Abstract
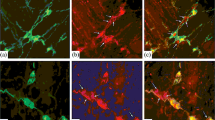
Double-labeling immunofluoresenct histochemistry demonstrates that calretinin, a calcium-binding protein, coexists with calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and substance P in the fibers innervating the lamina propria of the rat intestinal villi. An acetylcholinesterase histochemical stain revealed that the majority of calretinin-containing cells in the myenteric ganglia were cholinergic and that about one half of the submucosal calretinin-containing cells colocalized with acetylcholinesterase. In situ hybridization studies confirmed the presence of calretinin mRNA in the dorsal root ganglia, and a ribonuclease protection assay verified the presence of calretinin message in the intestine. The coexistence of calretinin in calcitonin-gene-related-peptide-containing cells that also contained substance P and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the dorsal root ganglia suggest that these ganglia are the source of the quadruple colocalization within the sensory fibers of the villi. Although the function of calretinin in these nerves is unknown, it is hypothesized that the coexistence of three potent vasodilatory peptides influences the uptake of metabolized food products within the vasculature of the villi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai R, Winsky L, Arai M, Jacobowitz DM (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of calretinin in the rat hindbrain. J Comp Neurol 310:21–44
Arai M, Arai R, Kani K, Jacobowitz DM (1993) Immunohistochemical localization of calretinin in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus and its retino-geniculate projection. Brain Res 596: 215–222
Baimbridge KG, Celio MR, Rogers JH (1992) Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci 15:303–308
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Brookes SJH, Steele PA, Costa M (1991) Calretinin immunoreactivity in cholinergic motor neurones, interneurones and vasomotor neurones in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 263:471–481
Brookes SJH, Song ZM, Steele PA, Costa M (1992) Identification of motor neurons to the longitudinal muscle of the guinea pig ileum. Gastroenterology 103:961–973
Buchan AMJ (1991) Neurofilament M and calbindin D28k are present in mutually exclusive subpopulations of enteric neurons in the rat submucous plexus. Brain Res 538:171–175
Buchan AMJ, Baimbridge KG (1988) Distribution and co-localization of calbindin D28k with VIP and neuropeptide Y but not somatostatin, galanin and substance P in the enteric nervous system of the rat. Peptides 9:333–338
Celio MR, Poncino A, Cantino D (1992) Presence of calretinin in neurons of the human intestine. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 68:25–29
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Cuello AC (1981) Projections of substance P-containing neurons within the guineapig small intestine. Neuroscience 6:411–424
Dhatt N, Buchan A (1994) Colocalization of neuropeptides with calbindin D28k and NADPH diaphorase in the enteric nerve plexuses of normal human ileum. Gastroenterology 107: 680–690
Domoto T, Yang H, Bishop AE, Polak JM, Oki M (1992) Distribution and origin of extrinsic nerve fibers containing calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and galanin in the rat upper rectum. Neuroscience Res 15:64–73
Duc C, Barak-Waller I, Droz B (1994) Innervation of putative rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors by calbindin- and calretinin-immunoreactive primary sensory neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 6:264–271
Furness JB, Keast JR, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC, Costa M, Emson PC, Lawson DEM (1988) Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of calcium-binding proteins in enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res 252:79–87
Gibbins IL (1992) Vasoconstrictor, vasodilator and pilomotor pathways in sympathetic ganglia of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 47:657–672
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, MacIntyre I, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S (1985) Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett 57:125–130
Gibson SJ, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Sabate IM, Mulderry PM, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Morrison JFB, Kelly JS, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and of eight other species. J Neurosci 4:3101–3111
Hara H, Hamill GS, Jacobowitz DM (1985) Origin of cholinergic nerves to the rat major cerebral arteries: coexistence with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Brain Res Bull 14:179–188
