Summary
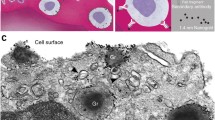
The potential of ultrasmall gold particles for the light microscopical detection of leukocyte cell surface differentiation antigens was investigated. Suspensions and cytocentrifuge preparations of peripheral blood leukocytes were first incubated with monoclonal antibodies and then with goat antimouse antibodies coupled to colloidal gold particles of 1-nanometer diameter. Cytocentrifuge preparations were made from the cell suspensions. Silver enhancement was performed on all preparations. Then they were counterstained with May-Grünwald Giemsa and examined in light microscopy. The immunostaining appeared as fine dark granules on the surface membrane of the cells. Labeling conditions were determined which gave a dense specific immunostaining and a low background. High dilutions of the ultrasmall gold probe could be used to detect all antigen expressing cells in the samples. The labeling efficiency of the IGSS method with the 1 nanometer probe was comparable to that described earlier for 5 nanometer gold particles. Lymphocyte subsets enumerated with this method in normal peripheral blood were similar to those found with immunofluorescence microscopy. We concluded that one nanometer probes do not offer a major advantage in comparison with 5 nanometer probes for the study of cell surface antigens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baschong W, Lucocq JM, Roth J (1985) Thiocyanate gold: small (2–3 nm) colloidal gold for affinity cytochemical labeling in electron microscopy. Histochemistry 83:409–411
Behnke O, Ammitzboll T, Jessen H, Klokker M, Nilausen K, Transum-Jensen J, Olsson L (1986) Nonspecific binding of proteinstabilized gold sols as a source of error in immunocytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol 41:326–338
Birrel GB, Hedberg KK, Hayes-Griffith O (1987) Pitfalls of immunogold labeling: analysis by light microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and photoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 35:843–853
Crockard A, Catovsky D (1983) Cytochemistry of normal lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies and immunocolloidal gold. Scand J Haematol 30:433–443
Danscher G (1981) Localization of gold in biological tissue. A photochemical method for light and electron microscopy. Histochemistry 71:81–88
Danscher G (1983) A silver method for counterstaining plastic embedded tissue. Stain Technol 58:365–372
Danscher G, Nörgaard R (1983) Light microscopic visualisation of colloidal gold in resin-embedded tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 31:1394–1398
De Mey J (1983) Colloidal gold probes in immunocytochemistry. In: Polak J, Van Noordende S (eds) Immunocytochemistry: applications in pathology and biology. Wright and Sons, London, pp 82–112
De Mey J (1984) Colloidal gold as marker and tracer in light-and electron microscopy. Electron Microsc Soc Am Bull 14:54
De Mey J, Moeremans M, Geuens G, Nuydens R, De Brabander M (1981) High resolution light and electron microscopic localization of tubulin with the IGS (immunogold staining) method. Cell Biol Int Rep 5:889–899
De Waele M (1984) Hematological electron immunocytochemistry. Detection of cell surface antigens with monoclonal antibodies. In: Polak J, Varndell I (eds) Immunolabeling for electron microscopy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 267–288
De Waele M (1989) Silver-enhanced colloidal gold for the detection of leukocyte cell surface antigens in darkfield and epipolarization microscopy. In: Hayat MA (ed) Colloidal gold: principles, methods and applications, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, Calif., USA, pp 443–467
De Waele M, De Mey J, Moeremans M, De Brabander M, Van Camp B (1983) Immunogold staining method for the light microscopic detection of leukocyte cell surface antigens with monoclonal antibodies. Its application to the enumeration of lymphocyte subpopulations. J Histochem Cytochem 31:376–381
De Waele M, De Mey J, Moeremans M, Broodtaerts L, Smet L, Van Camp B (1982) Colloidal gold as marker for the light microscope detection of leukocyte cell surface antigens with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Immunol 2:24–31
De Waele M, De Mey J, Renmans W, Labeur C, Jochmans K, Van Camp B (1986) Potential of immunogold-silver staining for the study of leukocyte subpopulations as defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem 34:1257–1263
