Summary
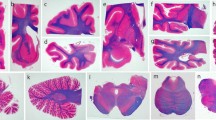
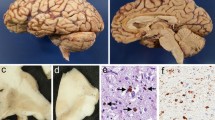
A case of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) with frontal lobe atrophy is reported, in which many senile plaques were widely distributed in the neocortex, the entorhinal cortex, the amygdala, and, to a lesser extent, the cerebellar cortex, but not in the hippocampus. Most of the plaques were of the diffuse and primitive types. They were well visualized by β-protein immunostaining, modified Bielschowsky staining and methenamine silver staining, but were not seen by Bodian staining. The widespread distribution of senile plaques in the cerebral and cerebellar cortices was far beyond that seen in normal aging, and was reminiscent of concomitant Alzheimer's disease (AD). Unlike AD, however, this case had neither senile changes in the hippocampus nor neurofibrillary tangles in the amygdala and entorhinal cortex. It seems that many senile plaques may appear widely in the cerebral cortex and even, to a lesser extent, in the cerebellar cortex of some patients with PSP. Additional case studies using sensitive silver and amyloid antibody preparations are required to elucidate the presence of senile plaques in the cerebral cortex of PSP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F, Ruberg M, Pillon B, Dubois B, Duyckaerts C, Hauw J-J, Baron J-C, Scatton B (1986) Progressive supranuclear palsy: anatomoclinical and biochemical considerations. In: Yahr MD, Bergmann KJ (eds) Advances in neurology, vol 45. Raven Press, New York, pp 191–206
Albert ML, Feldman RG, Willis AL (1974) The ‘subcortical dementia’ of progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37:121–130
Cole G, Williams P, Alldryck D, Singharo S (1989) Amyloid plaques in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Clin Neuropathol 8:188–191
Cummings JL, Benson DF (1964) Subcortical dementia. Arch Neurol 41:874–879
D'Antona R, Baron JC, Samson Y (1985) Subcortical dementia: frontal cortex hypometabolism detected by positron tomography in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 108:785–799
Davies PH, Bergeron C, McLachlan DR (1985) Atypical presentation of progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 17:337–343
Dayan AD (1970) Quantitative histological studies on the aged human brain. I. Senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in “normal” patients. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 16:85–94
Dickson DW, Farlo J, Davies P, Crystal H, Fuld P, Yen S-H (1988) Alzheimer's disease. A double-labeling immunohistochemical study of senile plaques. Am J Pathol 132:86–101
Goffinet AM, De Volder AG, Gillain C, Rectem D, Bol A, Michel C, Cogneau M, Labar D, Laterre C (1989) Positron tomography demonstrates frontal lobe hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 25:131–139
Ishino H, Otsuki S (1976) Frequency of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Sci 28:309–316
Joachim CL, Morris JH, Selkoe DJ (1989) Diffuse senile plaques occur commonly in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 135:309–319
Kang J, Lemaire H-G, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik KH, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Müller-Hill B (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 325:733–736
Katzman R, Terry R, DeTeresa R, Brown T, Davies P, Fuld P, Renbing X, Peck A (1988) Clinical, pathological, and neurochemical changes in dementia: a subgroup with preserved mental status and numerous neocortical plaques. Ann Neurol 23:138–144
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1105
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J, Prusiner SB (1987) Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloidosis. Lab Invest 57:230–236
Mann DMA, Esiri MM (1989) The pattern of acquisition of plaques and tangles in the brains of patients under 50 years of age with Down's syndrome. J Neurol Sci 89:169–179
Mann DMA, Jones D (1990) Deposition of amyloid (A4) protein within the brains of persons with dementing disorders other than Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome. Neurosci Lett 109:68–75
Mann DMA, Brown AMT, Prinja D, Jones D, Davies CA (1990) A morphological analysis of senile plaques in the brains of non-demented persons of different ages using silver, immunocytochemical and lectin histochemical staining techniques. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 16:17–25
Mann DMA, Jones D, Prinja D, Purkiss MS (1990) The prevalence of amyloid (A4) protein deposits within the cerebral and cerebellar cortex in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 80:318–327
Matsuyama H, Nakamura S (1978) Senile changes in the brain in the Japanese: incidence of Alzheimer neurofibrillary changes and senile plaques. In: Katzman R, Terry RD, Bick KL (eds) Alzheimer's disease: senile dementia and related disorders, Raven Press, New York, pp 287–297
Motte J, Williams RS (1989) Age-related changes in the density and morphology of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Down syndrome brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 77:535–546
Ogomori K, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, Sato Y, Suetsugu M, Abe M (1989) β-protein amyloid is widely distributed in the central nervous system of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 134:243–251
Pardrige WM, Vinters HV, Miller BL, Tourtellotte WW, Eisenberg JB, Yang J (1987) High molecular weight Alzheimer's disease amyloid peptide immunoreactivity in human serum and CSF is an immunoglobulin in G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145:241–248
Popovitch ER, Wisniewski HM, Barcikowska M, Silverman W, Bancher C, Sersen E, Wen GY (1990) Alzheimer neuropathology in non-Down's syndrome mentally retarded adults. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 80:362–367
Sako H, Nakamura H, Inoue K, Takada K, Tanaka J, Tabuchi Y (1986) Progressive supranuclear palsy — a case with a marked frontal atrophy. Neuropathology 7:7–14
Steele JC (1972) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 95:693–704
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Suenaga T, Hirano A, Llena JF, Ksiezak-Reding H, Yen S-H, Dickson DW (1990) Modified Bielschowsky and immunocytochemical studies on cerebellar plaques in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 49:31–40
Tagliavini F, Giaccone G, Frangione B, Bugiani O (1988) Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and non-demented individuals. Neurosci Lett 93:191–196
Tan N, Mastaglia FL, Masters CL, Beyreuther K, Kakulas BA (1988) Amyloid (A4) protein deposition in brain in progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) (abstract). Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2:264
Tomlinson BE, Corsellis JAN (1984) Aging and the dementias. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 951–1025
Tomlinson BE, Blessed G, Roth M (1968) Observation on the brains of non-demented old people. J Neurol Sci 7:331–356
Ulrich J (1985) Alzheimer changes in nondemented patients younger than sixty-five: possible early stages of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol 17:273–277
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Ihara Y (1988) A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of the Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by β protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 76:541–549
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Harigaya Y (1988) Diffuse type of senile plaques in the brains of Alzheimer-type dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 77:113–119
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Nakazato Y (1989) Diffuse type of senile plaques in the cerebellum of Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by β protein immunostain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 77:314–319
Yamaguchi H, Haga C, Hirai S, Nakazato Y, Kosaka K (1990) Distinctive, rapid, and easy labeling of diffuse plaques in the Alzheimer brains by a new methenamine silver stain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 79:569–572
Yamamoto T, Hirano A (1986) A comparative study of modified Bielschowsky, Bodian and thioflavin S stains on Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:3–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, S., Maruyama, S. & Toyoda, C. A case of progressive supranuclear palsy with widespread senile plaques. J Neurol 238, 345–348 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315336
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315336