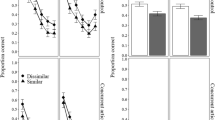
Summary
Paivio's dual coding hypothesis proposes that the retention of pictures and concrete words can be mediated by both visual and verbal codes. The present study investigates the time course of the formation and utilization of the visual and verbal codes of pictures and words in a “same”-“different” RT-task involving physical (Picture-Picture; Word-Word) and semantic (Word-Picture; Picture-Word) matches. The ISI was varied between 50 and 2000 msec. The four matching conditions were either constant within a block of trials (Exp. I) or partially mixed (Exp. II). Exp. I showed that at long ISIs (>500 msec.) the comparisons in all matching conditions were based on visual codes; Ss either retained the visual code of the first stimulus (physical matches) or generated the visual code of the expected second stimulus (semantic matches). Under the conditions of Exp. II the visual code of the first stimulus was not actively retained. Except for very short ISIs (≤250 msec.) only a single code, the verbal code was used for comparisons of all stimulus combinations. Paivio's dual code hypothesis thus must be modified to account for code utilization in a matching task. The comparison between “same” RTs of the physical match conditions from both experiments suggests that two stages of visual storage were involved in the task, viz. the visual sensory store for ISIs ≤250 msec. and the visual short-term store for ISIs ≥ 500 msec.
Zusammenfassung
In der „dual coding“ Hypothese von Paivio wird die Annahme gemacht, daß das Behalten von Bildern und konkreten Worten durch visuelle und verbale Codes vermittels werden kann. Die vorliegende Arbeit untersucht den zeitlichen Verlauf der Entstehung und Verwendung des visuellen und verbalen Codes von Bildern und Worten in einem „gleich“-„verschieden“ Paarvergleich RZ-Experiment, in dem „physische“ (Bild-Bild; Wort-Wort) und „semantische“ (Wort-Bild; Bild-Wort) Vergleiche zu leisten sind. Das Intervall zwischen den beiden Reizen wurde zwischen 50 und 2000 msec variiert. Die vier Vergleichsbedingungen wurden entweder in Versuchsdurchgängen getrennt (Exp. I) oder teilweise gemischt (Exp. II) geboten. Nach den Ergebnissen von Exp. I beruhten die Vergleiche bei längeren Intervallen (>500 msec) unter allen Bedingungen auf dem visuellen Code; die Vpn behielten entweder den visuellen Code des ersten Reizes („physische“ Vergleiche) oder erzeugten den visuellen Code des zu erwartenden zweiten Reizes („semantische“ Vergleiche). Unter den Bedingungen von Exp. II wurde der visuelle Code des ersten Reizes nicht aktiv behalten. Mit der Ausnahme sehr kurzer Intervalle (≤250 msec) beruhten die Vergleiche in allen Bedingungen ausschließlich auf dem verbalen Code. Damit muß Paivio's Hypothese modifiziert werden, wenn sie auf die Verwendung von Codes in einem Paarvergleich Experiment angewendet werden soll. Ein Vergleich der „gleich“ RZn von den „physischen“ Vergleichsbedingungen von Exp. I und II legt die Annahme nahe, daß zwei Stufen der visuellen Speicherung beim Vergleich eine Rolle spielen, nämlich der visuelle sensorische Speicher für Intervalle ≤250 msec und der visuelle Kurzzeit-speicher für Intervalle ≥ 500 msec.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, R. C., Shiffrin, R. M.: Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In: Spence, K. W., Spence, J. T. (Eds.): The psychology of learning and motivation: Advances in research and theory, Vol. II. New York: Academic Press 1968
Averbach, E., Coriell, A. S.: Short-term memory in vision. Bell Systems Technical Journal 40, 309–328 (1961)
Dick, A. O.: Perception as information processing: A stage analysis. In: Eliot, J. (Ed.): Human development and cognitive processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston 1971
