Abstract
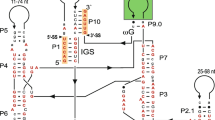
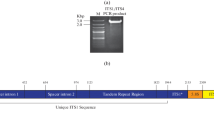
A 1 380-bp intervening sequence within the mitochondrial small subunit ribosomal RNA (mt SSU rRNA) gene of the fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum has been sequenced and identified as a group-I intron. This is the first report of an intron in the mt SSU rRNA gene. The intron shows close similarity in secondary structure to the subgroup-IC2 introns from Podospora (ND3i1, ND5i2, and COIi5) and Neurospora (ND5i1). The intron has an open reading frame (ORF) that encodes a putative protein of 420 amino acids which contains two copies of the LAGLI-DADG motif. The ORF belongs to a family of ORFs identified in Podospora (ND3i1, ND4Li1, ND4Li2, ND5i2, and COIi5) and Neurospora (ND5i1). The putative 420-aa polypeptide is also similar to a site-specific endonuclease in the chloroplast large subunit ribosomal RNA (LSU rRNA) gene of the green alga Chlamydomonas eugametos. In each clone of S. sclerotiorum examined, including several clones which were sampled over a 3-year period from geographically separated sites, all isolates either had the intron or lacked the intron within the mt SSU rRNA gene. Screening by means of Southern hybridization and PCR amplification detected the intron in the mt SSU rRNA genes of S. minor, S. trifoliorum and Sclerotium cepivorum, but not in other members of the Sclerotiniaceae, such as Botrytis anamorphs of Botryotinia spp., or in other ascomycetous and basidiomycetous fungi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410
Burke JM (1988) Molecular genetics of group-I introns: RNA structures and protein factors required for splicing—a review. Gene 73: 273–294
Burke JM, Belfort M, Cech TR, Davies RW, Schweyen RJ, Shub DA, Szostak JW, Tabak HF (1987) Structural conventions for group-I introns. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 7217–7221
Carbone I, Kohn LM (1993) Ribosomal DNA sequence divergence within internal transcribed spacer 1 of the Sclerotiniaceae. Mycologia 85: 415–427
Cech TR (1988) Conserved sequences and structures of group-I introns: building an active site for RNA catalysis—a review. Gene 73: 259–271
Collins RA (1988) Evidence of natural selection to maintain a functional domain outside of the ‘core’ in a large subclass of group-I introns. Nucleic Acids Res 16: 2705–2715
Cummings DJ, Domenico JM (1988) Sequence analysis of mitochondrial DNA from Podospora anserina. Pervasiveness of a class-I intron in three separate genes. J Mol Biol 204: 815–839
Cummings DJ, Domenico JM, Nelson J, Sogin ML (1989a) DNA sequence, structure, and phylogenetic relationship of the small subunit rRNA coding region of mitochondrial DNA from Podospora anserina. J Mol Evol 28: 232–241
Cummings DJ, Michel F, McNally KL (1989b) DNA sequence analysis of the 24.5-kilobase pair cytochrome oxidase subunit I mitochondrial gene from Podospora anserina: a gene with sixteen introns. Curr Genet 16: 381–406
Cummings DJ, McNally KL, Domenico JM, Matsuura ET (1990) The complete DNA sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Podospora anserina. Curr Genet 17: 375–402
Davies WR, Waring RB, Ray JA, Brown TA, Scazzocchio C (1982) Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature 300: 719–724
Dávila-Aponte JA, Huss VAR, Sogin ML, Cech TR (1991) A selfsplicing group-I intron in the nuclear pre-rRNA of the green alga, Ankistrodesmus stipitatus. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 4429–4436
De Bièvre C, Dujon B (1992) Mitochondrial DNA sequence analysis of the cytochrome oxidase subunit I and II genes, the ATPase9 gene, the NADH dehydrogenase ND4L and ND5 gene complex, and the glutaminyl, methionyl and arginyl tRNA genes from Trichophyton rubrum. Curr Genet 22: 229–234
De Jonckheere JF (1993) A group-I intron in the SSU rDNA of some Naegleria spp. demonstrated by polymerase chain reaction amplification. J Euk Microbiol 40: 179–187
DePriest PT, Been MD (1992) Numerous group-I introns with variable distributions in the ribosomal DNA of a lichen fungus. J Mol Biol 228: 315–321
De Wachter R, Neefs J-M, Goris A, Van de Peer Y (1992) The gene coding for small ribosomal subunit RNA in the basidiomycete Ustilago maydis contains a group-I intron. Nucleic Acids Res 20: 1251–1257
Embley TM, Dyal P, Kilvington S (1992) A group-I intron in the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene from Naegleria andersoni ssp. andersoni strain PPMFB-6. Nucleic Acids Res 20: 6411
Gauthier A, Turmel M, Lemieux C (1991) A group-I intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos encodes a double-strand endonuclease that cleaves the homing site of this intron. Curr Genet 19: 43–47
Gilbert DG (1990) LoopViewer, a Macintosh program for visualizing RNA secondary structure. Published electronically on the Internet, available via anonymous ftp to iubio. bio. indiana. edu.
