Abstract
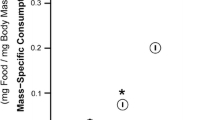
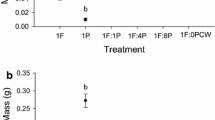
We used laboratory experiments to assess the degree of, and the underlying mechanism for, density dependence in the grazing rate of the pulmonate gastropod Physella virgata. Both fecal pellet production and uptake and incorporation of 14C radioisotopes from labeled periphyton were used as indices of grazing rates. Pronounced density-dependent reductions in grazing rate were observed, especially at densities above 4 snails/-25 cm2 periphyton grazing area. Radioisotope experiments also indicated that proportions of ingested 14C periphyton retained in snail tissue and respired as carbon dioxide increased at higher densities, suggesting that both assimilation efficiency and respiratory costs increase at higher densities. Constant replacement of water in aquaria did not remove density-dependent effects on grazing, suggesting that a dissolved metabolite is not responsible. Experiments where tiles were “pre-conditioned” with snails grazing at several densities actually stimulated grazing in subsequently added snails, suggesting that substrate-borne cues are also not responsible for density-dependent reductions in grazing rate. Behavioral inferference (in the form of shell-shaking after contacts with other snails) did, however, increase at higher densities, and may be partially reponsible for depressed grazing rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bronmark C, Klosiewski SP, Stein RA (1992) Indirect effects of predation in a freshwater benthic food chain. Ecology 73:1662–1674
Brown KM (1982) Resource overlap and competition in pond snails: an experimental analysis. Ecol 63:412–422
Brown KM (1985) Intraspecific life history variation in a pond snail: the roles of population divergence and phenotypic plasticity. Evolution 39:387–395
Brown KM (1991) Chapter 10: Mollusca: Gastropoda. In: Thorp J, Covich A (eds) The ecology and classification of freshwater invertebrates. Acad Press, Orlando, pp. 285–314
Brown KM DeVries DR (1985) Predation and the distribution and abundance of a pond snail. Oecologia 66:93–99
Burky AJ (1971) Biomass turnover, respiration, and interpopulation variation in the stream limpet Ferrissia rivularis. Ecol Monogr 41:235–251
Carman KR, Guckert JB (1994) Ingestion and assimilation of periphytic algae, bacteria, and adsorbed amino acids by an aquatic gastropod as determined from radiotracer techniques. J N Am Benthol Soc 13:80–88
Eisenberg RM (1970) The role of food in the regulation of the pond snail, Lymnaea elodes. Ecology 51:680–684
Hill WR (1992) Food limitation and interspecific competition in snail dominated streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 491257–1267
Hill WR, Weber SC Stewart AJ (1992) Food limitation of two lotic grazers: quantity quality and size-specificity. J N Am Benthol Soc 11:420–432
Hunter RD (1975) Growth, fecundity, and bioenergetics in three populations of Lymnaea palustris in upstate New York. Ecology 56:50–63
Kawata M (1993) Relative importance of direct and indirect interaction among individual snails. Res Popul Ecol 35:69–77
Lamberti GA, Gregory SV, Ashkenas LR, Steinman AD, McIntire CD (1989) Productive capacity of periphyton as a determinant of plant-herbivore interactions in streams. Ecology 70:1840–1856
Lodge DM, Brown KM, Klosiewski SP, Stein RA, Covich AP, Leathers BK, Bronmark C (1987) Distribution of freshwater snails: spatial scale and the relative importance of physicochemical and biotic factors. Am Malacol Bull 5:73–84
Lodge DM, Kershner DW, Aloi JE, Covich AP (1994) Effects of an omnivorous crayfish (Orconectes rusticus) on a freshwater littoral food web. Ecol 75:1265–1281
McCormick PV, Stevenson RJ (1989) Effects of snail grazing on benthic algal community structure in different nutrient environments. J N Am Benthol Soc 8:162–172
McMahon RF (1975) Growth, reproduction, and bioenergetic variation in three natural populations of freshwater limpet Laevapex fuscus. Proc Malacol Soc London 41:331–352
Mulholland PJ, Steinman AD, Palumbo AV, Elwood JW (1991) Role of nutrient cycling and herbivory in regulating periphyton communities in laboratory streams. Ecology 72:966–982
Osenberg CW (1989) Resource limitation, competition, and the influence of life history in a freshwater snail community. Oecologia 79:512–519
Rosemond AD, Mulholland PJ, Elwood JW (1993) Top-down and bottom-up control of stream periphyton: effects of nutrients and herbivores. Ecology 74:1264–1280
Sakata K, Kato K, Iwase Y, Okada H, Ina K, Machiguchi Y (1991) Feeding-stimulant activity of algal glycerolipids for marine herbivorous gastropods. J Chem Ecol 17:185–193
Sheldon SP (1987) The effects of herbivorous snails on submerged macrophyte communities in Minnesota lakes. Ecology 68:1920–1931
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981). Biometry. Freeman and Co., New York
Steinman AD, McIntire CD, Gregory SV, Lamberti GA, Ashkenas LR. (1987) Effects of herbivore type and density on taxonomic structure and physiognomy of algal assemblages in laboratory streams. J N Am Benthol Soc 6:175–188
Steinman AD, Mulholland PJ, Palumbo AV, Flum TF, DeAngelis DL (1991) Resilience of lotic ecosystems to a light-elimination disturbance. Ecology 72:1299–1313
Thomas JP, Goldsworthy GL, Aram RH (1975) Studies of the chemical ecology of snails: the effect of chemical conditioning by adult snails on the growth of juvenile snails. J Anim Ecol 44:1–28
Townsend CR, McCarthy TK (1980) On the defense strategy of Physa fontenalis (L.), a freshwater pulmonate snail. Oecologia 46:75–79
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, K.M., Carman, K.R. & Inchausty, V. Density-dependent influences on feeding and metabolism in a freshwater snail. Oecologia 99, 158–165 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317097
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317097