Summary
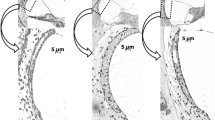
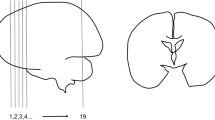
The topographic distribution of subependymal basement membranes of the ventricular system of the brain has been studied by light and electron microscopy in rabbits. The wall of the whole ventricular system contains numerous basement membranes forming labyrinths directed at the ventricle. A period-acid-bisulfit-aldehydthionine-method (Specht) permits to find the labyrinths lightmicroscopically, while they can be identified by electron microscopy. The results were recorded in “ventricular maps”.
Zusammenfassung
Die topographische Verteilung der subependymalen Basalmembranlabyrinthe im Ventrikelsystem des Kaninchengehirnes wurde licht- und elektronenmikroskopisch untersucht. Die Wand des gesamten Ventrikelsystems enthält zahlreiche Basalmembranen, die ventrikelwärts Labyrinthe bilden. Die Perjodsäure-Bisulfit-Aldehydthionin-Methode (Specht) ermöglicht es, diese Labyrinthe lichtmikroskopisch aufzufinden; sie können elektronenmikroskopisch identifiziert werden. Die Ergebnisse wurden in „Ventrikelkarten“ aufgezeichnet.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Andres, K. H.: Der Feinbau des Subfornikalogranes vom Hund. Z. Zellforsch. 68, 445–473 (1965).
Barer, R., Lederis, K.: Ultrastructure of the rabbit neurohypophysis with special reference to the release of hormones. Z. Zellforsch. 75, 201–239 (1966).
Brightman, M. W.: The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments. I. Ependymal distribution. J. Cell Biol. 26, 99–123 (1965).
Csillik, B., Földi, M.: Severe alterations in myelin structure in experimental lymphogenous encephalopathy. Experientia (Basel) 23, 835–836 (1967).
Dempsey, E. W., Wislocki, G. B.: An electron microscopic study of the blood-brain barrier in the rat, employing silver nitrate as a vital stain. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 245–256 (1955).
Desaga, U.: Licht- und elektronenmikroskopischer Nachweis subependymaler Basalmembranlabyrinthe im III. Ventrikel der Ratte. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. (im Druck).
Eberhardt, H. G.: Supravitale Farbstoffversuche zur Frage der Stoffverteilung im ZNS der Ratte, besonders in Hypothalamus und Infundibulum. Z. mikr. anat. Forsch. 83, 525–534 (1971).
Fleischhauer, K.: Fluorescenzmikroskopische Untersuchungen über den Stofftransport zwischen Ventrikelliquor und Gehirn. Z. Zellforsch. 62, 639–654 (1964).
Földi, M., Scanda, E., Obál, F., Madarász, I., Szeghy, G., Zoltán, Ö. T.: Über Wirkungen der Unterbindung der Lymphgefäße und Lymphknoten des Halses auf das Zentralnervensystem im Tierversuch. I. Mitt. Z. ges. exp. Med. 137, 483–510 (1963).
Földi, M., Scillik, B., Zoltán, Ö. T.: Lymphatic drainage of the brain. Experientia (Basel) 24, 1283–1287 (1968).
Franz, H., Stark, M.: Der Stoffwechselweg des Tetracyclins im Gehirn nach intraventrikulärer Applikation. Z. Zellforsch. (im Druck).
Hager, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Feinstruktur der Blutgefäße und perivasculären Räume im Säugetiergehirn. Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis der morphologischen Grundlagen der sog. Bluthirnschranke. Acta neuropath. (Berl.) 1, 9–33 (1961).
Kobayashi, H., Oota, Y., Uemura, H., Hirano, T.: Electron microscopic and pharmacological studies on the rat median eminence. Z. Zellforsch. 71, 387–404 (1966).
Leonhardt, H.: Über die Blutkapillaren und perivaskulären Strukturen der Area postrema des Kaninchens und über ihr Verhalten im Pentamethylentetrazol-(„Cardiazol“-)Krampf. Z. Zellforsch. 76, 511–524 (1967).
