNA transmission enhancer on the A. tumefaciens tumour-inducing plasmid. EMBO J 5:1137–1142
Rao RN, Rogers SG (1979) Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA fragments. Gene 7:79–82
Rubin RA (1986) Genetic studies on the role of octopine T-DNA border regions in crown gall tumor formation. Mol Gen Genet 202:312–320
Simpson RB, O'Hara PJ, Kwok W, Montoya AL, Lichtenstein C, Gordon MP, Nester EW (1982) DNA from the A6S/2 crown gall tumor contains scrambled Ti-plasmid sequences near its junctions with the plant DNA. Cell 29:1005–1014
Slightom JL, Jouanin L, Leach F, Drong RF, Tepfer D (1985) Isolation and identification of TL-DNA/plant junctions in Convolvulus arvensis transformed by Agrobacterium rhizogenes strain A4. EMBO J 4:3069–3077
Stachel SE, Nester EW (1986) The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J 5:1445–1454
Stachel SE, Zambryski P (1986) Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the susceptible plant cell: a novel adaptation of extracellular recognition and DNA conjugation. Cell 47:155–157
Stachel SE, Messens E, Van Montagu M, Zambryski P (1985) Identification of the signal molecules produced by wounded plant cells that activate T-DNA transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nature 318:624–629
Stachel SE, Timmerman B, Zambryski P (1986) Generation of single-stranded T-DNA molecules during the initial stages of T-DNA transfer from Agrobacterium tumefaciens to plant cells. Nature 322:706–712
Stachel SE, Timmerman B, Zambryski P (1987) Activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression generates multiple single-stranded T-strand molecules from the pTiA6 T-region: requirements for 5′ virD gene products. EMBO J 6:857–863
Van Lijsebettens M, Inzé D, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1986) Transformed cell clones as a tool to study T-DNA integration mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Mol Biol 188:129–145
Vieira J, Messing J (1982) The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene 19:259–268
Wang K, Herrera-Estrella L, Van Montagu M, Zambryski P (1984) Right 25-bp terminus sequences of the nopaline T-DNA is essential for and determines direction of DNA transfer from Agrobacterium to the plant genome. Cell 38:455–462
Wang K, Stachel S, Timmerman B, Van Montagu M, Zambryski P (1987) Site-specific nick in the T-DNA border sequence following vir gene expression in Agrobacterium. Science 235:587–591
Yadav NS, Vanderleyden J, Bennett DR, Barnes WM, Chilton M-D (1982) Short direct repeats flank the T-DNA on a nopaline Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6322–6326
Yanofsky MF, Porter SG, Young C, Albright LM, Gordon MP, Nester EW (1986) The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes a site-specific endonuclease. Cell 47:471–477
Zambryski P, Depicker A, Kruger K, Goodman H (1982) Tumor induction by Agrobacterium tumefaciens: analysis of the boundaries of T-DNA. J Mol Appl Genet 1:361–370
Zambryski P, Joos H, Genetello C, Leemans J, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1983) Ti plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity. EMBO J 2:2143–2150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Schell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Genetello, C., Van Montagu, M. et al. Sequence context of the T-DNA border repeat element determines its relative activity during T-DNA transfer to plant cells. Molec Gen Genet 210, 338–346 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00325703
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00325703