Abstract
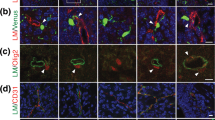
Changes in extracellular matrix composition and/or organisation, and in particular in the ratio of axonal growth-promoting components such as laminin to growth-inhibiting molecules, could contribute to the degenerative changes observed in the innervation of some peripheral tissues in old age. We have investigated this issue by evaluating laminin content or accessibility at various locations on blood vessels where we had previously studied age-related alterations in innervation density. We have employed a morphological approach, measuring laminin immunoreactivity by a densitometric application of confocal microscopy, because more conventional biochemical techniques would have been unable to distinguish specific, localized changes in laminin at sites accessible to nerves from heterogeneous changes in other areas of the vessel wall, such as the endothelial basal lamina. We found that in 24-month-old rats laminin immunoreactivity is decreased by 50% at the medial-adventitial border in association with the outer layer of smooth muscle cells, where a parallel decrease is observed in innervation density. Axonal terminals were shown to have access to laminin in this region of the blood vessel wall by double staining with laminin and a general neuronal marker. Changes in laminin immunore-activity were region-specific on the same blood vessel, thus excluding the possibility of a generalized decrease in immunoreactivity in old age. For example, in the basilar artery intensity of laminin immunoreactivity decreased in old age at the medial-adventitial border, but showed no change in endothelial cell basal lamina and in the adventitia. Moreover, we performed in oculo transplants of blood vessels displaying differences in laminin immunoreactivity and found that the density of innervation correlated with the intensity of laminin staining, thus lending further support to the hypothesis that laminin might play a role in nerve fibre atrophy in old age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews TJ, Cowen T (1991) Target-specific changes in autonomic nerve fibres in old age. Eur J Neurosci [Suppl] 4:187
Barde Y-A (1989) Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron 2:1525–1534
Baron-Van Evercooren A, Kleinman HK, Ohno S, Marangos P, Schwartz JP, Dubois-Dalq ME (1982) Nerve growth factor, laminin and fibronectin promote neurite growth in human fetal sensory ganglion cultures. J Neurosci Res 8:179–193
Bignami A, Chi N, Dahl D (1984) Laminin in rat sciatic nerve undergoing Wallerian degeneration. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 43:94–103
Bixby JL (1992) Diversity of axonal growth-promoting receptors and regulation of their function. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2:66–69
Bixby JL, Harris WA (1991) A comprehensive review of the known axonal growth-promoting molecules and transduction mechanisms. Annu Rev Cell Biol 7:117–159
Chaldakov GN, Andrews TJ, Burnstock G, Cowen T (1992) An ultrastructural study of ageing perivascular nerves and mast cell of the rat: accumulations of neurofilaments and muscle basal lamina in old age. Neurosci Letts [Suppl] 42:S28
Cowen T, Haven AJ, Wen Qin C, Gallen DD, Franc F, Burnstock G (1982) Development and ageing of perivascular adrenergic nerves in the rabbit. A quantitative fluorescence histochemical study using image analysis. J Auton Nerv Syst 5:317–336
Cowen T, Haven AJ, Burnstock G (1985) Pontamine sky blue: a counterstain for background autofluorescence in fluorescence and immunofluorescence histochemistry. Histochemistry 82:205–208
Cowen T, Alafaci C, Crockard HA, Burnstock G (1986) 5-HT-containing nerves to major cerebral arteries of the gerbil originate in the superior cervical ganglion. Brain Res 384:51–59
Curtis I de (1991) Neuronal interactions with the extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol 3:824–831
Dhall U, Cowen T, Haven AJ, Burnstock G (1986) Perivascular noradrenergic and peptide-containing nerves show different patterns of change during development and ageing in the guinea-pig. J Auton Nerv Syst 16:109–126
Dodd J, Jessell TM (1988) Axon guidance and the patterning of neuronal projection in vertebrates. Science 242:692–699
Edelman GM (1984) Modulation of cell adhesion during induction, histogenesis, and perinatal development of the nervous system. Ann Rev Neurosci 7:339–377
Edgar D (1989) Neuronal laminin receptors. TINS 12:248–251
Edgar D (1990) The expression and interactions of laminin in the developing nervous system. Cell Diff Develop 32:377–382
Edgar D, Thoenen H (1982) Modulation of NGF-induced survival of chick sympathetic neurons by contact with a conditioned medium factor bound to the culture substrate. Dev Brain Res 5:89–92
Edgar D, Timpl R, Thoenen H (1984) The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite out-growth and neuronal survival. EMBO J 3:1463–1468
Edgar D, Timpl R, Thoenen H (1988) Structural requirements for the stimulation of neurite outgrowth by two variants of laminin and their inhibition by antibodies. J Cell Biol 1069:1299–1306
Engvall E, Earwicker D, Haaparanta T, Ruoslahti E, Sanes JR (1990) Distribution and isolation of four laminin variants; tissue restricted distribution of heterotrimers assembled from five different subunits. Cell Regul 1:731–740
Ernsberger U, Edgar D, Rohrer H (1989) The survival of early chick sympathetic neurons in vitro is dependention a suitable substrate but independent of NGF. Develop Biol 135:250–262
