Abstract
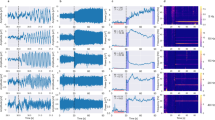
An original method is presented for the single sweep analysis of visual evoked potentials (VEP's). The introduced algorithm bases upon an AutoRegressive with eXogenous input (ARX) modelling. A Least Squares procedure estimates the coefficients of the model and allows to obtain a complete black-box description of the signal generation mechanism, besides providing a filtered version of the single sweep potential. The performance of the algorithm is verified on proper simulation tests and the experimental results put into evidence the noticeable improvement of signal-to-noise ratio with a consequent better recognition of the classical parameters of the peaks (latencies and amplitudes). The possibility of measuring these parameters on a single sweep basis enables to evaluate the dynamics of the Central Nervous System response during the entire course of the examination. A classification of the estimated evoked potentials in a small number of subsets, on the basis of their morphology, is also possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1970) Statistical predictor identification. Ann Inst Statist Math 22:203–217
Åström KJ (1970) Introduction to stochastic control theory. Academic Press, New York
Bellman KL, Walter DO (1984) Biological processing. Am J Physiol 246:R860-R867
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis, forecasting and control. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Carlton EH, Katz S (1980) Is Wiener filtering an effective method of improving evoked potential estimation? IEEE Trans BME-27:187–192
Cerutti S, Liberati D, Mascellani P (1985) Parameter extraction in EEG processing during riskful neurosurgical operation. Sign Proc 9:25–35. Cerutti S, Bersani V, Carrera A, Liberati D (1987) Analysis of visual evoked potentials through Wiener filtering applied to a small number of sweeps. J Biomed Eng 9:3–12
Chiappa KH (1983) Evoked potentials in clinical medicine. Raven, New York
Elko PP, Ackmann JJ, Wu SJ (1979) Digital filtering of on-line evoked potentials. Int J Bio-Med Comput 10:291–303
Eykhoff P (1971) System identification — parameter and state estimation. Wiley, New York
Gersch W (1970) Spectral analysis of EEG's by autoregressive decomposition of time series. Math Biosci 7:205–222
Gevins AS (1984) Analysis of the electromagnetic signals of the human brain: milestones, obstacles, and goals. IEEE Trans BME-31:833–850
Heinze HJ, Künkel H (1984) ARMA-filtering of evoked potentials. Method Inf Med 23:29–36
Heinze HJ, Künkel H, Massing W (1981) Selective filtering of single evoked potentials by high performance ARMA methods. In: Yamaguchi N, Fujisawa K (eds) Recent advances in EEG and EMG data processing. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 29–46
McGillem CD, Aunon JI, Yu K (1985) signals and noise in evoked brain potentials. IEEE Trans BME-32:1012–1016
Mocks J, Gasser T, Dinh Tuan P (1984) Variability of single visual evoked potentials evaluated by two new statistical tests. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 57:571–580
Ohshio T (1981) Wiener filtering and Kalman filter. In: Yamaguchi N, Fujisawa K (eds) Recent advances in EEG and EMG data processing. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 357–362
Perry NW Jr, Childers DG (1969) The human visual evoked response: method and theory. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield-Illinois
Rauner H, Wolf W, Appel U (1983) New perspectives to noise reduction in evoked potential processing. In: Schlusser HW (ed) Signal Processing II: Theories and applications. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 577–580
Regan D (1972) Evoked potential in psychology, sensory physiology, and clinical medicine. Chapman and Hall, London
Sandini G, Romano P, Scotto A, Traverso G (1983) Topography of brain electrical activity: a bioengineering approach. Med Progr Technol 10:5–19
Ungan P, Basar E (1976) Comparison of Wiener filtering and selective averaging of evoked potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 40:516–520
Walter DO (1969) A posteriori “Wiener filtering” of average evoked responses. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol (Suppl) 27:61–70
de Weerd JPC (1981) A posteriori time-varying filtering of averaged evoked potentials. I. Introduction and conceptual basis. Biol Cybern 41:211–222
de Weerd JPC, Martens WLJ (1978) Theory and practice of a posteriori “Wiener” filtering of average evoked potentials. Biol Cybern 30:81–94
de Weerd JPC, Uyen GJH, Johannesma PIM, Martens WLJ (1979) Estimation of signal and noise spectra by special averaging techniques with application to a posteriori “Wiener” filtering. Biol Cybern 32:153–164
Zetterberg L (1969) Estimation of parameters for a linear differences equation with application to EEG analysis. Math Biosci 5:227–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerutti, S., Baselli, G., Liberati, D. et al. Single sweep analysis of visual evoked potentials through a model of parametric identification. Biol. Cybern. 56, 111–120 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317986
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317986