Griffin DH (1992) Nucleic acids and nucleotides. In: Arora DK, Elander RP, Mukerji KG (eds) Handbook of applied mycology, vol 4: fungal biotechnology. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 445–473
Gutell RR, Weiser B, Woese CR, Noller HF (1985) Comparative anatomy of 16s-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 32: 155–216
Gutell RR, Noller HF, Woese CR (1986) Higher order structure in ribosomal RNA. EMBO J 5: 1111–1113
Hensgens LAM, Bonen L, De Haan M, Van der Horst G, Grivell LA (1983) Two intron sequences in the yeast mitochondrial COX1 gene: homology among URF-containing introns and strain-dependent variation in flanking exons. Cell 32: 379–389
Jaeger JA, Turner DH, Zuker M (1989) Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 7706–7710
Jaeger JA, Turner DH, Zuker M (1990) Predicting optimal and suboptimal secondary structure for RNA. In: Doolittle RF (ed) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 281–306
Kohli Y, Morrall RAA, Anderson JB, Kohn LM (1992) Local and trans-Canadian clonal distribution of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on canola. Phytopathology 82: 875–880
Kohli Y, Brunner LJ, Yoell H, Milgroom MG, Anderson JB, Morrall RAA, Kohn LM (in press) Clonal dispersal and spatial mixing in populations of the plant pathogenic fungus, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol Ecol
Kohn LM, Stasovski E, Carbone I, Royer J, Anderson JB (1991) Mycelial incompatibility and molecular markers identify genetic variability in field populations of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology 81: 480–485
Lambowitz AM, Belfort M (1993) Introns as mobile genetic elements. Annu Rev Biochem 62: 587–622
Leslie JF (1993) Fungal vegetative compatibility. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31: 127–151
Lipman DJ, Pearson WR (1985) Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science 227: 1435–1441
Michel F (1984) A maturase-like coding sequence downstream of the OXI2 gene of yeast mitochondrial DNA is interrupted by two GC clusters and a putative end-of-messenger signal. Curr Genet 8: 307–317
Michel F, Cummings DJ (1985) Analysis of class-I introns in a mitochondrial plasmid associated with senescence of Podospora anserina reveals extraordinary resemblance to the Tetrahymena ribosomal intron. Curr Genet 10: 69–79
Michel F, Westhof E (1990) Modeling of the three-dimensional architecture of group-I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol 216: 585–610
Michel F, Jacquier A, Dujon B (1982) Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie 64: 867–881
Mota EM, Collins RA (1988) Independent evolution of structural and coding regions in a Neurospora mitochondrial intron. Nature 332: 654–656
Neefs J-M, Van de Peer Y, De Rijk P, Chapelle S, De Wachter R (1993) Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res 21: 3025–3049
Nishida H, Blanz PA, Sugiyama J (1993) The higher fungus Protomyces inouyei has two group-I introns in the 18s rRNA gene. J Mol Evol 37: 25–28
Ragan MA, Bird CJ, Rice EL, Singh RK (1993) The nuclear 18s ribosomal RNA gene of the red alga Hildenbrandia rubra contains a group-I intron. Nucleic Acids Res 21: 3898
Sogin ML, Edman JC (1989) A self-splicing intron in the small subunit rRNA gene of Pneumocystis carinii. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 5349–5359
Stern S, Weiser B, Noller HF (1988) Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16s ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol 204: 447–481
Turmel M, Boulanger J, Schnare MN, Gray MW, Lemieux C (1991) Six group-I introns and three internal transcribed spacers in the chloroplast large subunit ribosomal RNA gene of the green alga Chlamydomonas eugametos. J Mol Biol 218: 293–311
Turmel M, Gutell RR, Mercier J-P, Otis C, Lemieux C (1993) Analysis of the chloroplast large subunit ribosomal RNA gene from 17 Chlamydomonas taxa: three internal transcribed spacers and 12 group-I intron insertion sites. J Mol Biol 232: 446–467
Van der Horst G, Inoue T (1993) Requirements of a group-I intron for reactions at the 3′ splice site. J Mol Biol 229: 685–694
Waring RB, Davies RW (1984) Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing—a review. Gene 28: 277–291
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 315–322
Wilcox LW, Lewis LA, Fuerst PA, Floyd GL (1992) Group-I introns within the nuclear-encoded small-subunit rRNA gene of three green algae. Mol Biol Evol 9: 1103–1118
Zolan ME, Pukkila PJ (1986) Inheritance of DNA methylation in Coprinus cinereus. Mol Cell Biol 6: 195–200
Zuker M (1989) On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science 244: 48–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Bertrand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carbone, I., Anderson, J.B. & Kohn, L.M. A group-I intron in the mitochondrial small subunit ribosomal RNA gene of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum . Curr Genet 27, 166–176 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313431
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313431