Heppelman B, Emson PC (1993) Distribution of calretinin mRNA in rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia: a study using nonradioactive in situ hybridization histochemistry. Brain Res 624:312–316
Holman JJ, Craig RK, Marshall I (1986) Human α- and β-CGRP and rat α-CGRP are coronary vasodilators in the rat. Peptides 7:231–235
Huidobro-Toro JP, Chela CA, Bahouth S, Nodar R, Musacchio JM (1982) Fading and tachyphylaxis to the contractile effects of substance P in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacolacol 81:21–34
Iacopino AM, Christakos S (1990). Specific reduction of calcium-binding protein (28-kilodalton calbindin-D) gene expression in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4078–4082
Ichikawa H, Jacobowitz DM, Winsky L, Helke CJ (1991) Calretinin-immunoreactivity in vagal and glossopharyngeal sensory neurons of the rat: distribution and coexistence with putative transmitter agents. Brain Res 557:316–321
Ichikawa H, Jacobowitz DM, Sugimoto T (1992) Calretinin-immunoreactivity in the oro-facial and pharyngeal regions of the rat. Neurosci Lett 146:155–158
Ichikawa H, Jacobowitz DM, Sugimoto T (1993) Calretinin-immunoreactive neurons in the trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia of the rat. Brain Res 617:96–102
Jacobowitz DM, Creed GJ (1983) Cholinergic projection sites of the nucleus of tractus diagonalis. Brain Res Bull 10:365–371
Jacobowitz DM, Koelle GB (1965) Histochemical correlations of acetylcholinesterase and catecholamines in postganglionic autonomic nerves of the cat, rabbit, and guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 148:225–237
Jacobowitz DM, Winsky L (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of calretinin in the forebrain of the rat. J Comp Neurol 304:198–218
Ju G, Hökfelt T, Brodin E, Fahrenkrug J, Fischer JA, Frey P, Elde RP, Brown JC (1987) Primary sensory neurons of the rat showing calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity and their relation to substance P-, somatostatin-, galanin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and cholecystokinin-immunoreactive ganglion cells. Cell Tissue Res 247:417–431
Kashiba H, Senba E, Kawai Y, Ueda Y, Tohyama M (1992) Axonal blockade induces the expression of vasoactive intestinal polypeptides and galanin in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res 577:19–28
Kerins C, Said SI (1973) Hyperglycemic and glycogenolytic effects of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 142:1014–1017
Koelle GB (1955) The histochemical identification of acetylcholinesterase in cholinergic, adrenergic and sensory neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 114:167–184
Kuźnicki J, Winsky L, Jacobowitz DM (1994) Ca2+-dependent and independent interactions of calretinin with hydrophobic resins. Biochem Mol Biol Int 33:713–721
Kuźnjcki J, Wang TCL, Martin BM, Winsky L, Jacobowitz DM (1995) Localization of Ca2+-dependent conformational changes of calretinin by limited tryptic proteolysis. Biochem J (in press)
Landis SC, Fredieu JR (1986) Coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide in cholinergic sympathetic innervation of rat sweat glands. Brain Res 377: 177–181
Larsson LT, Malmfors G, Sundler F (1988) Neuropeptide Y, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and galanin in Hirschsprung's disease: an immunocytochemical study. J Pediatr Surg 23:342–345
Leeman SE, Mroz EA (1974) Substance P. Life Sci 15:2033–2044
Lledo PM, Somasundaram B, Morton AJ, Emson PC, Mason WT (1992) Stable transfection of calbindin-D28k into the GH3 cell line alters calcium currents and intracellular calcium homeostasis. Neuron 9:943–954
Lembeck F, Holzer P (1979) Substance P as neurogenic meditor of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma estravasation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 310:175–183
Lenz HJ, Mortrud MT, Vale WW, Rivier JE, Brown MR (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide acts within the central nervous system to inhibit gastic acid secretion. Regul Pept 9:271–277
Lindh B, Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Elfvin LG, Fahrenkrug J, Fischer J (1987) Coexistence of CGRP- and VIP-like immunoreactivities in a population of neurons in the cat stellate ganglia. Acta Physiol Scand 131:475–476
Marshall I, Al-Kazwini SJ, Roberts PM, Shepperson NB, Adams M, Craig RK (1986) Cardiovascular effects of human and rat CGRP compared in the rat and other species. Eur J Pharmacol 123:207–216
Messenger JP (1993) Immunohistochemical analysis of neurons and their projections in the proximal colon of the guinea pig. Arch Histol Cytol 56:459–473
Parmentier M (1990) Calbindin D28k is essentially located in the colonic part of the toad intestine. Biol Cell 68:43–49
