Summary
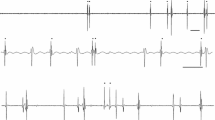
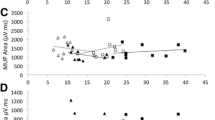
Fibre density and amplitudes of macro-EMG motor unit potentials were studied and compared with conventional EMG in the anterior tibial muscles from 51 patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The fibre density was increased in 46 muscles. Increased amplitudes of macro-EMG motor unit action potentials were found in 46 muscles, while the mean duration of motor unit potentials recorded with a concentric needle electrode was prolonged in only 26 muscles. Changes in the packing density of muscle fibres of surviving motor units are thought to influence the different electrophysiological parameters in different ways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballantyne JP, Hansen S (1974) Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials. 1. Control subjects and patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37:1187–1194
Buchthal F (1957) An introduction to electromyography. Scandinavian University Books, Gyldendal, Copenhagen
Buchthal F, Kamieniecka Z (1982) The diagnostic yield of quantified electromyography and quantified muscle biopsy in neuromuscular disorders. Muscle Nerve 5:265–280
Buchthal F, Pinelli P (1952) Analysis of muscle action potentials as a diagnostic aid in neuro-muscular disorders. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl] 266:315–327
Buchthal F, Pinelli P (1953) Action potentials in muscular atrophy of neurogenic origin. Neurology 3:591–603
Coërs C, Telerman-Toppet N, Gerard JM (1973). Terminal innervation ratio in neuromuscular disease. 2. Disorders of lower motor neurone, peripheral nerve and muscle. Arch Neurol 29:215–222
Dubowitz V, Brooke MH (1973) Muscle biopsy: a modern approach. Saunders, Philadelphia
Engel AG, Banker BQ (1986) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Erminio F, Buchthal F, Rosenfalck P (1959) Motor unit territory and muscle fibre concentration in paresis due to peripheral nerve injury and anterior horn cell involvement. Neurology 9:657–671
Fawcett PRW, Johnson MA, Schofield IS (1985) Comparison of electrophysiological and histochemical methods for assessing the spatial distribution of muscle fibres of a motor unit within a muscle. J Neurol Sci 69:67–79
Hansen S, Ballantyne JP (1978) A quantitative electrophysiological study of motor neurone disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 41:773–783
Hilton-Brown P, Stålberg E (1983) The motor unit in muscular dystrophy: a single fibre EMG and scanning EMG study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:981–995
Ludin HP (1980) Electromyography in practice. Thieme-Stratton. New York
McComas AJ, Fawcett PRW, Campbell MJ, Sica REP (1971) Electrophysiological estimation of the number of motor units within a human muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:121–131
McComas AJ, Sica REP, Campbell MJ, Upton ARM (1971) Functional compensation in partially denervated muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:453–460
Nandedkar S, Stålberg E (1983) Simulation of macro EMG motor unit potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 56:52–62
Nandedkar S, Sanders DB, Stålberg E (1984) Simulation of concentric needle EMG motor unit action potentials. Muscle Nerve 7:562
Schwartz MS, Stalberg E, Swash M (1980) Pattern of segmental motor involvement in syringomyelia: a single fibre study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:150–155
Stålberg E (1980) Macro EMG, a new recording technique. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:475–482
Stålberg E (1982) Electrophysiological studies of reinnervation in ALS. In: Rowland LP (ed) Human motor neuron diseases. Raven Press, New York, pp 47–59
Stålberg E (1983) Macro EMG. Muscle Nerve 6:619–630
Stålberg E, Fawcett PRW (1982) Macro EMG in healthy subjects of different ages. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:870–878
Stålberg E, Thiele B (1975) Motor unit fibre density in the extensor digitorum communis muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38:874–880
Stålberg E, Trontelj JV (1979) Single fibre electromyography. Mirvalle Press, Old Woking, Surrey
Stålberg E, Schwartz MS, Trontelj JV (1975) Single fibre electromyography in various processes affecting the anterior horn cell. J Neurol Sci 24:403–415
Stålberg E, Hilton-Brown P, Rydin E (1986) Capacity of the motor neuron to alter its peripheral field. In: Dimitrijevic M, Kakulas B, Vrbova (eds) Restorative procedures in neuromuscular diseases. Karger, Basel, pp 237–253
Swash M, Schwartz MS (1982) A longitudinal study of changes in motor units in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Sci 56:185–197
Telerman-Toppet N, Coërs C (1978) Motor innervation and fiber type pattern in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Muscle Nerve 1:133–139
Thage O (1974) Quadriceps weakness and wasting. A neurological, electrophysiological and histological study. Fadls, Copenhagen
Wiechers DO, Hubbell SL (1981) Late changes in the motor unit after acute poliomyelitis. Muscle Nerve 4:524–528
Wohlfart G (1957) Collateral regeneration from residual motor nerve fibres in ALS. Neurology 7:124–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tackmann, W., Vogel, P. Fibre density, amplitudes of macro-EMG motor unit potentials and conventional EMG recordings from the anterior tibial muscle in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 235, 149–154 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314305
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314305