Leonhardt, H.: Über Hirnödem bei unterschiedlichen perikapillären Strukturen verschiedener Grisea des Kaninchens, hervorgerufen durch Pentamethylentetrazol (Cardiazol). Z. Zellforsch. 84, 199–218 (1968).
Leonhardt, H.: Ependym. In: Zirkumventrikuläre Organe und Liquor (G. Sterba ed.). Jena: VEB G. Fischer 1969.
Leonhardt, H.: Subependymale Basalmembranlabyrinthe im Hinterhorn des Seitenventrikels des Kaninchengehirns. Zur Frage des Liquorabflusses. Z. Zellforsch. 105, 595–604 (1970).
Leonhardt, H., Eberhardt, H. G.: Dye transport from the median eminence to the hypothalamic wall. A model. In: Brain-endocrine interaction. Median eminence: Structure and function (K. M. Knigge, D. E. Scott, A. Weindl ed.). Basel-München-Paris-London-New York-Sydney: S. Karger 1972.
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Luse, S. A.: Histochemical implications of electron microscopy of the central nervous system; Symposion. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 8, 398–411 (1960).
Maynard, E. A., Schultz, R. L., Pease, D. C.: Electron microscopy of the vascular bed of rat cerebral cortex. Amer. J. Anat. 100, 409–433 (1957).
Mugnaini, E., Walberg, F.: Ultrastructure of neuroglia. Ergebn. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 37, 194–236 (1964).
Rodríguez, E. M.: Ultrastructure of the neurohaemal region of the toad median eminence. Z. Zellforsch. 93, 182–212 (1969).
Röhlich, P., Vigh, B., Teichmann, I., Aros, B.: Electron microscopic studies of the medial eminence in the rat. Acta physiol. Acad. Sci. hung., Suppl. 26, 49 (1965).
Rohr, V. U.: Zum Feinbau des Subfornikal-Organs der Katze. I. Der Gefäßapparat. Z. Zellforsch. 73, 246–271 (1966).
Romeis, B.: Mikroskopische Technik, 15. Aufl. München: Leibniz 1948.
Rudert, H., Schwink, A., Wetzstein, R.: Die Feinstruktur des Subfornikalorgans beim Kaninchen. Die Blutgefäße. Z. Zellforsch. 74, 252–270 (1966).
Schwanitz, W.: Die topographische Verteilung supraependymaler Strukturen in den Ventrikeln und im Zentralkanal des Kaninchengehirns. Z. Zellforsch. 100, 536–551 (1969).
Sjöstrand, F. S.: Electron microscopy of cells and tissues. In: Physical techniques in biological research III, ed. by L. Oster and A. Pollister. New York: Academic Press 1956.
Specht, W.: Färben mit Aldehydthionin. Eine Methode für den topochemischen Nachweis von Sulfonsäuren und Aldehyden. 65. Vers. Anat. Ges., Würzburg, 1970. (Im Druck.)
Stark, M., Franz, H.: Die Verteilung von fluoreszenzmarkiertem Tryptophan im Gehirn nach intraventrikulärer Injektion. Z. Zellforsch. (im Druck).
Stephens, R. J.: The development and fine structure of the allantoic placental barrier in the bat Tadarida brasiliensis cynocephala. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 28, 371–398 (1969).
Stober, B.: Über Bewegung und Drainage des Liquor cerebrospinalis beim Kaninchen. Untersuchungen mit einer standardisierten Methode. Z. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 135, 307–316 (1972).
Vollrath, L.: Über Bau und Funktion von Basalmembranen. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 93, 360–365 (1968).
Weindl, A., Schwink, A., Wetzstein, R.: Der Feinbau des Gefäßorgans der Lamina terminalis beim Kaninchen. Z. Zellforsch. 79, 1–48 (1967).
Wolff, J.: Beitrag zur Ultrastruktur der Kapillaren in der Großhirnrinde. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 409–431 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit dankenswerter Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Le 69/7). — Fräulein E. Östermann und Frau H. Zuther-Witzsch danke ich für vorzügliche technische Hilfe.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leonhardt, H. Über die topographische Verteilung der subependymalen Basalmembranlabyrinthe im Ventrikelsystem des Kaninchengehirns. Z.Zellforsch 127, 392–406 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306882
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306882