Parmentier M, Lefort A (1991) Structure of the human brain calcium-binding protein calretinin and its expression in bacteria. Eur J Biochem 196:79–85
Pompolo S, Furness JB (1993) Origins of synaptic inputs to calretinin immunoreactive neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Neurocytol 22:531–546
Ren K, Ruda MA, Jacobowitz DM (1993) Immunohistochemical localization of calretinin in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord of the rat. Brain Res Bull 31:13–22
Résibois A, Rogers JH (1992) Calretinin in rat brain: an immuno-histochemical study. Neuroscience 46:101–134
Résibois A, Vienne G, Pochet R (1988) Calbindin-D28k and the peptidergic neuroendocrine system in rat gut: an immunohis-tochemical study. Biol Cell 63:67–75
Rogers JH (1987) Calretinin: a gene for a novel calcium-binding protein expressed principally in neurons. J Cell Biol 105: 1343–1353
Rogers JH, Résibois A (1992) Calretinin and calbindin D28k in rat brain: patterns of partial colocalization. Neuroscience 51: 843–865
Schoor BA, Said SI, Makhlouf GM (1974) Inhibition of gastric secretion by synthetic vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). J Clin Res 22:23A
Schultzberg M, Dreyfus CF, Gershon MD, Hökfelt T, Elde R, Nilsson G, Said SI, Goldstein M (1980) VIP, enkephalin-, substance P-, and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in neurons intrinsic to the intestine: immunohistochemical evidence from organotypic tissue cultures. Brain Res 155:239–248
Schebalin M, Said SI, Makhlouf GM (1977) Stimulation of insulin and glucagon secretion by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Am J Physiol 232:E197-E200
Song Z-M, Brookes SJH, Steele PA, Costa M (1992) Projections and pathways of submucous neurons to the mucosa of the guinea pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 269:87–98
Steele PA, Brookes SJH, Costa M (1991) Immunohistochemical identification of cholinergic neurons in the myenteric plexus of guinea pig small intestine. Neuroscience 45:227–239
Sternini C, Anderson K (1992) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing neurons supplying the rat digestive system: differential distribution and expression pattern. Somatosens Motor Res 9:45–59
Strauss KI, Jacobowitz DM (1993a) Nucleotide sequence of rat calretinin cDNA. Neurochem Int 22:541–546
Strauss KI, Jacobowitz DM (1993b) Quantitative measurement of calretinin and β-actin mRNA in rat brain micropunches without prior isolation of RNA. Mol Brain Res 20:229–239
Strauss KI, Kuznicki J, Winsky L, Jacobowitz DM (1994) Recombinant and native calretinin share physiochemical properties. Protein Expr Purif 5:187–191
Su HC, Bishop AE, Power RF, Hamada Y, Polak JM (1987) Dual intrinsic and extrinsic origins of CGRP- and NPY-immunoreactive nerves of rat gut and pancreas. J Neurosci 7:2674–2687
Sutin E, Jacobowitz DM (1990) Detection of CCK mRNA in the motor nucleus of the rat trigeminal nerve in situ hybridization histochemistry. Mol Brain Res 8:63–68
Taché Y, Pappas T, Lauffenburger M, Goto Y, Walsh JH, Debas H (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide: potent peripheral inhibitor of gastric acid secretion in rats and dogs. Gastroenterology 87:344–349
Tsuto T, Okamura H, Fukui K, Obata-Tsuto HL, Terubayashi H, Yanagihara J, Iwai N, Majima S, Yanaihara N, Ibata Y (1985) Immunohistochemical investigations of gut hormones in the colon of patients with Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg 20:266–270
Walters JRF, Bishop AE, Facer P, Lawson EM, Rogers JH, Polak JM (1993) Calretinin and calbindinD28k immunoreactivity in the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 104:1381–1389
Weisenfeld-Hallin Z, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Forssmann WG, Reinecke M, Tschopp FA, Fischer JA (1984) Immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P coexist in sensory neurons to the spinal cord and interact in spinal behavioral responses of the rat. Neurosci Lett 52:199–204
Winsky L, Jacobowitz DM (1991) Radioimmunoassay of calretinin in the rat brain. Neurochem Int 19:517–522
Winsky L, Nakata H, Martin B, Jacobowitz DM (1989) Isolation, partial amino acid sequence and immunohistochemical localization of a brain-specific calcium-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:10139–10143
Young III WS, Bonner TL, Brann MR (1986) Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9827–9831
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isaacs, K.R., Winsky, L., Strauss, K.I. et al. Quadruple colocalization of calretinin, calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and substance P in fibers within the villi of the rat intestine. Cell Tissue Res 280, 639–651 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318366
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318366