Eriksen, C. W., Collins, J. F.: Some temporal characteristics of visual pattern perception. J. exp. Psychol. 74, 476–484 (1967)
Glanzer, M., Clark, W. H.: The verbal-loop hypothesis: Conventional figures. Amer. J. Psychol. 77, 621–626 (1964)
Haber, R. N., Standing, L. G.: Direct measures of short-term visual storage. Quart. J. exp. Psychol. 21, 43–54 (1969)
Kroll, N. E. A., Parks, T., Parkinson, S. R., Bieber, S. L., Johnson, A. L.: Short-term memory while shadowing: Recall of visually and of aurally presented letters. J. exp. Psychol. 85, 220–224 (1970)
Mackworth, J. F.: The visual image and the memory trace. Canad. J. Psychol. 16, 55–59 (1962)
Mackworth, J. F.: The duration of the visual image. Canad. J. Psychol. 17, 62–81 (1963)
Mackworth, J. F.: Some models of the reading process: learners and skilled readers. Reading Res. Quart. 7, 701–733 (1972)
Mitchell, D. C.: Short-term visual memory and pattern masking. Quart. J. exp. Psychol. 24, 394–405 (1972)
Nickerson, R. S.: Response time to the second of two successive signals as a function of absolute and relative duration of the intersignal interval. Percept. mot. Skills 21, 3–10 (1965)
Nickerson, R. S.: Psychological refractory phase and the functional significance of signals. J. exp. Psychol. 73, 303–312 (1967)
Nickerson, R. S.: Response time to the second of two signals following varied vs. constant intersignal intervals. Percept. Psychophys. 4, 78–80 (1968)
Nickerson, R. S.: Note on “same”-“different” response times. Percept. mot. Skills 27, 565–566 (1968)
Nickerson, R. S.: Binary classification reaction time: A review of some studies of human information processing capabilities. Psychon. Monogr. Suppl. Vol. 4, No. 17 (Whole No. 65) (1972)
Paivio, A.: Mental imagery in associative learning and memory. Psychol. Rev. 76, 241–263 (1969)
Paivio, A.: Imagery and verbal processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston 1971
Paivio, A., Yuille, J. C., Madigan, S.: Concreteness, imagery and meaningfulness values for 925 nouns. J. exp. Psychol. Monogr. Suppl. 76, (1 Pt. 2) (1968)
Paivio, A., Csapo, K.: Concrete-image and verbal memory codes. J. exp. Psychol. 80, 279–285 (1969)
Phillips, W. A., Baddeley, A. D.: Reaction time and visual short-term memory. Psychon. Sci. 22, 73–74 (1971)
Posner, M. I., Boies, S. J., Eichelman, W. H., Taylor, R. L.: Retention of visual and name codes of single letters. J. exp. Psychol. Monogr. 79, (1 Pt. 2) (1969)
Posner, M. I., Keele, S. W.: Decay of visual information from a single letter. Science 158, 137–139 (1967)
Posner, M. I., Konick, A. F.: Short-term retention of visual and kinesthetic information. Organiz. Behav. Hum. Perf. 1, 71–86 (1966)
Scheerer, E.: Simultane und sukzessive Informationsverarbeitung bei der Identifikation visueller Reizmuster. Ph. D. Dissertation, Bochum 1970
Smith, M.: Theories of the psychological refractory period. Psychol. Bull. 67, 202–213 (1967)
Sperling, G. A.: A model for visual memory tasks. Hum. Factors 5, 19–31 (1963)
Thorndike, E. L., Lorge, I.: The teacher's word book of 30,000 words. New York: Bureau of Publications, Teachers College, 1944
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study is based on the author's doctoral dissertation submitted to the University of Rochester, Rochester, N.Y., U.S.A. The research was supported by a grant from the U.S. Public Health Service (MH 10753) and by a grant from the Office of Education (OEG-0-72-0671), both to Dr. R. N. Haber. The author wishes to thank the members of her advisory committee, Dr. R. N. Haber, Dr. A. O. Dick, and Dr. H. K. Beller for their helpful comments and criticism.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheerer-Neumann, G. Formation and utilization of the visual and verbal codes of pictures and words. Psychol. Res 37, 81–106 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309080
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309080