Abstract
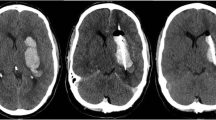
CT-stereotactic fibrinolysis is an effective alternative to surgical and conservative therapies for intracerebral hematoma. The method consists of stereotactically puncturing and partially evacuating the hematoma. After fibrinolysis using urokinase, the residual hematoma is completely evacuated through a catheter inserted in the cavity of the hematoma. The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia. Stereotactic methods are safer and less invasive than other methods. Since October 1985, a total of 85 patients have been treated with this method in the Department of Stereotaxy and Neuronuclear Medicine at the University of Freiburg Medical School. Although 25 patients died (29.4%) during the mean follow-up period of 20 months, only 16 (18.8%) died in the acute postoperative phase or within the first 60 days after evacuation. Eighteen patients (21.2%) had died six months after the operation. The quality of life of the 60 surviving patients, as measured on the Karnofsky Scale at follow-up, was very good to good in 70% and moderate in 23.3%. Only 6.7% of the patients were so disabled that they required special care and assistance or had to be placed in a nursing home. The long-term results are thus very encouraging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer LM, Th Auer, I Sayama: Indications for surgical treatment of cerebellar hemorrhage and infarction. Acta Neurochir 79 (1986) 74–79
Backlund E, M van Holst: Controlled subtotal evacuation of intracerebral hematomas by stereotactic technique. Surg Neurol 9 (1978) 99–101
Birg W, F Mundinger: Direct target point determination for stereotactic brain operations from CT data and the calculation of setting parameters for polar-coordinate stereotactic devices. Appl Neurophysiol 45 (1982) 387–395
Doi E, M Moriwaki, N Komai, M Iwamoto: Stereotactic evacuation of intracerebral hematomas. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 22 (1982) 461–467
Gänshirt H, R Keuler: Intracerebral Blutungen. Ursachen, Klinik, Verlauf, Spätprognose. Nervenarzt 51 (1980) 201–206
Higgins AC, BS Nashold: Stereotactic evacuation of large intracerebral haematomas. Appl Neurophysiol 43 (1980) 96–103
Higgins AC, BS Nashold: Modification of instruments for stereotactic evacuation of intracerebral haematoma. Technical note. Neurosurgery 7 (1980) 604–606
Higgins AC, BS Nashold, E Cosmann: Stereotactic evacuation of primary intracerebral haematomas — new instrumentation. Appl Neurophysiol 45 (1982) 438–442
Hondo H: CT-guided stereotactic evacuation of hypertensive intracerebral hematomas — “a new operative approach”. Exp Med (Tokushima) 30 (1983) 25–39
Janny P, I Papo, J Chazal, G Colnet, LC Barretto: Intracranial hypertension and prognosis in spontaneous intracerebral haematomas. A correlative study of 60 patients. Acta Neurochir 61 (1982) 181–186
Komai W, E Dot, H Moriwaki, E Nakai: Stereotactic evacuation of hypertensive thalamic hematomas using plaminogen activator (urokinase). Neurological Surgery 14 (Japan) (1986) 249–256
Matsumoto K, H Hondo: CT-guided stereotaxic evacuation of hypertensive intracerebral hematoma. J Neurosurg 61 (1984) 440–448
Mohadjer M: Combined CT-stereotactic method of evacuation and fibrinolysis of hypertensive intracranial haematomas. Haemostasis 18, Suppl 2 (1988) 180
Mohadjer M, E Ruh, DM Hiltl, H Neumüller, F Mundinger: CT-stereotactic evacuation and fibrinolysis of hypertensive intracranial haematoma. Fibrinolysis 2 (1988) 43–48
Mohadjer M, DF Braus, E Milios, A Myers, W Birg, F Mundinger: CT-stereotaktische Fibrinolyse bei spontanen intracerebralen Massenblutungen. Hämostaseologie 10 (1990) 39–44
Müke R, W Heienbrok, D Kühne: Spontane intracerebrale Hämatome. Neue Gesichtspunkte seit Einführung der Computertomographie. Ztb Neurochirurgie 39 (1978) 135–144
Mundinger F, W Birg: CT-stereotaxy in the clinical routine. Neurosurg Rev 7 (1984) 219–224
Niizuma H, T Otsuki, H Johkura, N Nakazato, J Suzuki: CT-guided stereotactic aspiration of intracerebral hematoma. Results of a hematoma-lysis method using urokinase. Appl Neurophys 48 (1985) 427–430
Niizuma H, Y Shimizu, T Yonemitsu, N Nakassato, J Suzuki: Results of stereotactic aspiration in 175 cases of putaminal hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 24 (1985) 814–819
Riechert T, F Mundinger: Beschreibung und Anwendung eines Zielgerätes für stereotaktische Hirnoperationen (2. Modell). Acta Neurochir 3 (1956) 308–337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohadjer, M., Braus, D.F., Myers, A. et al. CT-stereotactic fibrinolysis of spontaneous intracerebral hematomas. Neurosurg. Rev. 15, 105–110 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313504
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313504