Summary
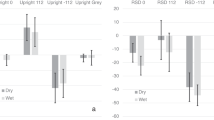
The dependence of the subjective vertical (SV, the angle β between a subjective vertical line and body median plane) on the gravity vertical (body tilt position, angle α) and on the ‘optical vertical’ (i.e., a field of parallel lines seen as background to the line to be adjusted) was investigated. The SV was measured under ‘dry’ and ‘wet’ conditions at different degrees of body tilt attained in either clockwise (CW) or counterclockwise (CCW) progression.
The measured difference in β between field-of-lines left and right of the line is smallest at the upright position (α=O°) and largest at α=150°/165°. All body positions show a β-difference between CW and CCW attainment (hysteresis), this too being least at upright and greatest at inverted body positions.
These results, and changes of β with test time, are discussed relative to the hypothesis that efficiency of the statolith organs decreases with body tilt increase, favouring increase of interference of somatoreceptors and the optical reference.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asch, S.E., Witkin, H.A.: Studies in Space Orientation I. Perception of the upright with displaced visual fields. J. Exp. Psychol. 38, 325–337 (1948a)
Asch, S.E., Witkins, H.A.: Studies in space orientation II. Perception of the upright with displaced visual fields and body titled. J. Exp. Psychol. 38, 455–477 (1948b)
Bischof, N.: Stellungs-, Spannungs- und Lagewahrnehmung. In: Handbuch der Psychologie, Bd 1; 409–497. Göttingen: Hogreve 1966
Bischof, N., Scheerer, E.: Systemanalyse der optisch-vestibulären Interaktion bei der Wahrnehmung der Vertikalen. Psychol. Forsch. 34, 99–181 (1970)
Boring, E.G.: Sensation and perception in the history of experimental psychology. N.Y., London: Appleton-Century-Crofts 1942
Brown, J.L.: Orientation to the vertical during water immersion. Aerospace Med. 32, 209–217 (1961)
Clark, B., Graybiel, A.: Perception of the postural vertical following prolonged bodily tilt in normals and subjects with labyrinthine defects. Acta-oto-laryng. 58, 143–148 (1964)
Day, R.H., Wade, N.J.: Visual spatial after-effect from prolonged head tilt. Science 154, 1201–1202 (1966)
Dichgans, J., Brandt, Th, Held, R.: The role of vision in gravitational orientation. Fortschr. Zool. 23, 255–261 (1975)
Fujita, Y., Rosenberg, J., Segundo, J.P.: Activity of cells in the lateral vestibular nucleus as a function of head position. J. Physiol. 196, 1–18 (1968)
Gibson, J.J., Mowrer, O.H.: Determinants of the perceived vertical and horizontal. Psychol. Rev. 45, 300–323 (1938)
Kleint, H.: Versuche über die Wahrnehmung. Z. Psychol. 138, 1–34 (1936)
Koffka, K.: Principles of Gestalt Psychology. New York: Harcourt 1935
Lechner-Steinleitner, S.: Interaction of labyrinthine and somatoreceptor imputs as determinants of the subjective vertical. Psychol. Res. 40, 65–76 (1978)
Lechner-Steinleitner, S., Schöne, H.: Hysteresis in orientation to the vertical (the effect of time of preceding tilt on the subjective vertical). In: Vestibular mechanism in health and disease, J.D. Hood (ed.), pp. 326–371. London, New York: Academic Press 1978
Lowenstein, O.E.: Comparative morphology and physiology. In: Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VI/1, pp 75–116 Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1974
Löwenstein, O.E., Roberts, T.D.M.: The equilibrium function of the otolith of the thornback ray. J. Physiol. 110, 392–415 (1949)
Nelson, J.G.: Effect of water immersion and body position upon perception of the gravitational vertical. Aerospace Med. 39, 806–811 (1968)
Nyborg, H.: Light intensity and perception of the vertical. Scand. J. Psychol. 13, 314–326 (1972)
Precht, W.: Neuronal operations in the vestibular systems. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1978
Ross, H.E., Crickman, S.D., Sills, N.V., Owen, P.E.: Orientation to the vertical in free divers. Aerospace Med. 40, 728–732 (1969)
Schöne, H.: On the role of gravity in human spatial orientation. Aerospace Med. 35, 746–772 (1964)
Schöne, H.: The ‘weight’ of the gravity organs signal in the control of perceptual and reflex type orientation at different body positions. Fortschr. Zool. 23, 1, 274–285 (1975)
Schöne, H., Lechner-Steinleitner, S.: The effect of preceding tilt on the perceived vertical. Acta Otolaryngol, 85, 68–73 (1978)
Schöne, H., Udo de Haes, H.: Space orientation in humans with special reference to the interaction of vestibular, somesthetic and visual inputs. Biokybernetik III, Mat. 2. Internat. Sympos. Biokyb., 172–191. Jena: VEB Fischer 1971
Udo de Haes, H.: Interaction between visual and gravireceptor stimulation with respect to the apparent vertical. Thesis, Leiden (1970)
Wade, N.J.: Visual orientation during and after lateral head, body and trunk tilt. Percept. Psychophys 3, 215–219 (1968)
Wade, N.J.: The effect of stimulus line variation on visual orientation with head upright and tilted. Aust. J. Psychol. 21, 177–185 (1969a)
Wade, N.J.: The effect of water immersion on perception of the visual vertical. Br. J. Psychol. 64, 3, 351–361 (1973)
Wertheimer, M.: Experimetelle Studien über das Sehen von Bewegung. Z. Psychol. 61, 161–265 (1912)
Witkin, H.A., Asch, S.E.: Studies in space orientation. III. Perception of the upright in the absence of a visual field. J. Exp. Psychol. 38, 603–614 (1948c)
Witkin, H.A., Asch, S.E.: Studies in space orientation. IV. Further experiments on the perception of the upright with displaced visual field. J. Exp. Psychol. 38, 762–782 (1948d)
Young, L.R., Oman, C.M., Dichgans, J.M.: Influence of head orientation on visually induced pitch and roll sensation. Aviat. Space and environm. Med. 264–268 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lechner-Steinleitner, S., Schöne, H. The subjective vertical under ‘dry’ and ‘wet’ conditions at clockwise and counterclockwise changed positions and the effect of a parallel-lined background field. Psychol. Res 41, 305–317 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308876
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308876