Abstract
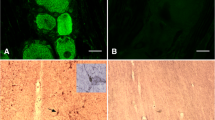
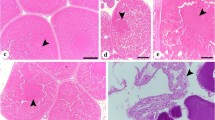
Luteinizing hormone beta (LHβ) and follicle stimulating hormone beta (FSHβ) subunits and their mRNAs were studied in the ram pars tuberalis following different seasonal (winter vs summer) and experimental (intact vs castrated animals) conditions. Hormone-containing cells were identified by immunohistochemistry, and mRNAs for LHβ and FSHβ by in situ hybridization using homologous double-stranded 35S-cDNAs. The labelling was quantified by image analysis. Immunohistochemical staining showed that cells containing LHβ and FSHβ were localized mainly in the ventral part of the pars tuberalis but that, in the summer, additional LHβ-containing cells were present in the dorsal part in intact rams. On the other hand, LHβ-mRNA labelling was found in the whole pars tuberalis in wethers but only in the ventral part in intact rams. The magnitude of LHβ-mRNA labelling was significantly greater in summer than in winter rams, and in castrated than in intact animals (P<0.001). However, the number of labelled cells was found to be the greatest in the winter (P<0.001) and was not affected by castration. FSHβ-mRNA expression was similar to that of LHβ-mRNA except that the level and extent were considerably lower. Thus, our results show an increase in the magnitude of gonadotropin β subunit-mRNA in the summer and following castration; this increase appears to involve the entire pars tuberalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Childs GV, Lloyd JM, Unabia G, Gharib SD, Wierman ME, Chin WW (1987) Detection of luteinizing hormone β messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) in individual gonadotropes after castration: use of a new in situ hybridization method with a photobiotinylated complementary RNA probe. Mol Endocrinol 1:926–932
Corbani M, Counis R, Starzec A, Jutisz M (1984) Effect of gonadectomy on pituitary levels of mRNA encoding gonadotropin subunits and secretion of luteinizing hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol 35:83–87
Courot M, Hochereau-de Reviers MT, PisseletC, Kilgour RJ, Dubois MP, Sairam MR (1984) Effect of passive immunization against βFSH on spermatogenesis in the ram. In: Courot M (ed) The male in farm animal reproduction. Nijhoff, Dordrecht, Boston, pp 75–78
Dacheux F, Dubois MP (1976) Ultrastructural localization of prolactin, growth hormone and luteinizing hormone by immunocytochemical techniques in the bovine pituitary. Cell Tissue Res 174:245–260
D'Angelo-Bernard G, Moumni M, Jutisz M, Counis R (1990) Cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for the precursor of the beta subunit of ovine luteinizing hormone. Nucleic Acids Res 18:2175
Dellmann HD, Stoeckel ME, Hindelang-Gertner C, Porte A, Stutinsky F (1974) A comparative ultrastructural study of the pars tuberalis of various mammals, the chicken and the newt. Cell Tissue Res 148:313–329
Garrel G, Lerrant Y, Ribot G, Counis R (1993) Messenger ribonucleic acids for α and β isoforms of cyclic adenosine 3′5′-monophosphate dependent protein kinase subunits present in the anterior pituitary. Regulation of RIIβ and Cα gene expression by the cyclic nucleotide and phorbol ester. Endocrinology 133:1010–1019
Gharib SD, Bowers SM, Need LR, Chin WW (1986) Regulation of rat luteinizing hormone subunit messenger ribonucleic acids by gonadal steroid hormones. J Clin Invest 77:582–589
Gharib SD, Wierman ME, Badger TM, Chin WW (1987) Sex steroid hormone regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone subunit messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) levels in the rat. J Clin Invest 80:294–299
Haisenleder DJ, Khoury S, Zmeili SM, Papavasiliou S, Ortolano GA, Dee C, Duncan JA, Marshall JC (1987) The frequency of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion regulates expression of α and luteinizing hormone β-subunit messenger ribonucleic acids in male rats. Mol Endocrinol 1:834–838
Hegarty CM, Jonassen JA, Bittman EL (1990) Pituitary hormone gene expression in male golden hamsters: interactions between photoperiod and testosterone. J Neuroendocrinol 2:567–573
Lehman MN, Karsch FJ (1993) Do gonadotropin-releasing hormone, tyrosine hydroxylase-, and β-endorphin-immunoreactive neurons contain estrogen receptors? A double-label immunocytochemical study in the Suffolk ewe. Endocrinology 133:876–886
Leung K, Kaynard AH, Negrini BP, Kim KE, Maurer RA, Landefeld D (1987) Differential regulation of gonadotropin subunit messenger ribonucleic acids by gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse frequency in ewes. Mol Endocrinol 1:724–728
Moumni M (1990) Construction de cDNA pour la sous-unité beta de l'hormone folliculo-stimulante chez le rat et le mouton et étude de la régulation de l'expression du gène. Thesis. Paris-Sud University, Orsay, France
Ortavant R, Daveau A, Garnier J, Pelletier J, Reviers MM de, Terqui M (1982) Diurnal variation in release of LH and testosterone in the ram. J Reprod Fertil 64:347–353
Papavasiliou SS, Zmeili S, Herbon L, Duncan-Weldon J, Marshall JC, Landefeld TD (1986) α and luteinizing hormone β messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) of male and female rats after castration: quantitation using an optimized RNA dot blot hybridization assay. Endocrinology 119:691–698
Pelletier J, Ortavant R (1970) Influence du photopériodisme sur les activités sexuelle, hypophysaire et hypothalamique du bélier Ile-de-France. In: Benoit J, Assenmacher I (eds) La photorégulation de la reproduction chez les oiseaux et les mammifères. CNRS, Paris, 172:483–495
Pelletier J, Ortavant R (1975) Photoperiodic control of LH release in the ram. II. Light-androgens interaction. Acta Endocrinol 78:435–441
Pelletier J, Counis R, Reviers MM de, Tillet Y (1992) Localization of luteinizing hormone β-mRNA by in situ hybridization in the sheep pars tuberalis. Cell Tissue Res 267:301–306
Saade G, London DR, Lalloz MRA, Clayton RN (1989) Regulation of LH subunit and prolactin mRNA by gonadal hormone in mice. J Mol Endocrinol 2:213–224
SAS (1992) SAS/STAT User's Guide. 4th edn. SAS Institute, Cary, N. C.
Tillet Y, Pelletier J, Tramu G, Reviers MM de (1990) The sheep pars tuberalis: an immunohistochemical study. Demonstration of the presence of glycoprotein and lipoprotein hormones. Histochemistry 94:403–408
Watanabe YG (1986) A comparative in vitro study on LHRH responsiveness of LH cells of the pars tuberalis and pars distalis. Cell Tissue Res 245:369–375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelletier, J., Counis, R., de Reviers, M.M. et al. Changes in LHβ-gene and FSHβ-gene expression in the ram pars tuberalis according to season and castration. Cell Tissue Res 281, 127–133 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307966
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307966