Frolkis VV (1982) Ageing and Life-Prolonging Processes. Springer, Wien New York
Gavazzi I, Cowen T (1993) Axonal regeneration from rat sympathetic ganglia transplanted in oculo is not impaired by age. Exp Neurol 122:57–64
Gavazzi I, Andrews TJ, Thrasivoulou C, Cowen T (1992) Influence of target tissues on their innervation in old age: a transplantation study. Neuroreport 3:717–720
Gordon-Weeks PR, Giffin N, Weekes CS E, Barben C (1989) Transient expression of laminin immunoreactivity in the developing rat hippocampus. J Neurocytol 18:451–463
Heaton MB (1989) Influence of laminin on the responsiveness of early chick embryo neural tube neurons to nerve growth factor. J Neurosci Res 22:390
Jenner CS, Gavazzi I, Gu Xiao Song, Cowen T (1994) Loss of responsiveness of ageing sympathetic neurons in vitro to laminin and NGF. Eur J Neurosci [Suppl] 7:185
Jucker M, Bialobok P, Hagg T, Ingram DK (1992) Laminin immunohistochemistry in brain is dependent on method of tissue fixation. Brain Res 586:166–170
Kalcheim C, Barde Y-A, Thoenen H, Le Douarin NM (1987) In vivo effect of brain/derived neurotrophic factor on the survival of the developing dorsal root ganglion cells. EMBO J 6: 2871–2873
Keller A, Williams R, Vahaviolos J, Auffray C, Rush RA (1990) Immunohistochemical localisation of nerve growth factor in a subpopulation of chick spinal ganglion neurons. J Neurosci Res 27:136
Krum JM, More NS, Rosenstein JM (1991) Brain angiogenesis: variations in vascular basement membrane glycoprotein immunoreactivity. Exp Neurol 111:152–165
Kuchel GA, Zigmond RE (1991) Functional recovery and collateral neuronal sprouting examined in young and aged rats following a partial neural lesion. Brain Res 540:195–203
Kuecherer-Ehret A, Graeber MB, Edgar D, Thoenen H, Kreutzberg GW (1990a) Immunoelectron microscopic localization of laminin in normal and regenerating mouse sciatic nerve. J Neurocytol 19:101–109
Kuecherer-Ehret A, Pottgiesser J, Kreutzberg GW, Thoenen H, Edgar D (1990b) Developmental loss of laminin from the interstitial extracellular matrix correlates with decreased laminin gene expression. Development 110:1285–1293
Laurie GW, Leblond CP, Inoue S, Martin GR, Chung A (1984) Fine structure of glomerular basement membrane and immunolocalization of five basement membrane components to the lamina densa (basal lamina) and its extensions in both glomeruli and tubules of the rat kidney. Am J Anat 169:463–481
Letourneau PC, Madsen AM, Palm SL, Furcht LT (1988) Immunoreactivity for laminin in the developing ventral longitudinal pathway of the brain. Dev Biol 125:135–144
Madri JA, Roll FJ, Furthmayr H, Foidart JM (1980) Ultrastructural localization of fibronectin and laminin in the basement membrane of the murine kidney. J Cell Biol 3:57–85
Martin GR, Timpl R (1987) Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol 3:57–85
Martinez-Hernandez A, Chung AE (1984) The ultrastructural localization of two basement membrane components: entactin and laminin in rat tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 32:289–298
Olson L, Malmfors T (1970) Growth characteristics of adrenergic nerves in the adult rat. Acta Phys Scand [Suppl] 348:1–111
Purves D (1988) Body and Brain, A Trophic Theory of Neural Connections. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Purves D, Voyvodic JT, Harris L, Pomeroy SL (1990) Dynamic Aspects of Innervation in the Peripheral Nervous System of Adult Mammals. In: Edelman GM, Gall WE, Cowan WM (eds) Signal and Sense. Local and Global Order in Perceptual Maps. Wiley, New York, pp 589–605
Reichardt LF, Tomaselli KJ (1991) Extracellular matrix molecules and their receptors: functions in neuronal development. Annu Rev Neurosci 14:531–570
Rossino P, Gavazzi I, Timpl R, Aumailley M, Abbadini M, Giancotti F, Silengo L, Marchisio PC, Tarone G (1990) Nerve growth factor induces increased expression of a laminin-binding integrin in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Exp Cell Res 189:100–108
Sanes JR (1989) Extracellular matrix molecules that influence neural development. Ann Rev Neurosci 12:491–516
Sanes JR, Engvall E, Butkowski R, Hunter DD (1990) Molecular heterogeneity of basal laminae: isoforms of laminin and collagen IV at the neuromuscular junction and elsewhere. J Cell Biol 111:1685–1699
Santer RM (1982) Fluorescence histochemical observations on the adrenergic innervation of the cardiovascular system in the aged rat. Brain Res Bull 9:667–672
Siironen J, Sandberg M, Vuorinen V, Roytta M (1992) Laminin-b1 and collagen type-IV gene expression in transected peripheral nerve — reinnervation compared to denervation. J Neurochem 59:2184–2192
Thompson RJ, Doran JF, Jackson P, Dhillon AP, Rode J (1983) PGP 9.5—a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res 278:224–228
Timpl R (1989) Structure and biological activity of basement membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem 180:487–502
Voyvodic JT (1989) Target size regulates calibre and myelination of sympathetic axons. Nature 342:430–433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavazzi, I., Boyle, K.S., Edgar, D. et al. Reduced laminin immunoreactivity in the blood vessel wall of ageing rats correlates with reduced innervation in vivo and following transplantation. Cell Tissue Res 281, 23–32 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307955
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307955