Summary
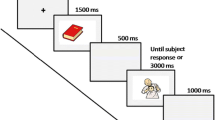
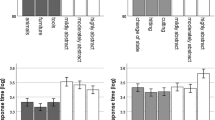
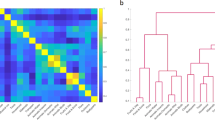
The study investigates the different contributions to semantic priming of two components of the semantic representation underlying a word. The two components are perceptually based information and conceptually based information. “Perceptual” information is based on physical attributes such as shape or color, while “conceptual” information consists of more abstract elements such as functional attributes. The question asked in this study was whether both components would produce an effect in semantic priming. Pairs of words either related because of a conceptual property (banana-apple), a perceptual property (ball-apple), or both because of a perceptual and conceptual property (cherry-apple) were presented as prime and target in a lexical decision and a word-naming task. The results showed independent contributions of perceptual and conceptual attributes to semantic priming.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antos SJ (1979) Processing facilitation in a lexical decision task. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 9:527–545
Becker CA (1980) Semantic context effects in visual word recognition: An analysis of semantic strategies. Mem Cognit 8:493–512
Becker CA, Killion TH (1977) Interaction of visual and cognitive effects in word recognition. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 3:389–401
Bower GH (1972) Mental imagery and associative learning. In: Gregg L (ed) Cognition in Learning and Memory. Wiley, New York
Carroll M, Kirsner K (1982) Context and repetition effects in lexical decision and recognition memory. J Verb Learn Verb Behav 21:55–69
Clark HH, Clark E (1977) Language and Psychology. Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich, New York, NY
Dallas M, Merikle PM (1976a) Response processes and semantic context effects. Bull Psychon Soc 8:441–444
Dallas M, Merikle PM (1976b) Semantic processing of non-attended visual information. Can J Psychol 30:15–21
Fischler I (1977) Associative facilitation without expectancy in a lexical decision task. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 3:18–26
Fischler I, Goodman GO (1978) Latency of associative activation in memory. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 4:455–470
Forster KI (1981) Priming and the effects of sentence and lexical context on naming time: Evidence for autonomous lexical processing. Quart J Exp Psychol 33a:465–495
Fowler CA, Wolford G, Slade R, Tassinary L (1981) Lexical access with and without awareness. J Exp Psychol Gen 7:123–134
de Groot AMB, Thomassen AJWM, Hudson PTW (1982) Associative facilitation of word recognition as measured from a neutral prime. Mem Cognit 10:358–370
Hoffmann J, Denis M, Ziessler M (1983) Figurative features and the construction of visual images. Psychol Res 45:39–54
Katz AN (1981) Knowing about the sensory properties of objects. Quart J Exp Psychol 33:39–49
Kieras D (1978) Beyond pictures and words: Alternative information processing models for imagery effects in verbal memory. Psych Bull 85:532–554
Kirsner K, Smith M (1974) Modality effects in word identification. Mem Cognit 2:637–640
Meyer DE, Schvaneveldt RW (1971) Facilitation in recognizing pairs of words: Evidence of a dependence between retrieval operations. J Exp Psychol 90:227–234
Meyer DE, Schvaneveldt RW, Ruddy MG (1975) Loci of contextual effects on visual word recognition. In: Rabbitt P, Dornic S (eds) Attention and Performance V. Academic Press, New York, NY
Neely JH (1977) Semantic priming and retrieval from lexical memory: Roles of inhibitionless spreading activation and limited capacity attention. J Exp Psychol Gen 106:226–254
Nelson K (1973) Structure and strategy in learning to talk. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development. 38(1–2), Serial No. 149
Nelson DL, Reed VS, McEvoy CL (1977) Learning to order pictures and words: A model of sensory and semantic encoding. J Exp Psychol Hum Learn Mem 3:485–497
Parkin AJ (1982) Phonological recoding in lexical decision: Effects of spelling-to-sound regularity depend on how regularity is defined. Mem Cognit 10:43–53
Scarborough DL, Cortese C, Scarborough H (1977) Frequency and repetition effects in lexical memory. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perf 3:1–17
Scarborough DL, Gerard L, Cortese C (1979) Accessing lexical memory: The transfer of word repetition effects across task and modality. Mem Cognit 7:3–12
Smith EE, Medin DL (1981) Categories and Concepts. Harvard University Press, Cambridge Mass
Smith EE, Shoben EJ, Rips LJ (1974) Structure and process in semantic memory: A featural model for semantic decisions. Psychol Review 81:214–241
Sperber RD, McCauley C, Ragain RD, Weil, CM (1979) Semantic priming effects on picture and word processing. Mem Cognit 7:339–345
Warren RE (1977) Time and the spread of activation in memory. J Exp Psychol Hum Learn Mem 3:458–466
West RF, Stanovich KE (1982) Source of inhibition in experiments on the effect of sentence context on word recognition. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cognit 5:385–399
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by a grant from the Dutch Organization for the Advancement of Pure Research (ZWO). All three authors are “senior” authors and have contributed to all parts of the project.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreuder, R., Flores d'Arcais, G.B. & Glazenborg, G. Effects of perceptual and conceptual similarity in semantic priming. Psychol. Res 45, 339–354 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309710
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309710