Abstract
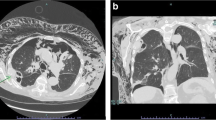
Pneumoperitoneum is most commonly caused by the perforation of a hollow viscus, in which case an emergency laparotomy is indicated. We report herein the case of a patient who, presented with the signs and symptoms of peritonitis, but who was found to have idiopathic pneumoperitoneum which was successfully managed by conservative treatment. A 70-year-old man presented with epigastric pain, nausea, and a severely distended and tympanitic abdomen. Abdominal examination revealed diffuse tenderness with guarding, but no rebound tenderness. He was febrile with leukocytosis and high C-reactive protein. Chest X-ray and abdominal computed tomography demonstrated a massive pneumoperitoneum without pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumortroperitoneum, or subcutaneous emphysema, and subsequent examinations failed to demonstrate perforation of a hollow viscus. Thus, a diagnosis of idiopathic pneumoperitoneum was made, and the patient was managed conservatively, which resulted in a successful outcome. This experience and a review of the literature suggest that idiopathic pneumoperitoneum is amenable to conservative management, even when the signs and symptoms of peritonitis are present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MaGlone PB, Vivion CG, Meir L (1966) Spontaneous pneumoperitoneum. Gastroenterology 51:393–398
Mason JM, Mason EM, Kesmodel KF (1946) Spontaneous pneumoperitoneum without peritonitis and without demonstrable cause. South Med J 39:620–623
Gantt CB Jr, Daniel WW, Hallenbeck GA (1977) Nonsurgical pneumoperitoneum. Am J Surg 134:411–414
Madura MJ, Craig RM, Shields TW (1982) Unusual causes of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum. Surg Gynecol Obstet 154:417–420
Van Gelder HM, Allen KB, Renz B, Sherman R (1991) Spontaneous pneumoperitoneum. A surgical dilemma. Am Surg 57:151–156
Hoover EL, Cole GD, Mitchell LS, Adams CZ Jr, Hassett J (1992) Avoiding laparotomy in nonsurgical pneumoperitoneum. Am J Surg 164:99–103
Gutkin Z, Iellin A, Meged S, Sorkine P, Geller E (1992) Spontaneous pneumoperitoneum without peritonitis. Int Surg 77:219–223
Ayres RW, Beeson CR, Scruggs JB Jr (1950) Idiopathic pneumoperitoneum. A review of the literature and report of one case. Am J Dig Dis 17:345–347
Zer M, Wolloch Y, Dintsman M (1978) “Spontaneous” pneumoperitoneum. Am J Proctol Gastroenterol Colon Rectal Surg 29:35–36, 38
Seaman WB (1977) The case of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum without peritonitis. Hosp Pract 12:105, 108
Nour S, Pereira NH, Mackinnon AE (1993) Pneumoperitoneum from a ruptured bronchus in a child. Br J Surg 80:212
Britt CI, Christoforidis AJ, Andrews NC (1961) Asymptomatic spontaneous pneumoperitoneum. Am J Surg 101:232–235
Kreel L (1986) Pneumoperitoneum. Postgrad Med 62:31–32
Steigman F, Singer HA (1936) Spontaneous pneumothorax simulating acute abdominal affections. Am J Med Sci 192:67–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tani, T., Shirai, Y., Sasagawa, M. et al. Conservative management of idiopathic pneumoperitoneum masquerading as peritonitis: Report of a case. Surg Today 25, 265–267 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311539
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311539