De Waele M, De Mey J, Renmans W, Labeur C, Reynaert Ph, Van Camp B (1986) An immunogold-silver staining method for the detection of cell surface antigens in light microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 34:935–939
De Waele M, Renmans W, Segers E, De Valck V, Jochmans K (1989) An immunogold-silver staining method for the detection of cell surface antigens in cell smears. J Histochem Cytochem 37:1855–1862
De Waele M, Renmans W, Segers E, Jochmans K, Van Camp B (1988) Sensitive detection of immunogold-silver staining with darkfield and epipolarization microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 36:679–683
Duhamel RC, Johnson DA (1985) Use of nonfat dry milk to block nonspecific nuclear and membrane staining by avidin conjugates. J Histochem Cytochem 33:711–714
Ellis IO, Bell J, Bancroft JD (1988) An investigation of optimal gold particle size for immunocytochemical immunogold and immunogold-silver staining to be viewed by polarized indirect light (epipolarization) microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 36:121–124
Faulk WP, Taylor GM (1971) An immunocolloid method for electron microscope. Immunochemistry 8:1081–1083
Geoghegan WD, Scillian JJ, Ackerman GA (1978) The detection of human B-lymphocytes by both light and electron microscopy utilizing colloidal gold-labelled anti-immunoglobulin. Immunol Commun 7:1–12
Holgate CS, Jackson P, Cowen PN, Bird CC (1983) Immunogoldsilver staining: a new method of immunostaining with enhanced sensitivity. J Histochem Cytochem 31:938–944
Horisberger M (1981) Colloidal gold: a cytochemical marker for light and fluorescent microscopy and for transmission and scanning electron microscopy. In: Johari O (ed) Scanning electron microscopy, vol. 2. SEM Inc. O'Hare, Chicago, p 9
Horisberger M, Rosset J (1977) Colloidal gold, a useful marker for transmission and scanning electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 25:295–305
Knapp W, Dörken B, Rieber P, Schmidt R, Stein H, Borne A von dem (1989) CD antigens 1989. Blood 74:1448–1450
Lah JJ, Hayes DM, Burry RW (1990) A neutral pH silver development method for the visualisation of 1-nanometer gold particles in preembedding electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 38:503–508
Manara G, Ferari C, Torresani C, Sansoni P, De Panfilis G (1990) The immunogold-silver staining approach in the study of lymphocyte subpopulations in transmission electron microscopy. J Immunol Methods 128:59–63
Matutes E, Catovsky D (1982) The fine structure of normal lymphocyte subpopulations — a study with monoclonal antibodies and the immunogold technique. Clin Exp Immunol 50:416–425
Pallesen G, Plesner T (1987) The Third International Workshop and Conference on Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens with an up-to-date overview of the CD Nomenclature. Leukemia 1:231–234
Romasko F, Rosenberg J, Wybran J (1985) An immunogold silver staining method for the light microscopic analyses of blood lymphocyte subsets with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol 84:307–316
Romano EL, Romano M (1977) Staphylococcus protein A bound to colloidal gold: a useful reagent to label antigen-antibody sites in electron microscopy. Immunochemistry 14:711–715
Roth J (1982) Applications of immunocolloids in light microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 30:691–696
Shaw S (1987) Characterization of human leukocyte differentiation antigens. Immunol Today 8:1–3
Vogt RF Jr, Philips DL, Henderson LO, Whitfield W, Spierto FW (1987) Quantitative differences among various proteins as blocking agents for ELISA microtiter plates. J Immunol Methods 101:43–50
Wybran J, Rosenberg J, Romasco F (1985) Immunogold-staining: an alternative method for lymphocyte subset enumeration. Comparison with immunofluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 76:229–238
Yokota S (1988) Effect of particle size on labeling density for catalase in protein A-gold immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 36:107–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Valck, V., Renmans, W., Segers, E. et al. Light microscopical detection of leukocyte cell surface antigens with a one-nanometer gold probe. Histochemistry 95, 483–490 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315744
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315744