Summary
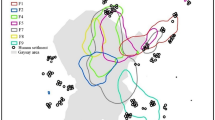
This paper presents analyses of habitat-use and home range size in the Blanford's fox. We predicted, from the resource dispersion hypothesis (RDH), that home ranges would encompass similar areas of combined fruitful habitats, but widely different areas of useless habitats, and thus that home ranges would be larger where such fruitful patches are fragmented and widely dispersed. Home range estimates of 0.5–2.0 km2 were calculated for 16 adult Blanford's foxes, using three different methods. There were no significant differences in home range size between sexes or study sites. One habitat, dry creekbed, was the most frequently visited in all home ranges. Dry creekbed provided abundant prey for the foxes and only sparse cover for their predators. Both the available area of creekbed in each range, and the area of creekbed patches that was used by the foxes, were independent of home range size. However, the variance in home range size was explained by the mean distance between the main denning area and the most frequently used patches of creekbed. These results are in accord with some predictions of the resource dispersion hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradbury JW, Vehrencamp SL (1976) Social organization and foraging in Emballonurid bats. A model for the determination of group size. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 1:383–404
Carr GM, Macdonald DW (1986) The sociality of solitary foragers: a model based on resource dispersion. Anim Behav 35:1540–1549
Catt DC, Staines BW (1987) Home range use and habitat selection by red deer (Cervus elaphus) in a Sitka spruce plantation as determined by radio-tracking. J Zool (Lond) 211:681–693
Ford G, Krumme DW (1979) The analysis of space use patterns. J Theor Biol 76:125–155
Garrott RA, Eberhardt LE (1987) Arctic fox. In: Novak M, Baker JA, Obbard ME, Malloch B (eds) Wild furbearer management and conservation in North America. Ministry of Natural Resources, Ontario, Canada, pp 394–406
Geffen E, Macdonald OW (1992) Small size and monogamy: spatial organization of the Blanford's fox, Vulpes cana. Anim Behav (in press)
Geffen E, Hefner R, Macdonald DW, Ucko M (In press a) Diet and foraging behavior of Blanford's Foxes, Vulpes nana, in Israel. J Mammal
Geffen E, Hefner R, Macdonald DW, Ucko M (In press b) Morphological adaptations and seasonal weight changes in the Blanford's fox, Vulpes cana. J Arid Environ
Ginsberg JR, Macdonald DW (1990) Foxes, wolves, jackals and dogs: an action plan for the conservation of canids. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland
Gittleman JL, Harvey PH (1982) Carnivore home range size, metabolic needs and ecology. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 10:57–63
Harestad AS, Bunnell FL (1979) Home range and body weight—a reevaluation. Ecology 60:389–402
Harris S, Rayner JMV (1986) Models for predicting urban fox (Vulpes vulpes) numbers in British cities and their application for rabies control. J Anim Ecol 55:593–603
Harrison DL, Bates PJJ (1989). Observations on two mammal species new to the Sultanate of Oman, Vulpes cana Blanford, 1877 (Carnivora: Canidae) and Nycteris thebaica Geoffroy, 1818 (Chiroptera: Nycteridae). Bonn Zool Beitr 40:73–77
Hersteinsson P, Macdonald DW (1982) Some comparisons between red and arctic foxes, Vulpes vulpes and Alopex lagopus, as revealed by radio tracking. Symp Zool Soc Lond 49:259–289
Ilany G (1983) Blanford's fox, Vulpes cana, Blanford, 1877, a new species in Israel. Isr J Zool 32:150
Karta (Firm) (1985) Atlas of Israel. Macmillan Publication Company, New York, USA
Kenward R (1987). Wildlife radio tagging: equipment, field techniques and data analysis. Academic Press, London, UK
Kruuk H, Macdonald DW (1985) Group territories of carnivores: empires and enclaves. In: Sibly RM, Smith RH (eds) Behavioural ecology: ecological consequences of adaptive behaviour. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK, pp 521–536
Kruuk H, Parish T (1982) Factors affecting population density, group size and territory size of the European badger, Meles meles. J Zool Lond 196:31–39
Lindsay IM, Macdonald DW (1986) Behaviour and ecology of the Ruppell's fox Vulpes ruppelli, in Oman. Mammalia 50:461–474
Macdonald DW (1981) Resource dispersion and social organization of the red fox, Vulpes vulpes. In: Chapman JA, Pursley D (eds) Proceedings of the worldwide furbearer conference. University of Maryland Press, Frostburg, Maryland, USA, pp 918–949
Macdonald DW (1983) The ecology of carnivore social behaviour. Nature 301:379–384
Macdonald DW, Carr GM (1989) Food security and the rewards of tolerance. In: Standen V, Foley RA (eds) Comparative socioecology: the behavioural Ecology of humans and other mammals. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK, pp 75–99
Macdonald DW, Ball FT, Hough NG (1980) The evaluation of home range size and configuration using radio tracking data. In: Amlaner CF, Macdonald DW (eds) A handbook on biotelemetry and radio tracking. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, pp. 402–424
Macdonald DW, Bunce RGH, Bacon PJ (1981) Fox populations, habitat characterization and rabies control. J Biogeog 8:145–151
Mendelssohn H, Yom-Tov Y, Ilany G, Meninger D (1987) On the occurrence of Blanford's fox, Vulpes cana, Blanford, 1877, in Israel and Sinai. Mammalia 51:459–462
Newdick MT (1983) The behavioural ecology of urban foxes, Vulpes vulpes, in Oxford. D Phil Dissertation. University of Oxford, UK
Roberts TJ (1977) The mammals of Pakistan. Ernest Benn Limited, London, UK
Voigt DR (1987) Red fox. In: Novak M, Baker JA, Obbard ME, Malloch B (eds) Wild furbearer management and conservation in North America. Ministry of Natural Resources, Ontario, Canada, pp 378–392
Voigt DR, Tinline RR (1980) Strategies for analyzing radio tracking data. In: Amlaner CF, Macdonald DW (eds) A handbook on biotelemetry and radio tracking. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, pp 387–404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geffen, E., Hefner, R., Macdonald, D.W. et al. Habitat selection and home range in the Blanford's fox, Vulpes cana: compatibility with the resource dispersion hypothesis. Oecologia 91, 75–81 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317244
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317244